<<–2/”>a >a href=”https://exam.pscnotes.com/nature-types-and-problems-of-unemployment-in-india/”>Nature, types and Problems of Unemployment in India:-Unemployment may be defined as “a situation in which the person is capable of working both physically and mentally at the existing wage rate, but does not get a job to work”.
India is one of those ill-fated underdeveloped countries which is suffering from a huge unemployment problem. But the unemployment problem in India is not the result of deficiency of effective demand in Keynesian term but a product of shortage of capital equipment’s and other complementary Resources accompanied by high rate of Growth of Population.
Present unemployment problem in India is mostly structural in nature.
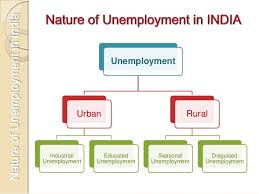
Unemployment problem of the country can now be broadly classified into:
(a) Rural unemployment and
(b) Urban unemployment.
(a) Rural Unemployment:
In India the incidence of unemployment is more pronounced in the rural areas.
Rural unemployment is again of two types:
(i) Seasonal Unemployment and
(ii) Disguised or perennial unemployment.
(i) Seasonal Unemployment:
agriculture, though a principal occupation in the rural areas of the country, is seasonal in nature. It cannot provide work to the rural population of the country throughout the year. In the absence of multiple Cropping system and subsidiary occupation in the rural areas, a large number of rural population has to sit idle 5 to 7-months in a year.
Seasonal Unemployment is also prevalent in some agro- based industries viz., Tea Industry, Jute Mills, Sugar Mills, Oil Pressing Mills, Paddy Husking Mills etc.
(ii) Disguised or Perennial Unemployment:
Indian Agriculture is also suffering from disguised or perennial unemployment due to excessive pressure of population. In Disguised Unemployment apparently it seems that everyone is employed but in reality sufficient full time work is not available for all.
In India, about 72 per cent of the working population is engaged in agriculture and allied activities. In 1951 more than 100 million persons were engaged in the agricultural and allied activities whereas in 1991 about 160 million persons are found engaged in the same sector resulting in as many as 60 million surplus population who are left with virtually no work in agriculture and allied activities.
(b) Urban Unemployment:
Urban unemployment has two aspects:
(i) Industrial unemployment and
(ii) Educated or middle class unemployment.
(i) Industrial Unemployment:
In the urban areas of the country, industrial unemployment is gradually becoming acute. With the increase in the size of urban population and with the exodus of population in large number from rural to the urban industrial areas to seek EMPLOYMENT, industrialization because of slow growth could not provide sufficient employment opportunities to the growing number of urban population.
Thus the rate of growth of employment in the Industrial Sector could not keep pace with the growth of urban industrial workers leading to a huge industrial unemployment in the country.
(ii) Educated or middle-class Unemployment:
Another distinct type of unemployment which is mostly common in almost all the urban areas of the country is known as educated unemployment. This problem is very much acute among the middle class people. With rapid expansion of general Education in the country the number of out-turn of educated people is increasing day by day.
But due to slow growth of technical and vocational educational facilities, a huge number of manpower is unnecessarily diverted towards general education leading to a peculiar educated unemployment problem in the country. The total number of educated unemployment increased from 5.9 lakh in 1962 to 230.50 lakh in 1994.
• Types of Unemployment
The most accepted Classification of Unemployment recognizes two broad types: Voluntary and Involuntary Unemployment.
Voluntary unemployment arises when an individual is not under any employment out of his own desire not to work. Could be from their total apprehension towards the concept itself, or it may be that an individual is unable to find work paying his desired wages and he doesn’t want to settle.
Involuntary unemployment encompasses all those factors that prevent a physically fit individual willing to work from getting an appointment. According to John Maynard Keynes, “involuntary unemployment arises due to insufficiency of effective demand which can be solved by stepping up Aggregate Demand through government intervention”. Involuntary Unemployment is further categorized into subheads;
1. Structural: Such employment stems from any structural change in the economy that leads to decline of specific industries. Long term changes in the market conditions, reorganization of the same, and sudden changes in the technological sector, creates a Skill Gap in the existing workers.
2. Regional: Globalization/”>Globalization-3/”>Globalization and relocation of jobs also leads to unemployment as workers are often unable to move to the new location where the employers currently hold positions.
3. Seasonal: In some industries production activities are season best and employment occurs only in peak seasons. Agro-based industries and tourism industries are examples of this form of unemployment.
4. Technological: This type of unemployment is either generated following the introduction of technologically advanced mechanization that renders manual labour redundant, or through inclusion of technology that the current labour force is ill-adapted to.
5. Frictional: This type of unemployment happens when the labour is either transitioning between jobs or is trying to find a job more suited to their skill set. Friction is generally referred to the time, energy and cost that a person invests while searching for a new job.
6. Educated: This form of unemployment happens when people with advanced degrees are unable to procure an engagement that is suited to their level of training.
7. Casual: Some occupations can only offer temporary employment to individuals and their engagements are subject to termination as soon as the demand subsides. Daily labourers who work on a day-to-day basis are example of such types of unemployment.
8. Cyclical: This type of unemployment refers to the periodic cycle of unemployment associated with cyclical trends of growth in business. Unemployment is low when business cycles are at their peak and high when the gross economic output is low. Several external factors like wars, strikes and political disturbances, natural calamities that affect business cycle are also contributors to cyclical unemployment.
9. Disguised: This is a scenario when more people are employed in a job than is actually required for it. This is hallmark of developing economies where availability of labour is abundant. It is primarily a feature of the agricultural and unorganized sectors.
Problems caused due to unemployment
Unemployment and POVERTY goes side by side. The problem of unemployment gives rise to the problem of poverty.
Young people after a long time of unemployment find the wrong way to earn Money.
To get rid from the unemployment Stress, they accept alcohol or drugs.
Unemployed youths accepts suicide as the last option of their life
Lower economic growth
Increase rate in Crimes. As the employed youth don’t have anything to do they start doing robbery, murder etc.
Health issues i.e it affects mentally as well as physically,
Unemployment is a major economic and social problem that affects millions of people around the world. It is defined as the state of being without paid work. The unemployment rate is the Percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
There are many causes of unemployment, including economic recessions, technological change, and globalization. Economic recessions occur when there is a decline in economic activity, which leads to businesses laying off workers. Technological change can lead to job losses when new technologies make existing jobs obsolete. Globalization can lead to job losses when businesses move production to countries with lower labor costs.
Unemployment has a number of negative consequences, both for individuals and for Society as a whole. For individuals, unemployment can lead to financial hardship, stress, and social isolation. For society as a whole, unemployment can lead to lower economic growth, crime, and social unrest.
There are a number of different types of unemployment, including cyclical unemployment, Structural Unemployment, and Frictional Unemployment. Cyclical unemployment is caused by fluctuations in the business cycle. Structural unemployment is caused by changes in the economy, such as technological change or globalization. Frictional unemployment is caused by the normal movement of workers between jobs.
The unemployment rate is calculated by dividing the number of unemployed people by the labor force. The labor force is the total number of people who are either employed or unemployed. The unemployment rate is a key indicator of the health of the economy.
Unemployment benefits are payments made to unemployed people to help them meet their basic needs while they are looking for work. Unemployment insurance is a government program that provides unemployment benefits. Unemployment programs are government programs that provide assistance to unemployed people, such as job training, placement Services, and financial assistance.
Unemployment statistics are data that are collected on the number of unemployed people, the unemployment rate, and other aspects of unemployment. Unemployment trends are changes in the unemployment rate over time. Unemployment policies are government policies that are designed to reduce unemployment. Unemployment solutions are strategies that can be used to reduce unemployment.
Unemployment research is research that is conducted on the causes, consequences, and solutions to unemployment. Unemployment history is the history of unemployment in the United States and other countries. Unemployment literature is the body of literature that is written on unemployment. Unemployment law is the body of law that governs unemployment. Unemployment policy is the body of policy that governs unemployment.
Unemployment is a complex issue with no easy solutions. However, there are a number of things that can be done to reduce unemployment, such as providing job training, creating jobs, and providing unemployment benefits.
Inflation/”>What is Inflation?
Inflation is a general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money.
What is Deflation?
Deflation is a general decrease in prices and rise in the purchasing value of money.
What is GDP?
GDP is the total market value of all Final Goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period, usually one year.
What is the stock market?
The stock market is a financial market where people can buy and sell Shares of companies.
What is a Recession?
A recession is a period of time when the economy shrinks and there is a decline in economic activity.
What is a depression?
A depression is a severe recession that lasts for a long period of time.
What is a financial crisis?
A financial crisis is a period of time when there is a lot of uncertainty and fear in the Financial Markets.
What is a bank run?
A bank run is when a large number of people withdraw their money from a bank at the same time.
What is a bailout?
A bailout is when the government gives money to a company or institution that is in financial trouble.
What is a stimulus package?
A stimulus package is a set of government policies that are designed to increase economic activity.
What is a Trade Deficit?
A trade deficit is when a country imports more goods and services than it exports.
What is a trade surplus?
A trade surplus is when a country exports more goods and services than it imports.
What is a budget deficit?
A budget deficit is when a government spends more money than it takes in.
What is a budget surplus?
A budget surplus is when a government takes in more money than it spends.
What is a national debt?
The national debt is the total amount of money that a country owes.
What is a Sovereign Debt Crisis?
A sovereign debt crisis is when a country is unable to repay its debts.
What is a currency crisis?
A currency crisis is when the value of a country’s currency falls sharply.
What is a financial contagion?
Financial contagion is when a financial crisis in one country spreads to other countries.
What is a Financial Stability Board?
The Financial Stability Board is an international organization that was created to promote financial stability.
What is the Basel Accords?
The Basel Accords are a set of international agreements that set standards for bank capital adequacy.
What is the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer protection Act?
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act is a United States federal law that was enacted in 2010 in response to the financial crisis of 2007â2008.
What is the Troubled Asset Relief Program?
The Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) was a program of the United States government to purchase toxic assets and Equity from financial institutions to prevent a collapse of the United States financial system.
What is the European Central Bank?
The European Central Bank is the central bank of the European Union.
What is the International Monetary Fund?
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international financial institution that was founded in 1944 to promote international monetary cooperation, exchange stability, and orderly exchange arrangements.
What is the World Bank?
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programs.
Which of the following is not a factor that can contribute to unemployment?
(A) A recession
(B) A natural disaster
(C) A technological advancement
(D) An increase in the minimum wageWhich of the following is the most common type of unemployment?
(A) Cyclical unemployment
(B) Structural unemployment
(C) Frictional unemployment
(D) Seasonal unemploymentWhich of the following is a government program that provides unemployment benefits to workers who have lost their jobs?
(A) Social Security
(B) Medicare
(C) Medicaid
(D) Unemployment insuranceWhich of the following is a policy that is designed to reduce unemployment?
(A) Monetary Policy
(B) Fiscal Policy
(C) Supply-side economics
(D) Demand-side economicsWhich of the following is a measure of the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed?
(A) The unemployment rate
(B) The labor force participation rate
(C) The employment-to-population ratio
(D) The underemployment rateWhich of the following is a measure of the number of jobs that are available for each unemployed worker?
(A) The unemployment rate
(B) The labor force participation rate
(C) The employment-to-population ratio
(D) The job vacancy rateWhich of the following is a measure of the number of people who are working part-time but would prefer to be working full-time?
(A) The unemployment rate
(B) The labor force participation rate
(C) The employment-to-population ratio
(D) The underemployment rateWhich of the following is a measure of the number of people who are not in the labor force but would like to be working?
(A) The unemployment rate
(B) The labor force participation rate
(C) The employment-to-population ratio
(D) The underemployment rateWhich of the following is a policy that is designed to increase the labor force participation rate?
(A) Expanding access to childcare
(B) Providing job training programs
(C) Offering tax breaks for businesses that hire workers
(D) All of the aboveWhich of the following is a policy that is designed to increase the employment-to-population ratio?
(A) Expanding access to childcare
(B) Providing job training programs
(C) Offering tax breaks for businesses that hire workers
(D) All of the above