United Nations and its specialized agencies
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization established on 24 October 1945 to promote international cooperation. It was founded to replace the League of Nations following World War II and to prevent another conflict. When it was founded, the UN had 51 Member States; there are now 193. Most nations are members of the UN and send diplomats to the headquarters to hold meetings and make decisions about global issues.
The UN system is based on five principal organs:
The General Assembly,
The Security Council,
The Justice/”>International Court of Justice.
The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC),
and
A sixth principal organ, the Trusteeship Council, suspended operations in 1994
Four of the five principal organs are located at the main UN Headquarters in New York City. The International Court of Justice is located in The Hague, while other major agencies are based in the UN offices at Geneva, Vienna, and Nairobi. Other UN institutions are located throughout the world. The six official languages of the UN, used in intergovernmental meetings and documents, are Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish.
- The General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), the only one in which all member nations have equal representation, and the main deliberative, policy-making and representative organ of the UN. Its powers are to oversee the budget of the UN, appoint the non-permanent members to the Security Council, receive reports from other parts of the UN and make recommendations in the form of General Assembly Resolutions. It has also established numerous subsidiary organs. Its current President is Peter Thomson.
- The Secretariat
The Secretariat is the United Nations’ executive arm. The Secretariat has an important role in setting the agenda for the UN’s deliberative and DECISION MAKING bodies of the UN (the General Assembly, Economic and Social Council, and Security Council), and the implementation of the decision of these bodies. The Secretary-General, who is appointed by the General Assembly, is the head of the secretariat. Present Sectary General is Antonio Guterres from Portugal.
- The International Court of Justice
The International Court of commonly referred to as the World Court, ICJ or The Hague) is the primary judicial branch of the United Nations (UN). Seated in the Peace Palace in The Hague, Netherlands, the court settles legal disputes submitted to it by states and provides advisory opinions on legal questions submitted to it by duly authorized international branches, agencies, and the UN General Assembly.
The ICJ is composed of fifteen judges elected to nine-year terms by the UN General Assembly and the UN Security Council from a list of people nominated by the national groups in the Permanent Court of Arbitration.
- The Security Council
It has charged with the maintenance of international peace and security as well as accepting new members to the United Nations and approving any changes to its United Nations Charter. Its powers include the establishment of peacekeeping operations, the establishment of international sanctions, and the authorization of military action through Security Council resolutions; it is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions to member states. The Security Council held its first session on 17 January 1946.
The Security Council consists of fifteen members. The great powers that were the victors of World War II—the Soviet Union (now represented by the Russian Federation), the United Kingdom, France, Republic of China (now represented by the People’s Republic of China), and the United States—serve as the body’s five permanent members. These permanent members can veto any substantive Security Council resolution, including those on the admission of new member states or candidates for Secretary-General. The Security Council also has 10 non-permanent members, elected on a regional basis to serve two-year terms. The body’s presidency rotates monthly among its members. Security Council resolutions are typically enforced by UN peacekeepers, military forces voluntarily provided by member states and funded independently of the main UN budget. Present President is Tekeda Alemu.
- The Economic and Social Council(ECOSOC)
The United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic, social, and related work of 15 UN specialised agencies, their functional commissions and five regional commissions. The ECOSOC has 54 members. It holds one four-week session each year in July, and since 1998, it has also held an annual meeting in April with finance ministers heading key committees of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
United Nation specialized agencies
The UN specialized agencies are autonomous organizations working with the United Nations. All were brought into relationship with the UN through negotiated agreements. Some existed before the First World War. Some were associated with the League of Nations. Others were created almost simultaneously with the UN. Others were created by the UN to meet emerging needs.
WORLD BANK (WB)
The World Bank focuses on POVERTY reduction and the improvement of living standards worldwide by providing low-interest loans, interest-free credit, and grants to developing countries for Education, Health, Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE, and communications, among other things. The World Bank works in over 100 countries through:
World Bank Group
• International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)
• International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID)
• International Development Association (IDA)
• International Finance Corporation (IFC)
• Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND (IMF)
- Created in 1945, it is an organization of 189 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high EMPLOYMENT and sustainable economic Growth and reduce poverty around the world.
- It does so by providing temporary financial assistance to countries to help ease Balance of Payments adjustment and technical assistance. The IMF currently has $28 billion in outstanding loans to 74 nations.
WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION (WHO)
- WHO began its work on April 7, 1948, the day we celebrate every year as World Health Day. Its goal is to build a better, healthier future for people all over the world. Working through offices in more than 150 countries.
- WHO staffs work side by side with governments and other partners to ensure the highest attainable level of health for all people.
- It also helps mothers and children survive and thrive so they can look forward to a healthy old age.
- WHO ensures the safety of the air people breathe, the food they eat, the water they drink and the medicines and Vaccines they need.
UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATOIN (UNESCO)
- Founded on Nov 1945, having 195 members and eight associate members, governed by the General Conference and the Executive Board focuses on everything from teacher training to helping improve education worldwide to protecting important historical and cultural sites around the world.
- It added about 28 new World Heritage Sites this year to the list of irreplaceable treasures that will be protected for today’s travelers and future generations.
- Headquarter is in Paris, France known as the heart of Paris.
- Thus UNESCO’s unique competencies in education, the sciences, culture and Communication and information contribute towards the realization of those goals.
- UNESCO is also a member of the United Nations Development Group and works for Millennium Development Goals.
INTERNATIONAL LABOUR ORGANISATION (ILO)
- Headquartered at Geneva, Switzerland, the ILO promotes international labor rights by formulating international standards on the freedom to associate, collective bargaining, the abolition of forced labor, and Equality of opportunity and treatment.
- The ILO has 187 member states: 186 of the 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands are members of the ILO.
- In 1969, the organization received the Nobel Peace Prize for improving peace among classes, pursuing decent work and justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to other developing nations.
- The Governing Body decides the agenda of the International Labour Conference, adopts the draft program and budget of the organization for submission to the conference, elects the director-general, requests information from member states concerning labour matters, appoints commissions of inquiry and supervises the work of the International Labour Office.
FOOD AND agriculture ORGANIZATION (FAO)
- Headquartered at Rome Italy, the FAO leads international efforts to defeat hunger. It is both a forum for negotiating agreements between developing and developed countries and a source of technical knowledge and information to aid development.
- Formed on Oct 16, 1945, presently having 194 members along with EU (a member organization) and the Faroe Island and Tokelau which are associate members.
THE INTERNATIONAL FUND FOR AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT (IFAD)
- The IFAD, since it was created in 1977, has focused exclusively on rural poverty reduction, working with poor rural populations in developing countries to eliminate poverty, hunger and Malnutrition; raise their productivity and incomes; and improve the quality of their lives.
- Headquartered in Rome, Italy, it has 176 members including 174 UN member states along with the Cook Island and Niue.
INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION (IMO)
- Also known as Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization (IMCO), the IMO has created a comprehensive shipping regulatory framework, addressing safety and environmental concerns, legal matters, technical cooperation, security, and efficiency.
- The IMO was established in Geneva in 1948 and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959, Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, the IMO has 172 Member States and three Associate Members.
- IMO is governed by an assembly of members and is financially administered by a council of members elected from the assembly.
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION (WMO)
- Founded in 1873 as International Meteorological Organisation, Established in 1950 headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has 191 members.
- The WMO facilitates the free international exchange of meteorological data and information and the furtherance of its use in aviation, shipping, security, and agriculture, among other things.
WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ORGANIZATION (WIPO)
- The WIPO protects intellectual property throughout the world through 23 international treaties.
- Created in 1967, currently having 189 member states 186 of the UN Members as well as the Cook Islands, Holy See and Niue are Members of WIPO. Non-members are the states of Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Nauru, Palau, Solomon Islands, South Sudan and East Timor. The Palestinians have observer status and its headquartered is in Geneva, Switzerland.
INTERNATIONAL CIVILIAN AVIATION ORGANIZATION (ICAO)
- The ICAO is a UN specialized agency, established by States in 1944 to manage the administration and governance of the Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention), headquartered in Montreal Canada.
- ICAO works with the Convention’s 191 Member States and Industry groups to reach consensus on international civil aviation Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) and policies in support of a safe, efficient, secure, economically sustainable and environmentally responsible civil aviation sector.
INTERNATIONAL Telecommunication UNION (ITU)
- The ITU is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies.
- It is committed to connecting the entire world’s people – wherever they live and whatever their means. Through its work, it protects and supports everyone’s fundamental right to communicate
- An organization based on public-private PARTNERSHIP since its inception, ITU currently has a membership of 193 countries and almost 800 private-sector entities and academic institutions. ITU is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has twelve regional and area offices around the world.
UNITED NATIONS INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATION (UNIDO)
- Headquartered in Vienna, Austria, the UNIDO is the specialized agency of the United Nations that promotes industrial development for poverty reduction, inclusive Globalization/”>Globalization-3/”>Globalization and environmental sustainability.
- Formed in 1966 with the mission described in the Lima Declaration adopted at the fifteenth session of the UNIDO General Conference in 2013, is to promote and accelerate Inclusive and Sustainable Industrial Development (ISID) in developing countries and economies in transition.
UNIVERSAL POSTAL UNION (UPO)
- It is the primary forum for cooperation between postal sector players. It helps to ensure a truly universal Network of up-to-date products and Services.
- Headquartered in Bern, Switzerland, Formed on October 9, 1874 contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration, the Postal Operation Council and the International bureau.
- It also oversees the Telematics and EMS cooperatives. Each member agrees to the same terms for conducting international postal duties.
OTHER ENTITIES/AGENCIES
UNAIDS
• The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS is co-sponsored by 10 UN system agencies: UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, the ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank and has ten goals related to stopping and reversing the spread of HIV/AIDS.
UNISDR
• The United Nations Office for Disaster Reduction serves as the focal point in the United Nations system for the coordination of disaster reduction.
UNOPS
• The United Nations Office for Project Services is an operational arm of the United Nations, supporting the successful implementation of its partners’ peace building, humanitarian and development projects around the world.
RELATED ORGANIZATIONS
IAEA
• The International Atomic Energy Agency is the world’s centre for cooperation in the nuclear field. The Agency works with its Member States and multiple partners worldwide to promote the safe, secure and peaceful use of nuclear technologies.
WTO
• The World Trade Organization is a forum for governments to negotiate trade agreements, and a place where member governments try to sort out the trade problems they face with each other.
CTBTO
• The Preparatory Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-test-Ban Treaty Organization promotes the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (which is not yet in force) and the build-up of the verification regime so that it is operational when the Treaty enters into force.
OPCW
• The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons is the implementing body of the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), which entered into force in 1997. OPCW Member States work together to achieve a world free of chemical weapons.
IOM
• The International Organization for Migration works to help ensure the orderly and humane management of migration, to promote international cooperation on migration issues, to assist in the search for practical solutions to migration problems and to provide humanitarian assistance to migrants in need, including refugees and internally displaced people.
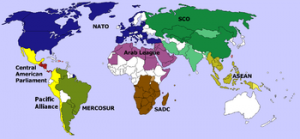
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) was formed in 1967 by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability. The member countries of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) are Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei Darussalam, Vietnam, Laos and Myanmar. The ASEAN Community is comprised of three pillars, the Political-Security Community, Economic Community and Socio-Cultural Community. Every year following the ASEAN Ministerial Meeting, ASEAN holds its Post-Ministerial Conference (PMC) to which the Secretary of State is invited. In 1994, ASEAN took the lead in establishing the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF), which now has 27 members.
Main objectives
To promote the economic, social and Cultural Development of the region through cooperative programmers
To safeguard the political and economic stability of the region against big power rivalry; and
To serve as a forum for the resolution of intra-regional differences.
· Asia Pacific Economic Co-operation (APEC)
The Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) was established in 1989 as an informal Ministerial-level dialogue group with twelve members. Today APEC has 21 member economies spread out over four continents. APEC Member Economies work together to sustain economic growth through a commitment to open trade, investment and economic reform. This is accomplished by progressively reducing tariffs and other barriers to trade. The participating APEC economies are: Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Chile, China, Hong Kong-China, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Chinese Taipei, Thailand, United States, and Vietnam. India is not member of Apec.
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation(SAARC)
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of nations in South Asia. Its member states include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, the Maldives, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. SAARC comprises 3% of the world’s area, 21% of the world’s Population and 3.8% (US$ 2.9 trillion) of the global economy, as of 2015.
SAARC was founded in Dhaka on 8th December, 1985. Its secretariat is based in Kathmandu, Nepal. The organization promotes development of economic and regional integration. It launched the South Asian Free Trade Area in 2006. SAARC maintains permanent diplomatic relations at the United Nations as an observer and has developed links with multilateral entities, including the European Union.
- European Union(EU
The European Union (EU) is a political and Economic Union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe. It has an area of 4,475,757 km2 (1,728,099 sq mi), and an estimated population of over 510 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services, and capital within the internal market, enact legislation in justice and home affairs, and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, Fisheries-2/”>Fisheries, and regional development. Within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished. A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002, and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.
- Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations (formerly the British Commonwealth), also known as simply the Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of 52 member states that are mostly former territories of the British Empire. The Commonwealth operates by intergovernmental consensus of the member states, organised through the Commonwealth Secretariat and non-governmental organisations, organised through the Commonwealth Foundation.
Member states have no legal obligation to one another. Instead, they are united by language, history, culture and their shared values of Democracy, free speech, Human Rights, and the Rule of Law.
The Commonwealth covers more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), 20% of the world’s land area, and spans all six inhabited continents; if all Commonwealth member states were to be united as a single land mass, the Commonwealth would be the largest country in the world by land area.
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation(SCO)
SCO was formulated in 1996 with five countries- Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, China, Tajikistan. Uzbekistan joined in the group in 2001. The primary motive behind the formation was to ensure stability along the borders. The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian political, economic, and security organisation, the creation of which was announced on 15 June 2001 in Shanghai, China by the leaders of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
India and Pakistan joined SCO as full members on 9 June 2017 in Astana, Kazakhstan.
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development(OECD)
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 35 member countries, founded in 1960 to stimulate economic progress and world trade.
It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seeking answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Most OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. OECD is an official United Nations Observer. The OECD’s headquarters are in Paris, France.
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization(NATO)
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between several North American and European states based on the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed on 4 April 1949.
NATO constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party. Three NATO members (the United States, France and the United Kingdom) are permanent members of the United Nations Security Council with the power to veto and are officially nuclear-weapon states. NATO Headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels, Belgium, while the headquarters of Allied Command Operations is near Mons, Belgium.
NATO is an alliance that consists of 29 independent member countries across North America and Europe. An additional 21 countries participate in NATO’s Partnership for Peace program, with 15 other countries involved in institutionalized dialogue programs. The combined military spending of all NATO members constitutes over 70% of the global total Members’ defence spending is supposed to amount to at least 2% of GDP
- Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries(OPEC)
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) in several other languages is an intergovernmental organization of 14 nations as of May 2017, founded in 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members (Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Venezuela), and headquartered since 1965 in Vienna. As of 2016, the 14 countries accounted for an estimated 44 percent of global oil production and 73 percent of the world’s “proven” oil reserves, giving OPEC a major influence on global oil prices that were previously determined by American-dominated multinational oil companies.
OPEC’s members are Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia (the de facto leader), United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela, while Indonesia is a former member. Two-thirds of OPEC’s oil production and reserves are in its six Middle Eastern countries that surround the oil-rich Persian Gulf.
- Mercosur
Mercosur, is a sub-regional bloc. Its full members are Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Venezuela is a full member but has been suspended since December 1, 2016.
Its associate countries are Bolivia, Chile, Peru, Colombia, Ecuador and Suriname. Observer countries are New Zealand and Mexico.
Its purpose is to promote free trade and the fluid movement of goods, people, and currency. The official languages are Spanish, Portuguese and Guarani.
,
The United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights. Due to its unique international character, and the powers vested in its founding Charter, the Organization can take action on the issues confronting humanity in the 21st century, such as peace and security, Climate change, Sustainable Development, human rights, disarmament, terrorism, humanitarian and health emergencies, Gender Equality, governance, food production, and more.
The UN System is made up of the UN itself and a family of specialized agencies, funds and programmes. The UN System works on a wide range of fundamental issues, from sustainable development, Environment and refugees protection, disaster relief, counter terrorism, disarmament and non-proliferation, to promoting democracy, human rights, gender equality and the advancement of Women, governance, economic and social development and international health, clearing landmines, expanding food production, and more, in order to achieve its goals and coordinate efforts for a safer world for this and future generations.
The UN System is funded by assessed and voluntary contributions from its Member States. The UN regular budget is assessed on the basis of the UN scale of assessments, which is determined by each Member State’s capacity to pay. Voluntary contributions are made by Member States and other donors to support specific UN programmes and activities.
The UN System is governed by the UN General Assembly, the UN Security Council, the UN Economic and Social Council, the UN Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the UN Secretariat. The UN General Assembly is the main deliberative organ of the UN. It is composed of all 193 Member States and meets in regular sessions every year. The UN Security Council is responsible for maintaining international peace and security. It has 15 members, five of which are permanent members (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and ten of which are elected by the General Assembly for two-year terms. The UN Economic and Social Council is responsible for promoting international economic and social cooperation and development. It has 54 members, elected by the General Assembly for three-year terms. The UN Trusteeship Council was established to oversee the administration of trust territories, which were territories that were not self-governing and were placed under the administration of a UN Member State. The International Court of Justice is the principal judicial organ of the UN. It settles legal disputes between states and gives advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by UN organs and specialized agencies. The UN Secretariat is the administrative organ of the UN. It is headed by the Secretary-General, who is appointed by the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the Security Council.
The UN System is a complex and ever-evolving organization. It is constantly adapting to meet the changing needs of the world. The UN System is a vital part of the international community and plays a key role in promoting peace, security, development, and human rights around the world.
The UN System is made up of the following specialized agencies:
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)
- International Labour Organization (ILO)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
- United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO)
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat)
- United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA)
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC)
- United Nations Office for the High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)
- United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA)
- United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA)
- United Nations System Staff College (UNSSC)
The UN System also includes the following regional organizations:
- African Union (AU)
- Arab League (AL)
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- Caribbean Community (CARICOM)
- Commonwealth of Nations
- European Union (EU)
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization of American States (OAS)
- Pacific Islands Forum (PIF)
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA)
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP)
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Europe (UNECE)
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC)
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about the United Nations (UN) and regional organizations:
What is the UN?
The UN is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights. Due to its unique international character, and the powers vested in its founding Charter, the Organization can take action on the issues confronting humanity in the 21st century, such as peace and security, Climate Change, sustainable development, human rights, disarmament, terrorism, humanitarian and health emergencies, gender equality, governance, food production, and more.What are the main organs of the UN?
The six principal organs of the United Nations are the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat.What are the functions of the UN?
The UN’s main functions are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, and promote social progress, better living standards and human rights.What are some of the UN’s achievements?
The UN has achieved a great deal in its over 70 years of existence. Some of its most notable achievements include the establishment of the International Court of Justice, the promotion of human rights, the provision of humanitarian assistance, and the peacekeeping missions that have helped to prevent or end conflicts around the world.What are some of the challenges facing the UN?
The UN faces a number of challenges, including the threat of terrorism, the proliferation of nuclear weapons, the spread of infectious diseases, and the growing gap between rich and poor. The UN is also struggling to adapt to the changing world order, as new powers emerge and old alliances shift.What is the future of the UN?
The future of the UN is uncertain. The Organization is facing a number of challenges, but it also has the potential to play a vital role in addressing the problems of the 21st century. The UN’s success will depend on the ability of its member states to work together to find common solutions to common problems.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about regional organizations:
What is a regional organization?
A regional organization is an intergovernmental organization that is composed of states that are located in a particular geographic region. Regional organizations can be formed for a variety of purposes, such as promoting economic cooperation, resolving political disputes, and providing security.What are some examples of regional organizations?
Some examples of regional organizations include the European Union, the African Union, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), and the Organization of American States (OAS).What are the benefits of regional organizations?
Regional organizations can provide a number of benefits to their member states. These benefits can include increased economic cooperation, improved political stability, and enhanced security. Regional organizations can also play a role in promoting democracy, human rights, and sustainable development.What are the challenges facing regional organizations?
Regional organizations face a number of challenges, including the lack of consensus among member states, the difficulty of implementing decisions, and the competition from other international organizations. Regional organizations must also contend with the Rise of Nationalism and populism, which can make it difficult to cooperate on common goals.What is the future of regional organizations?
The future of regional organizations is uncertain. The challenges facing regional organizations are significant, but these organizations also have the potential to play a vital role in addressing the problems of the 21st century. The success of regional organizations will depend on the ability of their member states to work together to find common solutions to common problems.
Which of the following is not a UN agency?
(A) The World Bank
(B) The International Monetary Fund
(C) The United Nations Children’s Fund
(D) The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural OrganizationThe UN Security Council has how many permanent members?
(A) 5
(B) 10
(C) 15
(D) 20The UN General Assembly has how many members?
(A) 5
(B) 10
(C) 15
(D) 193The UN Secretary-General is currently who?
(A) Ban Ki-moon
(B) Kofi Annan
(C) António Guterres
(D) Boutros Boutros-GhaliThe UN was founded in what year?
(A) 1945
(B) 1946
(C) 1947
(D) 1948The UN’s headquarters are located in what city?
(A) New York City
(B) Geneva
(C) Vienna
(D) NairobiThe UN’s primary purpose is to
(A) maintain international peace and security
(B) develop friendly relations among nations
(C) cooperate in solving international problems of an economic, social, cultural, or humanitarian character
(D) all of the aboveThe UN has six official languages. Which of the following is not one of them?
(A) Arabic
(B) Chinese
(C) English
(D) FrenchThe UN has a budget of approximately how much per year?
(A) $1 billion
(B) $10 billion
(C) $100 billion
(D) $1 trillionThe UN has awarded the Nobel Peace Prize how many times?
(A) 10
(B) 20
(C) 30
(D) 40The UN has peacekeeping missions in how many countries?
(A) 10
(B) 20
(C) 30
(D) 40The UN has specialized agencies that focus on specific issues. Which of the following is not a specialized agency?
(A) The World Bank
(B) The International Monetary Fund
(C) The United Nations Children’s Fund
(D) The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural OrganizationThe UN has regional organizations that focus on specific regions. Which of the following is not a regional organization?
(A) The African Union
(B) The European Union
(C) The Organization of American States
(D) The United Nations Security CouncilThe UN has a Human Rights Council that is responsible for promoting and protecting human rights. Which of the following is not a human right?
(A) The right to life
(B) The right to freedom from torture
(C) The right to education
(D) The right to own propertyThe UN has a Development Programme that is responsible for promoting economic and social development. Which of the following is not a Millennium Development Goal?
(A) Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
(B) Achieve universal primary education
(C) Promote gender equality and empower women
(D) Reduce child mortalityThe UN has a Environment Programme that is responsible for promoting environmental protection. Which of the following is not a major environmental issue?
(A) Climate change
(B) Deforestation
(C) Overpopulation
(D) PovertyThe UN has a Food and Agriculture Organization that is responsible for promoting Food Security. Which of the following is not a major food security issue?
(A) Hunger
(B) Malnutrition
(C) Obesity
(D) PovertyThe UN has a World Health Organization that is responsible for promoting health. Which of the following is not a major health issue?
(A) HIV/AIDS
(B) Malaria
(C) Tuberculosis
(D) PovertyThe UN has a World Bank that is responsible for providing financial assistance to developing countries. Which of the following is not a major World Bank program?
(A) The International Development Association
(B) The International Finance Corporation
(C) The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency
(D) The International Monetary FundThe UN has an International Monetary Fund that is responsible for promoting international monetary cooperation. Which of the following is not a major IMF program?
(A) The Stand