<–2/”>a >The Global Positioning System consists of 24 satellites, that circle the globe once every 12 hours, to provide worldwide position, time and velocity information. GPS makes it possible to precisely identify locations on the earth by measuring distance from the satellites. GPS allows you to record or create locations from places on the earth and help you navigate to and from those places.
GPS satellites circle the Earth twice a day in a precise orbit. Each satellite transmits a unique signal and orbital parameters that allow GPS devices to decode and compute the precise location of the satellite. GPS receivers use this information and trilateration to calculate a user’s exact location. Essentially, the GPS receiver measures the distance to each satellite by the amount of time it takes to receive a transmitted signal. With distance measurements from a few more satellites, the receiver can determine a user’s position.
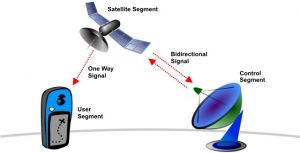
GPS System has three segments:-
Space Segment
The space segment consists of a nominal constellation of 24 operating satellites that transmit one-way signals that give the current GPS satellite position and time. The space segment consists of 24 satellites circling the earth at 12,000 miles in altitude. This high altitude allows the signals to cover a greater area. The satellites are arranged in their orbits so a GPS receiver on earth can always receive a signal from at least four satellites at any given time.
Control Segment
AF flight control officer The control segment consists of worldwide monitor and control stations that maintain the satellites in their proper orbits through occasional command maneuvers, and adjust the satellite clocks. It tracks the GPS satellites, uploads updated navigational data, and maintains Health and status of the satellite constellation.
User Segment
receiver The user segment consists of the GPS receiver equipment, which receives the signals from the GPS satellites and uses the transmitted information to calculate the user’s three-dimensional position and time.
GPS Aided Geo Augmentation Navigation (GAGAN) is a planned implementation of Satellite Based Navigation System (SBNS) developed by Airports Authority of India (AAI) and ISRO. GAGAN is expected to provide a civil aeronautical navigation signal consistent with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards and Recommended Practices as established by the Global Navigation Satellite System Panel. GAGAN was launched in August 2010. With this India has become the 4th Country in the World to have satellite based navigation system. It is a system to improve the accuracy of a GNSS receiver by providing reference signals.,
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth. It is maintained by the United States government and is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver.
GPS works by using a Network of 24 satellites that orbit the Earth at an altitude of about 12,550 miles. Each satellite transmits a signal that includes its position and time. A GPS receiver can determine its location by measuring the time it takes for signals from four or more satellites to reach it.
GPS was originally developed by the United States Department of Defense in the 1970s. It was first used by the military, but it was made available to the public in the 1980s. GPS has become an essential tool for navigation, tracking, and surveying. It is also used by the military, law enforcement, and emergency Services.
GPS is very accurate. It can determine your location to within a few feet. This accuracy is important for many applications, such as navigation and tracking. However, GPS can be affected by interference from buildings, Mountains, and other objects. This can make it less accurate in some areas.
There are some privacy concerns with GPS. GPS receivers can track your location without your knowledge or Consent. This information can be used to track your movements, monitor your activities, and even target you with advertising. It is important to be aware of these privacy concerns and to take steps to protect your privacy when using GPS.
The future of GPS is bright. GPS is already being used in a variety of new and innovative ways. For example, it is being used to develop self-driving cars, which could revolutionize transportation. GPS is also being used to monitor the Environment, track wildlife, and even fight crime. As GPS technology continues to develop, it is likely to become even more important in our lives.
Here are some additional details about the history, operation, and Applications of GPS:
- History: The development of GPS began in the 1950s, when the United States military was looking for a way to improve the accuracy of its navigation systems. The first GPS satellite was launched in 1978, and the system became fully operational in 1995.
- Operation: GPS works by using a network of 24 satellites that orbit the Earth at an altitude of about 12,550 miles. Each satellite transmits a signal that includes its position and time. A GPS receiver can determine its location by measuring the time it takes for signals from four or more satellites to reach it.
- Applications: GPS is used for a variety of purposes, including navigation, tracking, and surveying. It is also used by the military, law enforcement, and emergency services. Some specific applications of GPS include:
- Navigation: GPS is used in a variety of navigation devices, such as car navigation systems, handheld GPS units, and smartphone apps.
- Tracking: GPS is used to track the location of people, vehicles, and other assets.
- Surveying: GPS is used to survey land and to create maps.
- Military: GPS is used by the military for navigation, targeting, and other purposes.
- Law enforcement: GPS is used by law enforcement to track suspects and to monitor parolees.
- Emergency services: GPS is used by emergency services to find the location of people who need help.
- Accuracy: GPS is very accurate. It can determine your location to within a few feet. This accuracy is important for many applications, such as navigation and tracking. However, GPS can be affected by interference from buildings, mountains, and other objects. This can make it less accurate in some areas.
- Privacy concerns: There are some privacy concerns with GPS. GPS receivers can track your location without your knowledge or consent. This information can be used to track your movements, monitor your activities, and even target you with advertising. It is important to be aware of these privacy concerns and to take steps to protect your privacy when using GPS.
- Future: The future of GPS is bright. GPS is already being used in a variety of new and innovative ways. For example, it is being used to develop self-driving cars, which could revolutionize transportation. GPS is also being used to monitor the environment, track wildlife, and even fight crime. As GPS technology continues to develop, it is likely to become even more important in our lives.
What is a navigation system?
A navigation system is a device that helps you find your way around. It uses a variety of sensors, such as GPS, to track your location and provide directions.
How does a navigation system work?
A navigation system works by using a variety of sensors to track your location. These sensors can include GPS, accelerometers, and gyroscopes. The GPS sensor tracks your position using satellites in orbit around the Earth. The accelerometer and gyroscope sensors track your movement. The navigation system uses this information to provide you with directions.
What are the benefits of using a navigation system?
There are many benefits to using a navigation system. Navigation systems can help you find your way around unfamiliar areas, avoid traffic congestion, and get to your destination on time. They can also be used to find businesses and attractions in your area.
What are the drawbacks of using a navigation system?
There are a few drawbacks to using a navigation system. Navigation systems can be expensive, and they can be distracting while driving. They can also be inaccurate, especially in rural areas.
What are some tips for using a navigation system safely?
Here are some tips for using a navigation system safely:
- Keep your eyes on the road at all times.
- Don’t enter an address or destination while driving.
- Use voice-activated commands whenever possible.
- Be aware of your surroundings and obey all traffic laws.
What are some common mistakes people make when using a navigation system?
Some common mistakes people make when using a navigation system include:
- Not paying attention to the road.
- Entering an address or destination while driving.
- Not using voice-activated commands.
- Not being aware of their surroundings.
What are some alternative navigation systems?
There are a number of alternative navigation systems available, including:
- Paper maps
- Road atlases
- Smartphone apps
- Car navigation systems
What is the future of navigation systems?
The future of navigation systems is likely to be more integrated with other technologies, such as smartphones and cars. Navigation systems are also likely to become more accurate and user-friendly.
What is the name of the system that uses satellites to provide location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth?
(A) The Global Positioning System (GPS)
(B) The Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS)
(C) The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS)
(D) The Galileo Positioning System (Galileo)How many satellites are in the GPS constellation?
(A) 24
(B) 31
(C) 37
(D) 40What is the frequency of the GPS L1 signal?
(A) 1.57542 GHz
(B) 1.2276 GHz
(C) 1.17645 GHz
(D) 1.195 GHzWhat is the accuracy of GPS?
(A) 10 meters
(B) 1 meter
(C) 10 centimeters
(D) 1 centimeterWhat is the altitude accuracy of GPS?
(A) 100 meters
(B) 10 meters
(C) 1 meter
(D) 0.1 metersWhat is the time accuracy of GPS?
(A) 1 microsecond
(B) 100 nanoseconds
(C) 10 nanoseconds
(D) 1 nanosecondWhat is the principle of GPS?
(A) Triangulation
(B) Trilateration
(C) Multilateration
(D) RangingHow does GPS work?
(A) GPS satellites broadcast signals that are received by GPS receivers. The receivers use these signals to calculate their position, speed, and time.
(B) GPS satellites broadcast signals that are received by GPS receivers. The receivers use these signals to calculate their position, speed, and time. The receivers also use the signals to calculate the distance to each satellite. By knowing the distance to each satellite and the time it takes for the signal to travel from the satellite to the receiver, the receiver can calculate its position.
(C) GPS satellites broadcast signals that are received by GPS receivers. The receivers use these signals to calculate their position, speed, and time. The receivers also use the signals to calculate the distance to each satellite. By knowing the distance to each satellite and the time it takes for the signal to travel from the satellite to the receiver, the receiver can calculate its position and speed.
(D) GPS satellites broadcast signals that are received by GPS receivers. The receivers use these signals to calculate their position, speed, and time. The receivers also use the signals to calculate the distance to each satellite. By knowing the distance to each satellite and the time it takes for the signal to travel from the satellite to the receiver, the receiver can calculate its position, speed, and time.What are the benefits of GPS?
(A) GPS can be used for navigation, tracking, and timing.
(B) GPS is accurate, reliable, and available worldwide.
(C) GPS is affordable and easy to use.
(D) All of the above.What are the limitations of GPS?
(A) GPS can be affected by interference from buildings, trees, and other objects.
(B) GPS can be affected by atmospheric conditions, such as rain and snow.
(C) GPS can be affected by jamming and spoofing.
(D) All of the above.