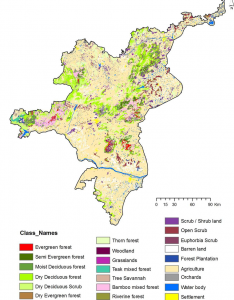
<–2/”>a >In Tamil Nadu, Forest vegetation is divided into 3 major groups according to temperature zones namely Tropical Forests, Montane Subtropical Forests and Montane Temperate Forests, which are sub divided into nine type groups based on moisture and physiognomic variation. They are
| S.No | Major Forest Type group |
| 1 | Tropical wet evergreen |
| 2 | Tropical semi evergreen |
| 3 | Tropical moist deciduous |
| 4 | Littoral and swamp |
| 5 | Tropical dry deciduous |
| 6 | Tropical thorn |
| 7 | Tropical dry evergreen |
| 8 | Sub-Tropical Broad-leaved hill |
| 9 | Montane wet temperate |
- TROPICAL EVERGREEN FOREST
This type of forest is present on the western ghats of Tirunelveli, Kanyakumarai, The Nilgiris and Coimbatore districts on the upper slopes and top hills and sometimes on the steep slope of lower down. Tree species present in this area are Hopeaparvi Flora, Artocarpus hirsuta, Syzygium cumini, Cinnamomum zeylanicum.
- TROPICAL SEMI EVERGREEN FOREST
This type occurs on slopes of hills and Mountains usually up to 1000 m. Canopy are of two or three storeys. This forest type present in Coimbatore, Tirunelvei and Kanyakumari districts between western tropical evergreen and the moist deciduous type with mixture of occasional evergreen and abundant moist deciduous tree species. The species present in this type are Artocarpus hirsuta, Hopea parviflora, Lagerstroemia lanceolata, Terminalia paniculata
- TROPICAL MOIST DECIDUOUS FORESTS
This type of forest lies below the zone of semi evergreen and evergreen forests. The trees reach a height of 30 to 30 m and are deciduous. Bamboos are common. Bombax ceiba, Dillenia pentagyna, Mitragyna parviflora and Terminalia spp., are the common trees
- LITTORAL AND SWAMP FORESTS
This type of forest is present in the coastal area in the river deltas along the edges of the delta streams, tails of islands and over sea face where accreation is in progress. The vegetation, typically evergreen of moderate height, with leathery leaves, vivipary usually, composed of trees specially adapted to survive on tidal mud, permanenetly wet with salt water and submerged every tide. The species present are Rhizophor amucronata, R. apiculata, Avicennia officinalis, A. marina, Clerodendrum inereme, Acanthus ilicifolius etc. Stilt roots are very typical notable in Rhizophora spp
- TROPICAL DRY DECIDUOUS FORESTS
These forests are found at about 400 m and above. The canopy is closed. Most of the species are deciduous. The undergrowth is usually dense. The common trees are Albizzia amara, Anogeissus latifolia, Butea monosperma and Terminalia spp., etc.
- TROPICAL THORN FORESTS
Those forests are found from plains up to 400 m the common trees of top storey are Acacia ferruginea, Acacia leucophloea, Albizzia amara and Azadirachta Indica
- TROPICAL DRY EVERGREEN FORESTS
A low forest consisting mostly of small coriaceous leaved Evergreen trees with short boles and spreading crowns. The proportion of deciduous species may be large locally and climbers are numerous. The important species are Manilkara hexandra, Albizzia amara, Memecylon umbellatum, Atlantia monophylla and Pheonix sylvestris
- MONTANE SUBTROPICAL FORESTS
The semi-evergreen type of forest, present in the subtropical region of the state. In Eastern Ghats it is found in the upper slopes and Plateau of Shevaroys, Kollimalai, and Pachamalai. Epiphytes are common. The important species are Cedrella toona, Atrocarpus lakoocha, A.hirsuta, A.heterophyllus and Mangifera indica.
- MONTANE TEMPERATE FORESTS
The montane forest mostly confined to moist and sheltered valleys, glens and hollows as in the Anamalais, Nilgiri and Palani at above 1000 m. they are known in Tamil as ‘sholas’. The trees are evergreen and usually short boled. Ilex denticulate, I.wigtiana, Michelia nilagrica and Syzygium spp., are the common trees.
,
Tamil Nadu is a state in southern India with a diverse landscape of mountains, forests, and coastal plains. The state’s vegetation is as varied as its terrain, with a wide range of plant life from tropical evergreen forests to dry deserts.
- Tropical evergreen forests are found in the state’s Western Ghats mountain range. These forests are characterized by their dense canopy of trees that remain green all year round. The trees in these forests are adapted to the humid Climate and receive an Average of 2,000-3,000 mm of rainfall per year. Some of the common trees found in these forests include teak, rosewood, and mahogany.
- Tropical deciduous forests are found in the state’s eastern plains. These forests are characterized by their Deciduous trees that lose their leaves during the dry season. The trees in these forests are adapted to the seasonal rainfall that occurs in the region. Some of the common trees found in these forests include sal, teak, and neem.
- Scrub forests are found in the state’s dry interior regions. These forests are characterized by their low-growing trees and shrubs. The trees in these forests are adapted to the dry climate and receive an average of 500-1,000 mm of rainfall per year. Some of the common trees found in these forests include acacia, thorny bushes, and succulents.
- Montane forests are found in the state’s higher elevations. These forests are characterized by their cooler climate and higher rainfall. The trees in these forests are adapted to the cooler climate and receive an average of 2,000-3,000 mm of rainfall per year. Some of the common trees found in these forests include oak, maple, and rhododendron.
- Mangrove forests are found along the state’s coastline. These forests are characterized by their salt-tolerant trees and shrubs. The trees in these forests are adapted to the saline Environment and receive an average of 1,000-2,000 mm of rainfall per year. Some of the common trees found in these forests include mangrove, casuarina, and avicennia.
- Grasslands are found in the state’s dry interior regions. These grasslands are characterized by their tall Grasses and lack of trees. The grasses in these grasslands are adapted to the dry climate and receive an average of 500-1,000 mm of rainfall per year. Some of the common grasses found in these grasslands include elephant grass, pampas grass, and bluestem.
- Wetlands are found in the state’s rivers, lakes, and marshes. These wetlands are characterized by their abundance of water and aquatic Plants. The plants in these wetlands are adapted to the wet environment and receive an average of 1,000-2,000 mm of rainfall per year. Some of the common plants found in these wetlands include lotus, water lilies, and reeds.
- Deserts are found in the state’s northern regions. These deserts are characterized by their hot, dry climate and lack of vegetation. The plants in these deserts are adapted to the hot, dry environment and receive an average of 500-1,000 mm of rainfall per year. Some of the common plants found in these deserts include cacti, succulents, and thorny bushes.
- Cultivated land is found throughout the state. This land is used for growing crops, raising Livestock, and other agricultural purposes. The crops grown in this land vary depending on the climate and Soil conditions. Some of the common crops grown in this land include rice, wheat, sugarcane, and Cotton.
The vegetation of Tamil Nadu is a vital part of the state’s ecosystem. The forests provide habitat for a variety of animals, the grasslands provide grazing land for livestock, and the wetlands provide a home for aquatic plants and animals. The state’s forests also play an important role in the water cycle, as they help to regulate rainfall and prevent flooding. The vegetation of Tamil Nadu is a valuable resource that must be protected.
What is the difference between a forest and a jungle?
A forest is a large area of land covered with trees and other plants. A jungle is a dense forest, especially one in a tropical region.
What are the different types of forests?
There are many different types of forests, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, boreal forests, and coniferous forests.
What are the benefits of forests?
Forests provide many benefits, including:
- Oxygen: Forests produce oxygen, which we need to breathe.
- Water: Forests help to regulate the water cycle.
- Soil: Forests help to prevent soil erosion.
- Wildlife: Forests provide habitat for many different types of wildlife.
- Climate Change: Forests help to mitigate climate change.
What are the threats to forests?
Forests are threatened by many things, including:
- Deforestation: Deforestation is the clearing of forests for other uses, such as agriculture or development.
- Climate change: Climate change is causing forests to change in many ways, including changes in temperature, Precipitation, and pests.
- Fire: Forest fires can be caused by natural causes, such as lightning, or by human activity, such as arson.
- Disease: Forest diseases can be caused by Fungi, bacteria, or viruses.
What can we do to protect forests?
There are many things we can do to protect forests, including:
- Reduce our consumption of paper and wood products.
- Recycle paper and wood products.
- Plant trees.
- Support organizations that are working to protect forests.
- Contact our elected officials and let them know that we support protecting forests.
What is the importance of Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity?
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth. It includes the variety of plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as the variety of genes and Ecosystems. Biodiversity is important for many reasons, including:
- It provides us with food, medicine, and other Resources.
- It helps to regulate the climate.
- It helps to prevent soil erosion.
- It provides us with places to enjoy nature.
What are the threats to biodiversity?
Biodiversity is threatened by many things, including:
- Habitat loss: Habitat loss is the destruction of natural habitats, such as forests, wetlands, and grasslands.
- Overexploitation: Overexploitation is the use of resources at a rate that is greater than the rate at which they can be replenished.
- Pollution: Pollution is the contamination of the environment with harmful substances.
- Climate change: Climate change is causing changes in the Earth’s climate, which is having a negative impact on biodiversity.
What can we do to protect biodiversity?
There are many things we can do to protect biodiversity, including:
- Reduce our consumption of resources.
- Recycle and reuse resources.
- Support organizations that are working to protect biodiversity.
- Contact our elected officials and let them know that we support protecting biodiversity.
Which of the following is not a type of vegetation found in Tamil Nadu?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Mangrove forestThe Western Ghats are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Mangrove forestThe Eastern Ghats are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Mangrove forestThe Nilgiri Hills are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Montane forestThe Palni Hills are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Montane forestThe Anamalai Hills are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Montane forestThe Cardamom Hills are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Montane forestThe Shevaroy Hills are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Montane forestThe Biligirirangan Hills are home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Montane forestThe Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve is home to which of the following types of vegetation?
(A) Tropical evergreen forest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Thorn forest
(D) Montane forest