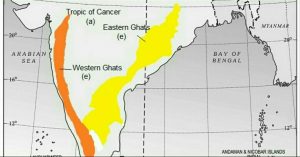
<–2/”>a >In this type of questions please try to make map of India and roughly show the location of western and eastern ghats.
| Basis | Western Ghats | Eastern Ghats |
| Direction | Run Parallel to west cost in north south direction | Eastern ghats run in a north east to south west direction parallel to the eastern cost. |
| Width | Avg width is 50-80km | Avg width 100-200km |
| Source of river | Act as a water divide. Source of many rivers like Krishna, Godavari, cauvery, koyna etc. | No big river originates |
| Rainfall | Almost perpendicular to south west direction leading to heavy rainfall. rainfall greater than 200cm in kerala region. | Eastern Ghats almost parallel to returning monsoon so less rainfall. |
| Physical division | Continuous in nature can be crossed through passes only. Like Palghat, thal ghat,naneghat | Not continuous , big rivers divide into fragments |
| Elevation | Elevation between 900-1100m | Average elevation 600 |
| Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity | Highly enriched. A biodiversity hotspot. Rich in Flora and Fauna. National parks and wild life sanctuaries are more in number. Tropical evergreen foreset, temperate evergreen forest is a speciality. | Not so enriched as compared to Western ghats. |
Note: Students may upload their answers of type their querries below or contact the program cordinator at shresth@pscnotes.com,
The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats are two mountain ranges that run parallel to the Indian coastline. The Western Ghats are located in the western part of India, while the Eastern Ghats are located in the eastern part of India. The Western Ghats are a UNESCO World Heritage Site, while the Eastern Ghats are not.
The Western Ghats are a mountain range that runs along the western coast of India. The range is about 1,600 kilometers (990 mi) long and 100 kilometers (62 mi) wide. The Western Ghats are the highest mountain range in India, with several peaks over 2,000 meters (6,600 ft) in elevation. The Western Ghats are home to a variety of plant and animal life, including many species that are found nowhere else in the world. The Western Ghats are also an important source of water for the Indian subcontinent.
The Eastern Ghats are a mountain range that runs along the eastern coast of India. The range is about 1,600 kilometers (990 mi) long and 50 kilometers (31 mi) wide. The Eastern Ghats are lower in elevation than the Western Ghats, with the highest peak being only 1,680 meters (5,510 ft) in elevation. The Eastern Ghats are also less forested than the Western Ghats. The Eastern Ghats are home to a variety of plant and animal life, but the range is not as well-studied as the Western Ghats. The Eastern Ghats are also an important source of water for the Indian subcontinent.
The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats are both important mountain ranges that play a vital role in the Indian ecosystem. The ranges are home to a variety of plant and animal life, and they are also an important source of water. The Western Ghats are a UNESCO World Heritage Site, while the Eastern Ghats are not. However, both ranges are important natural Resources that should be protected.
The Western Ghats are a major barrier to the flow of moisture from the Arabian Sea to the Indian interior. This barrier effect results in a much drier Climate in the Deccan Plateau than would otherwise be the case. The Western Ghats also receive a much higher rainfall than the Eastern Ghats. This is because the Western Ghats face the Arabian Sea, which is a source of moisture. The Eastern Ghats, on the other hand, face the Bay of Bengal, which is a much drier source of moisture.
The Western Ghats are also more forested than the Eastern Ghats. This is because the Western Ghats receive more rainfall and have a higher elevation. The higher elevation of the Western Ghats results in a cooler climate, which is more favorable for the Growth of forests. The Eastern Ghats, on the other hand, have a lower elevation and a warmer climate. This warmer climate is less favorable for the growth of forests.
The Western Ghats are also more of a tourist destination than the Eastern Ghats. This is because the Western Ghats are more accessible and have more developed Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE. The Western Ghats are also home to a number of popular tourist destinations, such as the hill station of Mahabaleshwar and the National Park of Bandhavgarh. The Eastern Ghats, on the other hand, are less accessible and have less developed infrastructure. The Eastern Ghats are also home to fewer popular tourist destinations.
In conclusion, the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats are two important mountain ranges that play a vital role in the Indian ecosystem. The ranges are home to a variety of plant and animal life, and they are also an important source of water. The Western Ghats are a UNESCO World Heritage Site, while the Eastern Ghats are not. However, both ranges are important Natural Resources that should be protected.
The Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats are two mountain ranges that run parallel to the west and east coasts of India, respectively. They are both important features of the Indian landscape, and they play a significant role in the country’s climate and ECOLOGY.
The Western Ghats are a much older mountain range than the Eastern Ghats, and they are also much higher. The Western Ghats are home to a wide variety of plant and animal life, and they are a popular destination for tourists. The Eastern Ghats are not as high as the Western Ghats, and they are not as well-known for their biodiversity. However, they are still an important part of the Indian landscape, and they play a significant role in the country’s climate and ecology.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats:
| Feature | Western Ghats | Eastern Ghats |
|—|—|—|
| Age | 300 million years old | 100 million years old |
| Height | Up to 2,695 meters (8,842 feet) | Up to 1,680 meters (5,515 feet) |
| Length | 1,600 kilometers (994 miles) | 1,500 kilometers (932 miles) |
| Location | Runs parallel to the west coast of India | Runs parallel to the east coast of India |
| Biodiversity | Home to a wide variety of plant and animal life | Not as well-known for its biodiversity |
| Tourism | A popular destination for tourists | Not as well-known as a tourist destination |
| Climate | The Western Ghats have a more humid climate than the Eastern Ghats | The Eastern Ghats have a more dry climate than the Western Ghats |
| Ecology | The Western Ghats play a significant role in the Indian monsoon | The Eastern Ghats play a less significant role in the Indian monsoon |
I hope this information is helpful. Please let me know if you have any other questions.
The Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats are two mountain ranges that run parallel to the west and east coasts of India, respectively. They are both important features of the Indian landscape, and they play a significant role in the country’s climate and ecology.
The Western Ghats are a much older mountain range than the Eastern Ghats, and they are also much higher. The Western Ghats are home to a wide variety of plant and animal life, and they are a popular destination for tourists. The Eastern Ghats are not as high or as well-known as the Western Ghats, but they are still an important part of the Indian landscape.
Here is a table that summarizes the differences between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats:
| Feature | Western Ghats | Eastern Ghats |
|—|—|—|
| Age | 300 million years old | 150 million years old |
| Height | Average height of 1,000 meters | Average height of 600 meters |
| Length | 1,600 kilometers | 1,900 kilometers |
| Location | Runs parallel to the west coast of India | Runs parallel to the east coast of India |
| Climate | Tropical rainforest climate | Tropical monsoon climate |
| Vegetation | Tropical rainforest | Tropical deciduous forest |
| Wildlife | Elephants, tigers, leopards, monkeys, snakes, birds | Tigers, leopards, elephants, deer, birds |
| Tourism | Popular tourist destination | Not as popular tourist destination |
Here are some MCQs about the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats:
- Which mountain range is older: the Western Ghats or the Eastern Ghats?
- Which mountain range is higher: the Western Ghats or the Eastern Ghats?
- Which mountain range is located along the west coast of India?
- Which mountain range is located along the east coast of India?
- Which mountain range has a tropical rainforest climate?
- Which mountain range has a tropical monsoon climate?
- Which mountain range is home to elephants, tigers, leopards, monkeys, snakes, and birds?
- Which mountain range is home to tigers, leopards, elephants, deer, and birds?
- Which mountain range is a popular tourist destination?
- Which mountain range is not as popular a tourist destination?