<<–2/”>a >a href=”https://exam.pscnotes.com/atomic-structure/”>Atomic structure
In 1897 J.J. Thomson discovered electron as a constituent of atom. He determined that an electron had a negative charge and had very little mass as compared to that of the atom. Since an atom was found to be electrically neutral it was inferred that some source of positive charge must be present in the atom. This soon led to the experimental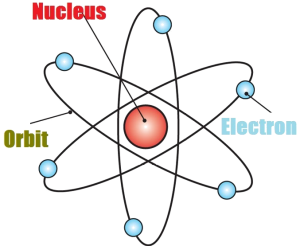
Various theories put forwarded regarding the structure are as follows:-
Dalton’s atomic theory
John Dalton used the Greek concept of an atom and the laws of definite proportions, conservation of mass and multiple proportions to give the atomic theory on scientific basis. Dalton’s atomic theory states that all matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible, all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties,compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms and a Chemical Reaction is a rearrangement of atoms.
J . J. Thompson Plum pudding model
The discovery that atoms contained electrons caused Thompson to predict an atomic structure, according to which the whole atom was considered to be a positive sphere,
with negatively charged electrons embedded in it like a plum in a pudding. Thompson’s model did not have any nucleus in it.
But, with the discovery of the nucleus and positively charged proton and neutrally charged neutrons, two more important models of atomic structure were put forward:
Rutherford atomic model
Rutherford atomic model, though a major breakthrough with a central nucleus and surrounding electrons, did not explain how an electron keeps revolving around the nucleus without losing energy.
Bohr’s atomic structure
Niels Bohr expanded Rutherford’s theory further and gave a clear concept of balancing the attractive force and the centrifugal force of the revolving electrons.
The atomic theory put forward by Niel’s Bohr, was completely successful, except for certain corrections, like replacement of the orbits of Bohr by orbitals, etc.,
Subatomic Particles
The atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics is impossible, and quantum mechanics must be used instead.
The atom is composed of three types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, which is at the center of the atom. Electrons orbit the nucleus.
Protons have a positive electric charge, neutrons have no electric charge, and electrons have a negative electric charge. The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number. The number of neutrons is called the neutron number. The sum of the atomic number and the neutron number is called the mass number.
The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells. The outermost shell is called the valence shell. The electrons in the valence shell are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons that are involved in chemical bonding.
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule that has a net electrical charge. Ions can be formed when atoms or Molecules gain or lose electrons. Atoms or molecules that lose electrons become positively charged ions, while atoms or molecules that gain electrons become negatively charged ions.
Isotope
An isotope is a variant of an element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties but different physical properties.
Atomic Number
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The atomic number is unique for each element. For example, all carbon atoms have 6 protons in their nucleus, and all Oxygen atoms have 8 protons in their nucleus.
Mass Number
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The mass number is not unique for each element. For example, carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
Atomic Mass
The atomic mass is the Average mass of an atom of an element. The atomic mass is calculated by taking the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element.
Atomic Radius
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron shell. The atomic radius is typically measured in picometers (pm).
Ionization Energy
The ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. The ionization energy is typically measured in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol).
Electronegativity
The electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons. The electronegativity is typically measured on a scale of 0 to 4, with fluorine having the highest electronegativity and cesium having the lowest electronegativity.
Electron Affinity
The electron affinity is the energy released when an electron is added to an atom. The electron affinity is typically measured in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol).
Electron Configuration
The electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The electron configuration is typically written as a series of superscripts, with each superscript representing the number of electrons in that shell.
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) is a theory that predicts the shape of a molecule based on the number of valence electrons in the molecule. The VSEPR theory states that the valence electrons will repel each other as much as possible, and that the shape of the molecule will be the one that minimizes the electron-electron repulsion.
Lewis Structure
A Lewis structure is a diagram that shows the bonding between atoms in a molecule. Lewis structures are typically drawn using dots to represent electrons. The number of dots around an atom represents the number of valence electrons in the atom.
Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) is a theory that describes the bonding in molecules using quantum mechanics. MO theory states that the electrons in a molecule are shared by all of the atoms in the molecule. The electrons are not localized between two atoms, but instead are spread out over the entire molecule.
Hybridization
Hybridization is a concept in chemistry that describes the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new orbitals. Hybrid orbitals are used to form covalent Bonds. The type of hybridization that occurs depends on the number of valence electrons in the atom.
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that holds the atoms together. Chemical
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics is impossible. Instead, quantum mechanics must be used to correctly describe and predict their behavior.
What are the parts of an atom?
The three main parts of an atom are the nucleus, the electron cloud, and the electron shells. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons, which are held together by the strong force. The electron cloud is a region of space around the nucleus where electrons are found. The electron shells are regions of space around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
The nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons have a negative charge. The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number, and it determines the chemical element of the atom. For example, all atoms with 6 protons in their nucleus are carbon atoms.
What is the electron cloud of an atom?
The electron cloud is a region of space around the nucleus where electrons are found. The electron cloud is not a solid object, but rather a region of space where there is a high Probability of finding electrons. The shape of the electron cloud is determined by the number of electrons in the atom and the energy of the electrons.
What are the electron shells of an atom?
The electron shells are regions of space around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found. The first shell can hold up to two electrons, the second shell can hold up to eight electrons, the third shell can hold up to 18 electrons, and so on. The electrons in the outermost shell are called valence electrons, and they determine the chemical properties of the atom.
What are the different types of atoms?
There are over 100 different types of atoms, called Elements. Each element has a different number of protons in its nucleus. The elements are arranged in the periodic table, which is a table of the elements that is organized by their atomic number.
What are the properties of atoms?
The properties of atoms are determined by the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. The number of protons determines the chemical element of the atom. The number of neutrons determines the isotope of the atom. The number of electrons determines the chemical properties of the atom.
What are the uses of atoms?
Atoms are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Chemistry: Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and they are used in a variety of chemical reactions.
- Physics: Atoms are studied in physics to understand their properties and behavior.
- Biology: Atoms are the building blocks of life, and they are used in a variety of biological processes.
- Technology: Atoms are used in a variety of technologies, including computers, electronics, and energy production.
The smallest unit of matter that retains all of the chemical properties of an element is called an:
(A) atom
(B) molecule
(C) ion
(D) electronThe nucleus of an atom is made up of:
(A) protons and neutrons
(B) electrons and neutrons
(C) protons and electrons
(D) neutrons and electronsThe number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the:
(A) atomic number
(B) mass number
(C) charge number
(D) electron numberThe number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the:
(A) atomic number
(B) mass number
(C) charge number
(D) electron numberAtoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called:
(A) isotopes
(B) ions
(C) molecules
(D) compoundsThe number of electrons in an atom is equal to the:
(A) atomic number
(B) mass number
(C) charge number
(D) electron numberThe electrons in an atom are arranged in shells around the nucleus. The outermost shell is called the:
(A) valence shell
(B) core shell
(C) inner shell
(D) subshellThe electrons in the valence shell are the electrons that are involved in chemical bonding.
(A) True
(B) FalseAtoms of different elements can combine to form molecules.
(A) True
(B) FalseA molecule is made up of two or more atoms that are held together by chemical bonds.
(A) True
(B) False