- The circulatory system can be compared to a system of interconnected, one-way roads that range from superhighways to back alleys.
- Like a Network of roads, the job of the circulatory system is to allow the transport of materials from one place to another.
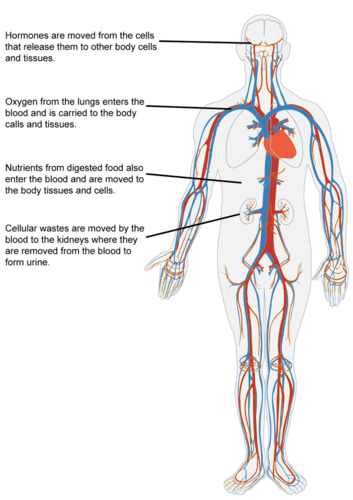
- As described in Figure below, the materials carried by the circulatory system include HORMONES, Oxygen, cellular wastes, and nutrients from digested food.
- Transport of all these materials is necessary to maintain homeostasis of the body. The main components of the circulatory system are the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Each of these components is described in detail below
The Heart
- The heart is a muscular organ in the chest. It consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue and pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions.
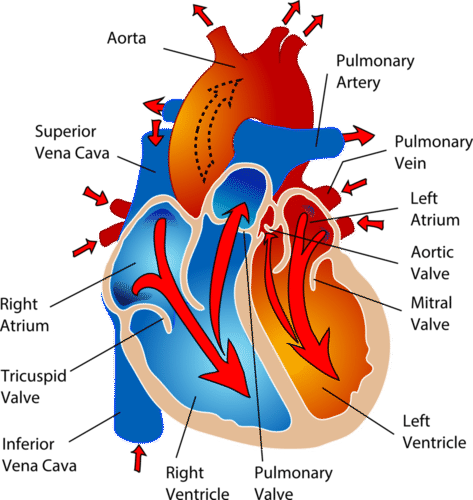
- The heart has four chambers, as shown in Figurebelow: two upper atria (singular, atrium) and two lower ventricles. Valves between chambers keep blood flowing through the heart in just one direction
Blood Flow through the Heart
Blood flows through the heart in two separate loops, which are indicated by the arrows in Figure above.
- Blood from the body enters the right atrium of the heart. The right atrium pumps the blood to the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs. This loop is represented by the blue arrows in Figure
- Blood from the lungs enters the left atrium of the heart. The left atrium pumps the blood to the left ventricle, which pumps it to the body. This loop is represented by the red arrows in Figure
Heartbeat
- Unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle contracts without stimulation by the nervous system. Instead, specialized cardiac muscle cells send out electrical impulses that stimulate the contractions.
- As a result, the atria and ventricles normally contract with just the right timing to keep blood pumping efficiently through the heart
Blood Vessels
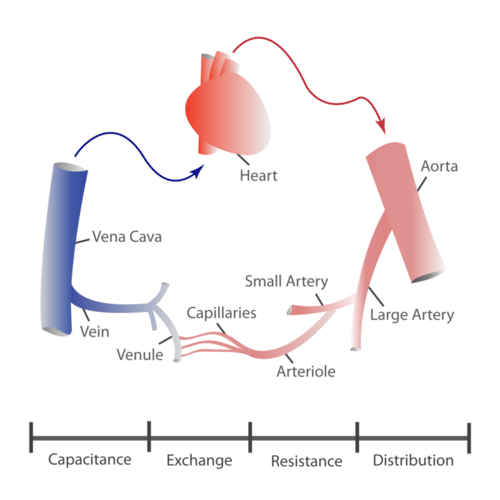
- Blood vessels form a network throughout the body to transport blood to all the body cells.
- There are three major types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries. All three are shown in Figurebelow and described below
- Arteriesare muscular blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. They have thick walls that can withstand the pressure of blood being pumped by the heart. Arteries generally carry oxygen-rich blood. The largest artery is the aorta, which receives blood directly from the heart.
- Veinsare blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart. This blood is no longer under much pressure, so many veins have valves that prevent backflow of blood. Veins generally carry deoxygenated blood. The largest vein is the inferior vena cava, which carries blood from the lower body to the heart.
- Capillariesare the smallest type of blood vessels. They connect very small arteries and veins. The exchange of gases and other substances between cells and the blood takes place across the extremely thin walls of capillaries
Blood Vessels and Homeostasis
- Blood vessels help regulate body processes by either constricting (becoming narrower) or dilating (becoming wider).
- These actions occur in response to signals from the autonomic nervous system or the Endocrine System.
- Constriction occurs when the muscular walls of blood vessels contract. This reduces the amount of blood that can flow through the vessels. Dilation occurs when the walls relax.
- This increases blood flows through the vessels. Constriction and dilation allow the circulatory system to change the amount of blood flowing to different organs.
- For example, during a fight-or-flight response, dilation and constriction of blood vessels allow more blood to flow to skeletal muscles and less to flow to digestive organs.
- Dilation of blood vessels in the skin allows more blood to flow to the body surface so the body can lose heat. Constriction of these blood vessels has the opposite effect and helps conserve body heat.
Blood Vessels and Blood Pressure
- The force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels is called blood pressure. Blood pressure is highest in arteries and lowest in veins.
- When you have your blood pressure checked, it is the blood pressure in arteries that is measured. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a serious Health risk but can often be controlled with lifestyle changes or medication
Pulmonary Circulation
- Pulmonary circulation is the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and lungs (the term pulmonary means “of the lungs”).
- It is illustrated in Figure below. Deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle through pulmonary arteries, which transport it to the lungs.
- In the lungs, the blood gives up carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen. The oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium of the heart through pulmonary veins
Systemic Circulation
- Systemic circulation is the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and body. It is illustrated in Figure below.
- Oxygenated blood leaves the left ventricle through the aorta.
- The aorta and other arteries transport the blood throughout the body, where it gives up oxygen and picks up carbon dioxide.
- The deoxygenated blood then returns to the right atrium through veins
,
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is located in the chest, behind the sternum (breastbone). The heart is divided into four chambers: two upper chambers called atria and two lower chambers called ventricles. The atria are smaller than the ventricles and receive blood from the body and lungs. The ventricles are larger than the atria and pump blood out of the heart.
The heart is connected to the blood vessels by arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, and veins carry blood back to the heart. The arteries are thick and muscular, and they can withstand the high pressure of blood being pumped out of the heart. The veins are thinner and less muscular, and they carry blood back to the heart at a lower pressure.
The capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. They connect the arteries and veins, and they allow oxygen and nutrients to pass from the blood to the Tissues, and carbon dioxide and waste products to pass from the tissues to the blood.
Blood is a fluid that circulates through the body. It is made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is the liquid part of blood. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the tissues. White blood cells fight infection. Platelets help to form clots to stop bleeding.
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels that helps to remove waste products from the body. It also helps to fight infection.
Circulation is the process of blood flowing through the body. It is divided into two circuits: the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit. The pulmonary circuit carries blood from the heart to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen. The systemic circuit carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body, where it delivers oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and picks up carbon dioxide and waste products.
A heart attack is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the heart is blocked. This can happen due to a clot, a narrowing of the arteries, or a spasm of the arteries. A heart attack can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. If not treated, a heart attack can lead to death.
A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is blocked. This can happen due to a clot, a narrowing of the arteries, or a spasm of the arteries. A stroke can cause paralysis, speech problems, and other symptoms. If not treated, a stroke can lead to death.
Angina is a condition that occurs when the heart muscle does not get enough oxygen. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. Angina is usually caused by coronary artery disease, which is a narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the heart.
Heart failure is a condition that occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can cause shortness of breath, fatigue, and other symptoms. Heart failure can be caused by a number of conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, and cardiomyopathy.
Arrhythmia is a condition that occurs when the heart beats irregularly. This can cause a number of symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness. Arrhythmias can be caused by a number of conditions, including heart disease, infection, and certain medications.
Cardiomyopathy is a condition that occurs when the heart muscle is weak or enlarged. This can cause a number of symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain. Cardiomyopathy can be caused by a number of conditions, including heart disease, infection, and certain medications.
Congenital heart disease is a condition that occurs when a baby is born with a heart defect. This can cause a number of symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and cyanosis (blue skin). Congenital heart disease can be caused by a number of factors, including genetics, infections, and certain medications.
Hypertension is a condition that occurs when the blood pressure is too high. This can cause a number of problems, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Hypertension can be caused by a number of factors, including genetics, obesity, and Stress.
Atherosclerosis is a condition that occurs when the arteries become narrowed and hardened. This can cause a number of problems, including heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Atherosclerosis can be caused by a number of factors, including genetics, smoking, and high cholesterol.
Peripheral artery disease is a condition that occurs when the arteries that carry blood to the arms and legs become narrowed and hardened. This can cause a number of problems, including pain, numbness, and ulcers. Peripheral artery disease can be caused by a number of factors, including smoking, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Varicose veins are veins that are swollen and twisted. They are most commonly found in the legs. Varicose veins can be caused by a number of factors, including genetics
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is located in the chest, between the lungs. The heart is divided into four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The atria are the upper chambers, and the ventricles are the lower chambers. The heart is connected to the blood vessels by arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, and veins carry blood back to the heart.
The heart works by contracting and relaxing. When the heart contracts, it pumps blood out of the ventricles. When the heart relaxes, it fills with blood from the atria. The heart beats about 100,000 times per day.
The blood vessels are a network of tubes that carry blood throughout the body. The arteries carry blood away from the heart, and the veins carry blood back to the heart. The blood vessels are divided into three main types: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
The arteries are the largest blood vessels. They carry blood away from the heart. The arteries are divided into two main types: the aorta and the pulmonary arteries. The aorta is the largest artery in the body. It carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the heart to the lungs.
The veins are the smallest blood vessels. They carry blood back to the heart. The veins are divided into two main types: the vena cava and the pulmonary veins. The vena cava is the largest vein in the body. It carries blood from the rest of the body back to the heart. The pulmonary veins carry blood from the lungs to the heart.
The capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. They connect the arteries to the veins. The capillaries are very thin, and they allow oxygen and nutrients to pass from the blood to the tissues, and waste products to pass from the tissues to the blood.
The heart and blood vessels are essential for life. They work together to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the tissues, and to remove waste products from the tissues.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the structure and working of the heart and blood vessels:
What is the heart?
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.What are the four chambers of the heart?
The four chambers of the heart are the left atrium, the right atrium, the left ventricle, and the right ventricle.What are the functions of the heart?
The functions of the heart are to pump blood throughout the body, to regulate blood pressure, and to produce blood clots.What are the blood vessels?
The blood vessels are a network of tubes that carry blood throughout the body.What are the three main types of blood vessels?
The three main types of blood vessels are arteries, veins, and capillaries.What are the functions of the blood vessels?
The functions of the blood vessels are to carry blood to and from the heart, to regulate blood pressure, and to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the tissues.What are the causes of heart disease?
The causes of heart disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and diabetes.What are the symptoms of heart disease?
The symptoms of heart disease include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.How is heart disease treated?
Heart disease is treated with medication, surgery, and lifestyle changes.What are the complications of heart disease?
The complications of heart disease include heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.How can heart disease be prevented?
Heart disease can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and not smoking.
- The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is located in the chest, between the lungs.
- The heart has four chambers: two upper chambers called atria, and two lower chambers called ventricles.
- The atria receive blood from the body and the lungs, respectively. The ventricles pump blood out of the heart to the body and the lungs, respectively.
- The heart is connected to the blood vessels by arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, and veins carry blood back to the heart.
- The heart is a vital organ that is essential for life. If the heart stops beating, death will occur.
Here are some multiple choice questions about the heart and blood vessels:
The heart is located in the:
(a) head
(b) chest
(c) abdomen
(d) legsThe heart has four chambers:
(a) two atria and two ventricles
(b) three atria and one ventricle
(c) one atrium and three ventricles
(d) four atria and no ventriclesThe atria receive blood from the:
(a) body and the lungs
(b) lungs and the body
(c) heart and the lungs
(d) heart and the bodyThe ventricles pump blood out of the heart to the:
(a) body and the lungs
(b) lungs and the body
(c) heart and the lungs
(d) heart and the bodyThe heart is connected to the blood vessels by:
(a) arteries and veins
(b) capillaries
(c) lymphatic vessels
(d) nervesArteries carry blood away from the heart:
(a) True
(b) FalseVeins carry blood back to the heart:
(a) True
(b) FalseThe heart is a vital organ that is essential for life:
(a) True
(b) FalseIf the heart stops beating, death will occur:
(a) True
(b) FalseThe heart is a muscular organ:
(a) True
(b) False