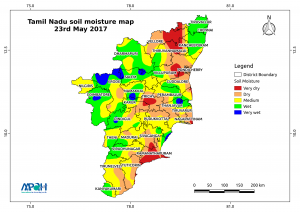
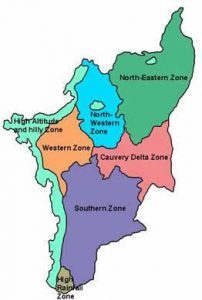
Soil is one of the most important non-renewable basic Resources on the earth’s surface.
The major soil groups of Tamil Nadu are:
- Red soils, (62 per cent)
- Black soils (12 per cent)
- Laterite soils (3 per cent) and
- Coastal soils (7 per cent)
The red soils are further classified as:
- Red loamy (30 per cent)
- Red sterile (6 per cent)
- Red-sandy (6 per cent)
- Thin red (2 per cent) and
- Deep red loamy soils (8 per cent)
As per the USDA system of soil Classification (Taxonomy), the soils of Tamil Nadu are classified in to Six orders viz,
- Entisols
- Inceptisols
- Alfisols
- Mollisols
- Ultisols and
- Vertisols
About 50 per cent of the total area of Tamil Nadu state is occupied by Inceptisol, 30 per cent by Alfisols, 7 per cent by Vertisols, 6 per cent by Entisols, 01 per cent by ultisols and very negligible area by Mollisols.
- Entisols : Young river alluvium, sandy and eroded red and laterite soils.
- Inceptisols: Moderately deep red, laterite and black soils are included under Inceptisol.
- Alfisols : Deep red and laterite soils
- Ultisols : Highly weathered laterite soils
- Vertisols: Deep black Cotton soils and old alluvial soils are classified under vertisol.
Classification of Tamil Nadu Soils
- Red loan: Pats of Kancheepuram, Cuddalore, Salem, Dharmapuri, Coimbatore, Tiruchirappalli, Thanjavur, Ramanathapuram, Madurai, Tirunelveli, Sivagangai, Thoothukudi, Virudhunagar, Dindigul and Nilgiris districts.
- Laterite soil: Parts of Nilgiris district.
- Black soil: Parts of Kancheepuram, Cuddalore, Vellore, Tiruvannamalai, Salem, Dharmapuri, Madurai, Ramanathapuram, Tirunelveli, Sivagangai, Thoothukudi, Virudhunagar, Dindigul and Nilgiris districts.
- Sandy coastal alluvial soil: Along the coasts in Ramanathapuram, Thanjavur, Nagapattinam, Cuddalore, Tiruvarur, Kancheepuram and Kanniyakumari districts.
- Red Sandy soils: Small patches in Coimbatore and Nilgiris districts.
- Riverine alluvial soils: Parts of Kancheepuram, Tiruvallur, Villupuram, Cuddalore, Thanjavur, Nagapattinam, Tiruvarur, Ramanathapuram and Thoothukudi
,
Soils of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is a state in southern India. It is the sixth-largest state in India by area and the third-most populous state. The state is home to a diverse range of soils, which are classified into seven major types: alluvial soils, black cotton soils, laterite soils, red soils, saline and alkaline soils, sandy soils, and Vertisols.
Alluvial soils are formed by the deposition of sediments from rivers and streams. They are typically found in floodplains and deltas. Alluvial soils are usually fertile and well-drained. They are suitable for a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, sugarcane, and cotton.
Black cotton soils are also known as Vertisols. They are formed in semi-arid and arid regions. Black cotton soils are rich in iron and aluminum oxides. They are also known for their high shrink-swell potential. Black cotton soils are suitable for growing crops such as cotton, sorghum, and millet.
Laterite soils are formed in tropical and subtropical regions. They are rich in iron and aluminum oxides. Laterite soils are typically red or yellow in color. They are also known for their low fertility. Laterite soils are suitable for growing crops such as coffee, tea, and rubber.
Red soils are formed in tropical and subtropical regions. They are rich in iron oxides. Red soils are typically red or yellow in color. They are also known for their low fertility. Red soils are suitable for growing crops such as rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
Saline and alkaline soils are formed in arid and semi-arid regions. They are rich in salts and alkalis. Saline and alkaline soils are typically white or gray in color. They are also known for their low fertility. Saline and alkaline soils are not suitable for growing most crops. However, some salt-tolerant crops, such as barley and alfalfa, can be grown on saline and alkaline soils.
Sandy soils are formed in areas with low rainfall. They are typically loose and well-drained. Sandy soils are not very fertile. Sandy soils are suitable for growing crops such as wheat, barley, and sugarcane.
Vertisols are formed in semi-arid and arid regions. They are rich in iron and aluminum oxides. Vertisols are typically black in color. They are also known for their high shrink-swell potential. Vertisols are suitable for growing crops such as cotton, sorghum, and millet.
The soils of Tamil Nadu are a valuable resource. They support a variety of crops and provide habitat for a variety of Plants and animals. It is important to manage these soils wisely to ensure their long-term productivity.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about soils:
What is soil?
Soil is a mixture of Minerals, organic matter, water, air, and living organisms. It is the loose material on the surface of the Earth that plants grow in.What are the different Types of Soil?
There are many different types of soil, but they can be grouped into three main categories: mineral soils, organic soils, and mixed soils. Mineral soils are made up of minerals from rocks and other minerals. Organic soils are made up of the remains of plants and animals. Mixed soils are a combination of mineral and organic soils.What are the properties of soil?
The properties of soil include texture, structure, drainage, fertility, and pH. Texture refers to the size of the particles in the soil. Structure refers to the way the particles in the soil are arranged. Drainage refers to how well water moves through the soil. Fertility refers to the ability of the soil to support plant Growth. pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of the soil.What are the functions of soil?
Soil has many functions, including:- Providing a medium for plant growth
- Storing water
- Regulating temperature
- Providing habitat for organisms
- Cycling nutrients
Protecting the Environment
How is soil formed?
Soil is formed over time by the weathering of rocks and minerals. The weathering process is caused by physical, chemical, and biological factors. Physical Weathering is the breaking down of rocks by physical forces, such as wind and water. Chemical Weathering is the breaking down of rocks by chemical reactions. Biological Weathering is the breaking down of rocks by living organisms, such as plants and animals.How is soil used?
Soil is used for many purposes, including:- agriculture
- Construction
- Recreation
- Landscaping
Mining
What are the threats to soil?
Soil is threatened by many factors, including:- Soil erosion
- Soil contamination
- Soil compaction
- Soil Salinization
Soil acidification
What can be done to protect soil?
There are many things that can be done to protect soil, including:- Reducing soil erosion
- Reducing soil contamination
- Reducing soil compaction
- Reducing soil salinization
Reducing soil acidification
What is the importance of soil?
Soil is essential for life on Earth. It provides a medium for plant growth, stores water, regulates temperature, provides habitat for organisms, cycles nutrients, and protects the environment.What is the future of soil?
The future of soil is uncertain. Soil is threatened by many factors, and it is important to take steps to protect it.
Which of the following is not a type of soil?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the most common type of soil in the world?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the best type of soil for growing crops?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the least fertile type of soil?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the most fertile type of soil?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the most common type of soil in India?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the best type of soil for building houses?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the least suitable type of soil for building houses?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the most suitable type of soil for growing trees?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of TamilnaduWhich of the following is the least suitable type of soil for growing trees?
(A) Sandy soil
(B) Clay soil
(C) Loam soil
(D) Soil of Tamilnadu