INTRODUCTION
Soil is an important matter for cultivation of crops. Soil supplies all the important factors for the Growth of the crop Plants. The yielding potential is largely dependent on the soil in which the crops are grown. The type and properties of soil directly affect the crop growth and yield, hence management and conservation of soil should be done with interest. Climate also is a factor that affects the crop growth and productivity. As we all know Indian agriculture is largely dependent on climatic conditions. The changing weather scenario affect the yield and quality of crop plants and one should find the ways to tackle the problem of such weather effects
Soil Types are classified according to many more factors. They are classified on the basis of colour, depth, pH, productivity, texture and process of formation.
Soil types according to depth are as follows:
1) Shallow Soil – Soil depth less than 22.5cm. Only shallow rooted crops are grown in such soil, e.g. Paddy, Nagli.
2) Medium deep soil – Soil depth is 22.5 to 45cm. Crops with medium deep roots are grown in this type of soil e.g. Sugar cane, Banana, Gram.
3) Deep soil – Soil depth is more than 45cm. Crops with long and deep roots are grown in this type a soil e.g. Mango, coconut.
Major types of soils in India
The main types of soil in India are as follows:
1) Red soils
2) Laterites and lateritic soil
3) Black soil
4) Alluvial soils
5) Forest & hill soils
6) Peaty and marshy soils
(1) Red soils
Red soils have two broad classes:
- a) Red loam with cloddy structure and allow content of concretionary materials; and
- b) Red earths with loose, Permeable top soil and a high content of secondary concretions. Generally these soils are Light textured with porous and friable structure and there is absence of lime Kankar and free carbonates. They have neutral to acidic reaction and are deficient in nitrogen humus, phosphoric acid and lime.
2) Laterites and Lateritic soils
These soils are red to reddish yellow in colour and low in N, P, K, lime and magnesia. These soils are formed in-situ under conditions of high rainfall with alternation dry and wet periods. On account of heavy rainfall there is an excessive leaching of soil colloids and silica hence the soils are porous.
3) Black soils
These are mostly clay soils and form deep cracks during dry season. An accumulation of lime is generally noticed of varying depths. They are popularly known as “Black Cotton soils” because of their dark brown colour and suitability for growing cotton. These are also known as Indian regurs.These soils are deficient in nitrogen, phosphoric acid and organic matter but rich in calcium, potash and magnesium.
4) Alluvial soils
These soils occur along rivers and represent the soil materials that have been deposited by the rivers duing flood. Usually they are very productive soils but many are deficient in nitrogen, humus and phosphorus.
5) Forest and hill soils
These soils occur at high elevations as well as at low elevations, where the rainfall is sufficient to support trees. These soils are very shallow, steep, stony, and infertile for the production of field crops. However, they serve a very useful purpose by supplying forest product such as timber and fuel.
6) Desert soils
These are mostly Sandy soils that occur in the low rainfall track. They are well supplied with soluble salts but are low in nitrogen and organic matter and have a high pH value. These are quite productive. These are often subjected to wind erosion.
7) Saline & Alkaline soils
These soils occur in areas having a little more rainfall than the areas of desert soils. They show white incrustation of salts of calcium &Magnesium and sodium on the surface. These are poor in drainage and are infertile.
8) Peaty and Marshy soils
These types of soils are found in Kerala, coastal track of Orissa, Sunderban area of W.B. When the vegetation growing in such wet places dies, it decomposes very slowly dues to excessive wetness of soils and after several hundreds of year a layer of partly decayed organic matter accumulates on the surface, giving rise to such peaty and marshy soils. These are black coloured, heavy and highly acidic soils. When properly drained and fertilized, these soils produce good crops of rice.
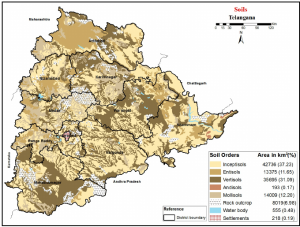
Telanagana is a newly formed state which is bifurcated from Andhra pradesh on June 2, 2013. Its area of 114,840 km2 makes it the 12th largest state in the country. The state consist of various types of soil.
1.Red soils:
Most of the part in Telangana state is covered by Red soils which is about 48%.
These soils formed due to weathering of ancient Metamorphic Rocks.
Red color is due to presence of iron oxides.
These soils cover large part in Mahabubnagar, Nalgonda, Karimnagar, Khammam, Rangareddy, Nizamabad districts and very less in Adilabad district.
- Black soils
These soils accounts for 25% of total area of Telanagan. These are made up of volcanic rocks and lava flow. These are also called as regur soils.
These soils are very much suitable for Cotton crop.
The black color is due to fe, mg oxides. Water holding capacity of these soils is high.
You can found most of the parts in Adilabad, Rangareddy, Nizama bad districts and less parts of KNR, WGL, MBN districts.
- Laterite soils
Covers 7% of the area. These soils formed due to intense leaching where high temperature and high rainfall occurs. These soils are sticky in nature.
Found in Medak and Khammam districts.
- Alluvial soils
These soils are formed by the deposition of sediments by rivers. These are rich in humas and very fertile. You can see soils present at river banks.
,
Soil is a complex and dynamic natural resource that is essential for life on Earth. It provides a medium for plant growth, helps to regulate the climate, and filters water. Soil is also a major source of nutrients and Minerals for plants and animals.
Telangana is a state in India that is located in the southern part of the country. The state has a total area of 100,000 square kilometers and a Population of over 35 million people. Telangana is a land of contrasts, with a variety of landscapes, including Mountains, forests, plains, and deserts.
The soil of Telangana is highly diverse, reflecting the state’s varied climate and topography. The major soil types in Telangana are:
- Alluvial soils: These soils are found in the river valleys and are characterized by their high fertility.
- Black soils: These soils are found in the Deccan Plateau and are characterized by their high clay content.
- Red soils: These soils are found in the eastern part of the state and are characterized by their high iron content.
- Laterite soils: These soils are found in the southern part of the state and are characterized by their high acidity.
Soil formation is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors, including climate, parent material, topography, and time. In Telangana, soil formation is primarily influenced by the state’s tropical climate and its diverse topography. The state’s long history of human activity has also had a significant impact on soil formation.
Soil fertility is the ability of a soil to support plant growth. Soil fertility is determined by a number of factors, including the soil’s texture, structure, pH, and nutrient content. The soil of Telangana is generally fertile, but it can be affected by a number of factors, including soil erosion, Salinization, and nutrient depletion.
Soil conservation is the practice of protecting and managing soil Resources. Soil conservation is important to prevent soil erosion, salinization, and nutrient depletion. Soil conservation practices include:
- Terrace farming: This practice involves creating terraces on sloping land to reduce soil erosion.
- Contour farming: This practice involves planting crops in rows that follow the contours of the land to reduce soil erosion.
- Strip Cropping: This practice involves planting different crops in alternating strips to reduce soil erosion.
- Cover cropping: This practice involves planting cover crops, such as legumes, to protect the soil from erosion and improve its fertility.
- Soil mulching: This practice involves covering the soil with a layer of organic matter, such as straw or leaves, to protect it from erosion and improve its fertility.
Soil Pollution is the contamination of soil by harmful substances. Soil pollution can be caused by a variety of sources, including industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and urban runoff. Soil pollution can have a number of negative impacts on human Health, the Environment, and the economy.
Soil management is the practice of managing soil resources to ensure their long-term productivity. Soil management practices include:
- Soil conservation: This practice involves protecting and managing soil resources to prevent soil erosion, salinization, and nutrient depletion.
- Soil fertility management: This practice involves managing soil fertility to ensure that it is adequate for plant growth.
- Soil health management: This practice involves managing soil health to ensure that it is conducive to plant growth and the activities of soil organisms.
Soil is a vital resource that is essential for life on Earth. It is important to protect and manage soil resources to ensure their long-term productivity.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about the soil of Telangana:
- What are the different types of soil found in Telangana?
The different types of soil found in Telangana are:
- Black soil: This type of soil is found in the eastern part of the state and is very fertile. It is good for growing crops like rice, cotton, and sugarcane.
- Red soil: This type of soil is found in the western part of the state and is not as fertile as black soil. It is good for growing crops like Millets, pulses, and oilseeds.
- Alluvial soil: This type of soil is found in the river valleys and is very fertile. It is good for growing crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
Laterite soil: This type of soil is found in the hilly areas and is not very fertile. It is good for growing crops like coffee, tea, and cashew nuts.
What are the factors that affect the type of soil found in Telangana?
The factors that affect the type of soil found in Telangana are:
- The climate: The Climate of Telangana is tropical, with hot summers and mild winters. This climate is ideal for the growth of black soil.
- The topography: The topography of Telangana is varied, with plains, hills, and valleys. The different types of soil are found in different parts of the state, depending on the topography.
The geology: The geology of Telangana is also varied, with different Types of Rocks and minerals. The different types of soil are found in different parts of the state, depending on the geology.
What are the problems associated with the soil of Telangana?
The problems associated with the soil of Telangana are:
- Soil erosion: Soil erosion is a major problem in Telangana. The state is prone to floods and droughts, which can cause soil erosion. Soil erosion can lead to loss of fertility and productivity of the soil.
- Salinity: Salinity is another major problem in Telangana. The state has a high water table, which can cause the soil to become saline. Salinity can make the soil unsuitable for agriculture.
Waterlogging: Waterlogging is a problem in some parts of Telangana. The state receives heavy rainfall, which can cause the soil to become waterlogged. Waterlogging can make the soil unsuitable for agriculture.
What are the solutions to the problems associated with the soil of Telangana?
The solutions to the problems associated with the soil of Telangana are:
- Soil conservation: Soil conservation is the process of preventing soil erosion. Soil conservation can be done by planting trees, terracing the land, and using Crop Rotation.
- Drainage: Drainage is the process of removing excess water from the soil. Drainage can be done by building canals, ditches, and drains.
Irrigation: Irrigation is the process of providing water to the soil. Irrigation can be done by using canals, wells, and pumps.
What are the future prospects of the soil of Telangana?
The future prospects of the soil of Telangana are good. The state has a number of initiatives in place to improve the quality of the soil. These initiatives include soil conservation, drainage, and irrigation. The state also has a number of programs in place to promote Sustainable Agriculture. These programs will help to protect the soil and ensure its long-term productivity.
The soil of Telangana is classified into four major types:
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Black soil
(c) Red soil
(d) Laterite soilThe alluvial soil is found in the river valleys and is the most fertile type of soil in Telangana.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe black soil is found in the eastern part of Telangana and is suitable for growing cotton.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe red soil is found in the western part of Telangana and is suitable for growing pulses and oilseeds.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe laterite soil is found in the hilly areas of Telangana and is not suitable for agriculture.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe main crops grown in Telangana are:
(a) Rice
(b) Cotton
(c) Pulses
(d) OilseedsThe main irrigation sources in Telangana are:
(a) Canals
(b) Tanks
(c) Wells
(d) All of the aboveThe main industries in Telangana are:
(a) Textiles
(b) Electronics
(c) Pharmaceuticals
(d) All of the aboveThe main tourist attractions in Telangana are:
(a) Golconda Fort
(b) Charminar
(c) Qutb Shahi Tombs
(d) All of the aboveThe capital of Telangana is:
(a) Hyderabad
(b) Warangal
(c) Nizamabad
(d) Karimnagar