<–2/”>a >The doctrine of the Separation of Powers finds its roots in the ancient world, where the concepts of governmental functions, and the theories of mixed and balanced government, were evolved. These were essential Elements in the development of The doctrine of the separation of powers. Their transmission through medieval writings, to provide the basis of the ideas of Constitutionalism In England, enabled the doctrine of the separation of powers to emerge as an alternative, but closely related, formulation of the proper articulation of the parts of government.
The power to govern should be distributed between the Parliament, the Executive and the Judiciary to avoid one group having all the power. Each group should work within defined areas of responsibility so that each keeps a check on the actions of the others.
The principle of separation of powers deals with the mutual relations among the three organs of the government, namely legislature, executive and judiciary. The doctrine of the separation of powers tries to bring exclusiveness in the functioning of the three organs and hence a strict demarcation of power is the aim sought to be achieved by this principle. This doctrine signifies the fact that one person or body of persons should not exercise all the three powers of the government.Its based on checks and balances of government functions.
Main features of separation of power are:-
- That the same persons should not form part of more than one of the three organs of Government, e.g. the Ministers should not sit in Parliament;
- One organ of the Government should not control or interfere with the exercise of its function by another organ, e.g. the Judiciary should be independent of the Executive or that Ministers should not be responsible to Parliament;
- One organ of the Government should not exercise the functions of another, e.g. the Ministers should not have legislative powers.
India follows constitutional Democracy which offers a clear separation of powers. The judiciary branch is fairly independent of the other two branches with the power to interpret the constitution. Parliament has the legislative powers. Executive powers are vested with the President who is advised by the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister. The constitution of India vested the duty of protecting, preserving and defending the constitution with the President as common head of the executive, parliament, armed forces, etc. not only for the union 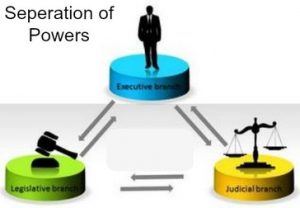
- President can set aside a law passed by the legislative or an advise given by the Union Council of Ministers when it is inconsistent with the constitution of India.
- Even president accepts a law passed duly by the legislative, it can be repealed by The Supreme Court after a fair trial if it is against the Basic structure of the constitution. Any citizen of India can approach the Supreme Court directly to repeal the unconstitutional laws made by the legislative or executive.
- President can be impeached after conducting a fair trial by the parliament for his unconstitutional orders/decisions.
- President can be asked to step down by the judiciary for his unconstitutional orders/decisions on the grounds of losing eligibility criteria of the president.
- Parliament can impeach judges of Supreme Court and High Courts of states for their incompetence and malafides. Higher bench of judges can set aside the incorrect judgement of smaller bench of judges to uphold the constitution.
,
The separation of powers is a System of Government in which the government is divided into branches, each with separate and independent powers. This system is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
The three branches of government are the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch. The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. The executive branch is responsible for carrying out the laws. The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws.
The separation of powers is important because it helps to protect the rights of the people. It also helps to ensure that the government is accountable to the people.
Legislative branch
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. The legislative branch is made up of the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives has 435 members, who are elected every two years. The Senate has 100 members, two from each state, who are elected every six years.
The legislative branch has the power to pass laws, declare war, raise taxes, and borrow Money. The legislative branch also has the power to impeach the president and other federal officials.
Executive branch
The executive branch is responsible for carrying out the laws. The executive branch is headed by the president, who is elected every four years. The president is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces and has the power to veto laws passed by Congress.
The executive branch also includes the vice president, the cabinet, and the various departments and agencies of the federal government.
Judicial branch
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws. The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme Court, which has nine justices who are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate. The Supreme Court has the power to strike down laws that it deems unconstitutional.
The judicial branch also includes the lower federal courts, which are responsible for hearing cases that are appealed from the state courts.
Checks and balances
The system of checks and balances is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. The legislative branch can check the executive branch by impeaching the president and other federal officials. The executive branch can check the legislative branch by vetoing laws. The judicial branch can check both the legislative and executive branches by striking down laws that it deems unconstitutional.
Federalism is a system of government in which power is shared between the national government and the state governments. The national government is responsible for matters that affect the entire country, such as Foreign Policy and national defense. The state governments are responsible for matters that affect only their own states, such as Education and law enforcement.
Federalism is important because it helps to protect the rights of the states. It also helps to ensure that the government is accountable to the people.
Separation of church and state
The separation of church and state is the principle that the government should not interfere with religion, and religion should not interfere with the government. This principle is enshrined in the First Amendment to the United States Constitution, which states that “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof.”
The separation of church and state is important because it protects the religious freedom of all Americans. It also helps to ensure that the government is not influenced by any particular religion.
The separation of powers, checks and balances, federalism, and separation of church and state are all important principles of the American government. These principles help to protect the rights of the people and ensure that the government is accountable to the people.
What is the separation of powers?
The separation of powers is the idea that the government should be divided into three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. Each branch should have its own powers and responsibilities, and no one branch should have too much power.
What are the benefits of the separation of powers?
The separation of powers helps to prevent tyranny. If one branch of government becomes too powerful, it can become tyrannical and oppress the people. The separation of powers helps to ensure that no one branch of government can become too powerful.
What are the drawbacks of the separation of powers?
The separation of powers can make it difficult for the government to act quickly and efficiently. Because each branch has its own powers and responsibilities, it can be difficult for the government to pass laws or take action on important issues.
What are some examples of the separation of powers in action?
The United States government is a good example of the separation of powers. The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. The executive branch is responsible for carrying out the laws. The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws.
What are some challenges to the separation of powers?
One challenge to the separation of powers is the rise of the administrative state. The administrative state is a Network of government agencies that are responsible for carrying out the laws. These agencies have become increasingly powerful, and some people worry that they are undermining the separation of powers.
Another challenge to the separation of powers is the rise of political polarization. When the two major Political Parties are deeply divided, it can be difficult for the government to function effectively. This is because each party is more likely to try to obstruct the other party than to work together to solve problems.
What are some reforms that have been proposed to address the challenges to the separation of powers?
Some people have proposed reforms that would make it more difficult for the administrative state to become too powerful. These reforms would include giving Congress more control over the agencies and making it easier for citizens to sue the agencies.
Others have proposed reforms that would make it easier for the government to function effectively in a time of political polarization. These reforms would include encouraging more bipartisanship and making it easier for the government to pass laws.
Here are some multiple choice questions about the topics of the separation of powers, the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch:
Which of the following is not a power of the legislative branch?
(A) To make laws
(B) To declare war
(C) To ratify treaties
(D) To appoint judgesWhich of the following is not a power of the executive branch?
(A) To enforce laws
(B) To declare war
(C) To appoint judges
(D) To veto lawsWhich of the following is not a power of the judicial branch?
(A) To interpret laws
(B) To declare laws unconstitutional
(C) To try cases
(D) To appoint judgesWhich of the following is a check on the power of the legislative branch?
(A) The executive branch can veto laws.
(B) The judicial branch can declare laws unconstitutional.
(C) The people can vote for new representatives.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a check on the power of the executive branch?
(A) The legislative branch can impeach the president.
(B) The judicial branch can declare executive orders unconstitutional.
(C) The people can vote for a new president.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a check on the power of the judicial branch?
(A) The legislative branch can impeach judges.
(B) The executive branch can appoint judges.
(C) The people can vote for new judges.
(D) None of the above.Which of the following is an example of the separation of powers in action?
(A) The president vetoes a bill passed by Congress.
(B) The Supreme Court declares a law unconstitutional.
(C) The Senate confirms a presidential appointment.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is an example of the checks and balances system in action?
(A) The president vetoes a bill passed by Congress.
(B) The Supreme Court declares a law unconstitutional.
(C) The Senate confirms a presidential appointment.
(D) All of the above.The separation of powers is important because it helps to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe checks and balances system is important because it helps to ensure that no one branch of government can become too powerful.
(A) True
(B) False