<<–2/”>a >a href=”https://exam.pscnotes.com/the-doctrine-of-the-separation-of-powers/”>The doctrine of the Separation of Powers finds its roots in the ancient world, where the concepts of governmental functions, and the theories of mixed and balanced government, were evolved. These were essential Elements in the development of the doctrine of the separation of powers. Their transmission through medieval writings, to provide the basis of the ideas of Constitutionalism In England, enabled the doctrine of the separation of powers to emerge as an alternative, but closely related, formulation of the proper articulation of the parts of government.
The power to govern should be distributed between the Parliament, the Executive and the Judiciary to avoid one group having all the power. Each group should work within defined areas of responsibility so that each keeps a check on the actions of the others.
The principle of separation of powers deals with the mutual relations among the three organs of the government, namely legislature, executive and judiciary. The doctrine of the separation of powers tries to bring exclusiveness in the functioning of the three organs and hence a strict demarcation of power is the aim sought to be achieved by this principle. This doctrine signifies the fact that one person or body of persons should not exercise all the three powers of the government.Its based on checks and balances of government functions.
Main features of separation of power are:-
- That the same persons should not form part of more than one of the three organs of Government, e.g. the Ministers should not sit in Parliament;
- One organ of the Government should not control or interfere with the exercise of its function by another organ, e.g. the Judiciary should be independent of the Executive or that Ministers should not be responsible to Parliament;
- One organ of the Government should not exercise the functions of another, e.g. the Ministers should not have legislative powers.
India follows constitutional Democracy which offers a clear separation of powers. The judiciary branch is fairly independent of the other two branches with the power to interpret the constitution. Parliament has the legislative powers. Executive powers are vested with the President who is advised by the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister. The constitution of India vested the duty of protecting, preserving and defending the constitution with the President as common head of the executive, parliament, armed forces, etc. not only for the union 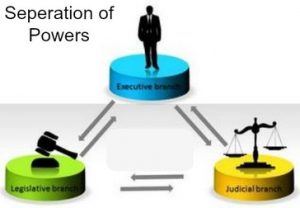
- President can set aside a law passed by the legislative or an advise given by the Union Council of Ministers when it is inconsistent with the constitution of India.
- Even president accepts a law passed duly by the legislative, it can be repealed by The Supreme Court after a fair trial if it is against the Basic structure of the constitution. Any citizen of India can approach the Supreme Court directly to repeal the unconstitutional laws made by the legislative or executive.
- President can be impeached after conducting a fair trial by the parliament for his unconstitutional orders/decisions.
- President can be asked to step down by the judiciary for his unconstitutional orders/decisions on the grounds of losing eligibility criteria of the president.
- Parliament can impeach judges of Supreme Court and High Courts of states for their incompetence and malafides. Higher bench of judges can set aside the incorrect judgement of smaller bench of judges to uphold the constitution.
,
The separation of powers is a System of Government in which the powers of the government are divided among different branches. This system is designed to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. The three branches of government in the United States are the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch.
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. The legislative branch is made up of the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives has 435 members, who are elected every two years. The Senate has 100 members, two from each state, who are elected every six years.
The executive branch is responsible for carrying out the laws. The executive branch is headed by the president, who is elected every four years. The president also has the power to veto laws passed by Congress.
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws. The judicial branch is made up of the Supreme Court and lower federal courts. The Supreme Court has nine justices, who are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate.
The separation of powers is important because it helps to protect the rights of the people. It also helps to ensure that the government is accountable to the people. The system of checks and balances helps to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. For example, the president can veto laws passed by Congress, but Congress can override a veto with a two-thirds vote. The Supreme Court can declare laws unconstitutional, but Congress can pass new laws or amend the Constitution.
Federalism is a system of government in which power is shared between the national government and the state governments. The United States is a federal republic, which means that the national government is limited in its powers. The Tenth Amendment to the Constitution states that “The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.”
Impeachment is a process by which a public official can be removed from office. The House of Representatives has the power to impeach, or charge, a public official with a crime. The Senate then has the power to try the official. If the official is found guilty, they are removed from office.
Recall is a process by which voters can remove an elected official from office before their term is up. A recall petition must be signed by a certain number of voters, and if enough signatures are collected, a special election is held to determine whether the official should be removed from office.
Term limits are laws that limit the number of terms that an elected official can serve. Term limits are designed to prevent elected officials from becoming too powerful and to give new people a chance to serve in office.
The separation of powers, federalism, impeachment, recall, and term limits are all important parts of the American system of government. These systems help to protect the rights of the people and to ensure that the government is accountable to the people.
What is the difference between a republic and a democracy?
A republic is a form of government in which the people hold power, but they do not rule directly. Instead, they elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. A democracy is a form of government in which the people rule directly. They do this by voting on laws and policies themselves.
What are the three branches of government?
The three branches of government are the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch. The legislative branch makes the laws, the executive branch enforces the laws, and the judicial branch interprets the laws.
What is the role of the president?
The president is the head of the executive branch of the government. The president is responsible for enforcing the laws, appointing federal judges, and commanding the armed forces.
What is the role of Congress?
Congress is the legislative branch of the government. Congress is responsible for making laws, declaring war, and approving treaties.
What is the role of the Supreme Court?
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land. The Supreme Court is responsible for interpreting the Constitution and deciding whether laws are constitutional.
What is the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights is the first 10 Amendments to the Constitution. The Bill of Rights guarantees certain rights to the people, such as freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and the right to bear arms.
What is the First Amendment?
The First Amendment guarantees freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and the right to assemble.
What is the Second Amendment?
The Second Amendment guarantees the right to bear arms.
What is the Fourth Amendment?
The Fourth Amendment protects people from unreasonable searches and seizures.
What is the Fifth Amendment?
The Fifth Amendment protects people from self-incrimination and double jeopardy.
What is the Sixth Amendment?
The Sixth Amendment guarantees the right to a speedy and public trial by jury.
What is the Seventh Amendment?
The Seventh Amendment guarantees the right to a jury trial in civil cases.
What is the Eighth Amendment?
The Eighth Amendment prohibits excessive bail, excessive fines, and cruel and unusual punishment.
What is the Ninth Amendment?
The Ninth Amendment states that the rights listed in the Constitution are not the only rights that people have.
What is the Tenth Amendment?
The Tenth Amendment states that any powers not given to the federal government by the Constitution are reserved for the states or the people.
Which of the following is not a branch of government?
(A) Legislative
(B) Executive
(C) Judicial
(D) MilitaryThe President of the United States is the head of which branch of government?
(A) Legislative
(B) Executive
(C) Judicial
(D) MilitaryThe Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States. It is part of which branch of government?
(A) Legislative
(B) Executive
(C) Judicial
(D) MilitaryWhich of the following is not a power of the President of the United States?
(A) To veto laws passed by Congress
(B) To appoint Supreme Court justices
(C) To declare war
(D) To command the armed forcesWhich of the following is not a power of Congress?
(A) To make laws
(B) To declare war
(C) To levy taxes
(D) To impeach the PresidentWhich of the following is not a power of the Supreme Court?
(A) To interpret the Constitution
(B) To overturn laws passed by Congress
(C) To decide cases involving federal law
(D) To try criminal casesWhich of the following is a check on the power of the President?
(A) Congress can impeach the President.
(B) The Supreme Court can overturn laws passed by Congress.
(C) The President can veto laws passed by Congress.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a check on the power of Congress?
(A) The President can veto laws passed by Congress.
(B) The Supreme Court can overturn laws passed by Congress.
(C) The President can appoint Supreme Court justices.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a check on the power of the Supreme Court?
(A) Congress can impeach Supreme Court justices.
(B) The President can appoint Supreme Court justices.
(C) Congress can pass laws that overturn Supreme Court decisions.
(D) All of the above.The system of checks and balances is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. True or False?
Answers:
1. (D)
2. (B)
3. (C)
4. (C)
5. (D)
6. (D)
7. (D)
8. (D)
9. (D)
10. True