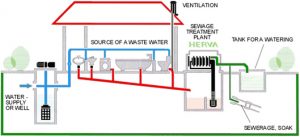
Sanitation and Water Disposal
- The seriousness of the challenges associated with urban Water supply and sanitation in India have been recognised in recent times.
- After decades of neglect, the first national effort to invest in the urban water and sanitation sector commenced in the 1970s, but was accorded considerable priority in the subsequent two decades as a part of different national- and state level schemes, culminating most recently in the ‘Swacch Bharat Mission’.
- As most of the recent reports and commentaries have highlighted, the problems of the urban water and sanitation sector in India are complex and shall need concerted efforts to sustain the policy momentum.
CASE FOR URBAN WATER AND SANITATION
Why meeting the challenge of urban water and sanitation is important in order to meet desirable public Health and environmental outcomes.
Imperatives for Public Health
- There are severe public health consequences of inadequate urban water and sanitation. Globally, diarrhoeal diseases are the second leading cause for children under 5 (UNICEF, 2010), and 25 per cent of global diarrhoeal deaths occur in India (WHO, 2009).
- Around 88 per cent of diarrhoeal deaths can be attributed to inadequate sanitation hygiene and water (UNICEF, 2010). Increasingly, it is been recognised that sanitation is a cause of malnourishment, leading to stunting and long-term cognitive diseases (Spears, 2013).
- one in every 10 deaths in India is from causes related to inadequate sanitation and hygiene (WSP, 2010).
- Lack of sanitation in India has led to economic losses for the country (6.4 % of India’s GDP) (WSP, 2010). This study also highlighted that urban households in the poorest quintile bear the highest per capita economic impact of inadequate sanitation—1.75 times the national Average per capita losses and 60 per cent more than the urban average (WSP, 2010a).
Imperatives for Environmental Protection
- The largest environmental concern, posed by the current urban water and sanitation systems in India, is pollution of water bodies.
- ‘Organic matter and bacterial pollution of fecal origin’ remains the largest Water Pollution problem in India (CPCB, 2012).
- Water quality, as measured by BOD levels, and the presence of Total Coliform and Fecal Coliform, has declined steadily over the period of 1995–2011 (CPCB, 2012).
- The main cause of this pollution is the inability of large urban centres to adequate treat their wastewater, as will be examined in detail in later sections of the paper. Inadequate sanitation is also a cause for contamination of groundwater aquifers. Untreated sewage also remains the single biggest land-based source of pollution for coastal areas of India (CPCB).
- Apart from pollution, the other critical concern faced by urban areas is its growing water demand, within the context of decreasing water availability. With 2.4 per cent of the world land area, India is home to about 17 per cent of the total world Population but has only about 4 per cent of the world’s renewable freshwater Resources (Ministry of Water Resources, 2012).
- In a country like India which is densely and relatively uniformly populated, the growing water demand and the resultant search for newer sources of water is bound to come face-to-face with ecological limits.
- In the case of India, while per capita renewable water resource availability in 1951 was 5,177 cubic meters (cu.m) per capita per year, this became 1,588 cu.m by 2010, placing the country well within the water-stressed category
RURAL SANITATION
- A large section of Indian population lives in villages and is mainly engaged in agriculture. They belong to weaker section of the Society.
- There is a definite trend of rural population migrating to the urban areas due to lack of EMPLOYMENT opportunities, low earnings, insufficient means of transport and insanitary living conditions.
- The latter is mainly responsible to repel the educated youth from working in rural areas. One source of insanitary condition in rural areas is the drainage of waste water from bathing and cooking areas of dwellings over the kutcha roads and lanes having inadequate slopes.
- The situation is further aggravated due to the movements of carts and animals which result in the creation of pot holes and ditches that gets filled up with dirty stagnant water.
- The mosquitoes and flies find good breeding centres in these places and spread diseases. Some of the village roads are brick paved with drains for waste water disposal. But these have not served the required purpose due to improper slopes, insufficient maintenance and unpredictable flow of water. Rural dwellings having their own source of water supply like hand pumps discharge more water on the streets.
- Furthermore, the agricultural waste and domestic refuse collect in drains obstructing the flow of water and ultimately, all these things appear on the streets.
- Some of the village panchayats have suggested individual pits for collection of waste water and its disposal by intermittent sprinkling on large areas, either in the courtyard or on the streets.
- The villagers adopt this practice for some time, but their enthusiasm dies with time. A few progressive farmers have access to the technical know-how and capacity to invest finance to make large sized soakage pits filled with brickbats (to dispose off water underground). These are frequently choked with ash and Soil used by the villagers to clean their utensils. This requires cleaning of the pit and involves considerable expenditure. The high cost of construction and costly maintenance make it beyond the reach of the poor.
- A detailed study of the problem, including the living habits of rural population, was conducted by the Central Building Research Institute, Roorkee.
- The urban type of underground Drainage System was not found suitable because of the settlement of silt and ash in drains; insufficient quantity of water for self-cleaning of the drains; high maintenance and running cost.
- The lack of interest in the maintenance of community Services leads one to conclude that the proposed system should be such that it should make the individuals responsible to run their own waste water disposal system. At the same time, the system should be within the economic reach of a villager who can maintain it without outside help.
Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin)
- Safe sanitation is an essential requirement for the well-being of every society. Though India has come a long way in improving its sanitation coverage status, it is still well short of desired levels.
- In the rural context, Safe Sanitation comprises of the following components
Personal & Household Level
- Safe disposal of human excreta
- Personal hygiene
- Safe handling of drinking water
- Domestic sanitation & food hygiene
Community
- Safe disposal of waste water
- Management of solid waste
- Clean Environment (No littering)
- Management of Community Toilet Complex
- The sanitation programme needs to take care of the above components.
- To tackle the challenge, the Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin) was launched on 2nd October 2014, and is a community-led and people-oriented programme aimed at universalizing safe sanitation, by providing flexibility to states in the implementation of the programme.
,
Sanitation is the process of ensuring that human waste is disposed of safely and hygienically. It includes the collection, treatment, and disposal of sewage and wastewater, as well as the management of solid waste.
Water supply and sanitation (WSS) is a term used to describe the provision of Safe drinking water and adequate sanitation facilities to people. It is a basic human right and essential for public health.
Wastewater treatment is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater so that it can be safely returned to the environment. It includes physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove pollutants such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Waterborne diseases are diseases that are caused by the consumption of contaminated water. They include diarrheal diseases, cholera, typhoid fever, dysentery, poliomyelitis, hepatitis A, schistosomiasis, guinea worm disease, onchocerciasis, trachoma, and leprosy.
Diarrheal diseases are the most common type of waterborne disease. They are caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Diarrheal diseases can cause severe dehydration and Malnutrition, and can be fatal, especially in young children.
Cholera is a bacterial disease that causes severe diarrhea and vomiting. It can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Typhoid fever is a bacterial disease that causes fever, headache, and abdominal pain. It can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Dysentery is a bacterial disease that causes severe diarrhea and blood in the stool. It can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Poliomyelitis is a viral disease that can cause paralysis. It is now rare in most parts of the world due to vaccination.
Hepatitis A is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the liver. It can cause jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain.
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease that causes inflammation of the intestines and bladder. It can cause chronic diarrhea, anemia, and malnutrition.
Guinea worm disease is a parasitic disease that causes a worm to grow inside the body. It can cause severe pain and disability.
Onchocerciasis is a parasitic disease that causes skin and eye problems. It can cause blindness.
Trachoma is a bacterial disease that causes inflammation of the cornea. It can cause blindness.
Leprosy is a bacterial disease that causes skin and nerve damage. It can be treated with antibiotics.
Environmental sanitation is the practice of keeping the environment clean and safe. It includes activities such as garbage collection, sewage treatment, and pest control.
Handwashing is the act of cleaning one’s hands with soap and water. It is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of disease.
Food safety is the practice of ensuring that food is safe to eat. It includes activities such as proper cooking, food storage, and personal hygiene.
Personal hygiene is the practice of keeping oneself clean and healthy. It includes activities such as bathing, brushing teeth, and washing hands.
Solid Waste Management is the process of collecting, treating, and disposing of solid waste. It includes activities such as garbage collection, recycling, and composting.
Air Pollution is the contamination of the air with harmful substances. It can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
Water pollution is the contamination of water with harmful substances. It can cause gastrointestinal problems, reproductive problems, and cancer.
Land pollution is the contamination of land with harmful substances. It can cause soil erosion, water pollution, and air pollution.
Climate change is the long-term change in the Earth’s climate. It is caused by the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide. Climate Change can cause extreme weather events, sea level rise, and changes in agricultural yields.
Sustainable Development is the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It includes the goals of Economic Development, social development, and environmental protection.
Goal 6: Clean water and sanitation is one of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It aims to ensure that everyone has access to safe drinking water and adequate sanitation by 2030.
Goal 14: Life below water is another SDG. It aims to conserve and sustainably use the Oceans, seas, and Marine Resources for sustainable development.
Goal 17: Partnerships for the goals is the SDG that aims to strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global PARTNERSHIP for sustainable development.
Sanitation is essential for public health and sustainable development. It is a basic human right that everyone should have access to.
What is sanitation?
Sanitation is the process of keeping people and the environment clean and healthy. It includes things like providing clean water, disposing of waste safely, and preventing the spread of disease.
What is water disposal?
Water disposal is the process of getting rid of wastewater. This includes things like sewage, industrial wastewater, and storm water.
What are the benefits of sanitation?
Sanitation has many benefits, including:
- Improved health: Sanitation helps to prevent the spread of diseases like cholera, typhoid, and diarrhea.
- Increased productivity: When people are healthy, they are able to work more and earn more Money.
- Reduced POVERTY: Sanitation can help to reduce poverty by improving people’s health and productivity.
- Improved Education: When children are healthy, they are able to attend school and learn.
- Improved Equality/”>Gender Equality: Sanitation can help to improve gender equality by giving Women and girls more opportunities to participate in society.
- Reduced environmental impact: Sanitation can help to reduce the environmental impact of human waste by treating it safely and disposing of it properly.
What are the challenges of sanitation?
There are many challenges to sanitation, including:
- Lack of access to clean water: Many people around the world do not have access to clean water. This makes it difficult to practice good sanitation.
- Lack of access to sanitation facilities: Many people around the world do not have access to toilets or other sanitation facilities. This makes it difficult to dispose of waste safely.
- Poverty: Poverty can make it difficult to afford sanitation facilities and services.
- Lack of education: Many people do not know about the importance of sanitation or how to practice it safely.
- Gender inequality: In some cultures, women and girls are not allowed to use toilets or other sanitation facilities. This can make it difficult for them to stay healthy.
- Conflict: Conflict can damage sanitation Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE and make it difficult to provide sanitation services.
What can be done to improve sanitation?
There are many things that can be done to improve sanitation, including:
- Investing in sanitation infrastructure: Governments and other organizations can invest in building and maintaining sanitation infrastructure, such as toilets and water treatment Plants.
- Providing sanitation services: Governments and other organizations can provide sanitation services, such as collecting and treating wastewater.
- Educating people about sanitation: Governments and other organizations can educate people about the importance of sanitation and how to practice it safely.
- Empowering women and girls: Governments and other organizations can empower women and girls to have access to sanitation facilities and services.
- Addressing conflict: Governments and other organizations can address conflict in order to protect sanitation infrastructure and services.
What is the future of sanitation?
The future of sanitation looks bright. There is a growing awareness of the importance of sanitation and a commitment to improving it. Governments and other organizations are investing in sanitation infrastructure and services, and educating people about the importance of sanitation. With continued effort, we can make sure that everyone has access to safe and clean sanitation.
Sure, here are some multiple choice questions about the following topics:
Water Pollution
Which of the following is not a major source of water pollution?
(A) Agriculture
(B) Industry
(C) Sewage
(D) Air pollutionWhich of the following is the most common type of water pollution?
(A) Organic pollution
(B) Inorganic pollution
(C) Thermal pollution
(D) SedimentationWhich of the following is the most effective way to prevent water pollution?
(A) Reduce, reuse, and recycle
(B) Treat wastewater before it is released into the environment
(C) Monitor water quality and take action to address problems
(D) All of the aboveAir Pollution
Which of the following is not a major source of air pollution?
(A) Transportation
(B) Industry
(C) Agriculture
(D) Natural sourcesWhich of the following is the most common type of air pollution?
(A) Particulate matter
(B) Ozone
(C) Sulfur dioxide
(D) Nitrogen oxidesWhich of the following is the most effective way to prevent air pollution?
(A) Reduce, reuse, and recycle
(B) Use cleaner energy sources
(C) Plant trees
(D) All of the aboveClimate Change
Which of the following is not a major cause of climate change?
(A) Burning fossil fuels
(B) Deforestation
(C) Agriculture
(D) Natural sourcesWhich of the following is the most significant Impact Of Climate Change?
(A) Sea level rise
(B) Extreme weather events
(C) Droughts and floods
(D) All of the aboveWhich of the following is the most effective way to address climate change?
(A) Reduce greenhouse gas emissions
(B) Invest in RENEWABLE ENERGY
(C) Protect forests
(D) All of the aboveDeforestation
Which of the following is not a major cause of deforestation?
(A) Agriculture
(B) Mining
(C) Logging
(D) Natural disastersWhich of the following is the most significant impact of deforestation?
(A) Loss of Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity
(B) Soil erosion
(C) Climate change
(D) All of the aboveWhich of the following is the most effective way to address deforestation?
(A) Reduce demand for wood products
(B) Plant trees
(C) Protect forests
(D) All of the aboveOverpopulation
Which of the following is not a major cause of overpopulation?
(A) High birth rates
(B) Low death rates
(C) Migration
(D) Natural disastersWhich of the following is the most significant impact of overpopulation?
(A) Environmental Degradation
(B) Poverty
(C) Hunger
(D) All of the aboveWhich of the following is the most effective way to address overpopulation?
(A) Reduce population Growth
(B) Improve access to education and family planning
(C) Promote sustainable development
(D) All of the above
I hope these questions were helpful!