Properties of polythene
Polyethylene is a thermoplastic polymer with variable crystalline structure and an extremely large range of applications depending on the particular type. It is one of the most widely produced plastics in the world (tens of millions of tons are produced worldwide each year). The commercial process (the Ziegler-Natta catalysts) that made PE such a success was developed in the 1950s by German and Italian scientists Karl Ziegler and Giulio Natta.
There are a vast array of applications for polyethylene in which certain types are more or less well suited. Generally speaking, High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is much more crystalline, has a much higher density, and is often used in completely different circumstances than Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE). For example, LDPE is widely used in plastic packaging such as for grocery bags or plastic wrap. HDPE by contrast has common applications in construction (for example in its use as a drain pipe). Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW) has high performance applications in things such as medical devices and bulletproof vests.
What Are The Different Types of Polyethylene?
Polyethylene is commonly categorized into one of several major compounds of which the most common include LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE, and Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polypropylene. Other variants include Medium Density Polyethylene (MDPE), Ultra-low-molecular-weight polyethylene (ULMWPE or PE-WAX), High-molecular-weight polyethylene (HMWPE), High-density cross-linked polyethylene (HDXLPE), Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX or XLPE), Very-low-density polyethylene (VLDPE), and Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE).
- Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a very flexible material with very unique flow properties that makes it particularly suitable to plastic film applications like shopping bags. LDPE has high ductility but low tensile strength which is evident in the real world by its propensity to stretch when strained.
- Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) is very similar to LDPE with the added advantage that the properties of LLDPE can be altered by adjusting the formula constituents and that the overall production process for LLDPE is typically less energy intensive than LDPE.
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a strong, high density, moderately stiff plastic with a highly crystalline structure. It is frequently used as a plastic for milk cartons, laundry detergent, garbage bins, and cutting boards.
- Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW) is an extremely dense version of polyethylene with molecular weights typically an order of magnitude greater than HDPE. It can be spun into threads with tensile strengths many times greater than steel and is frequently incorporated into high performance equipment like bulletproof vests.
What are the Characteristics of Polyethylene?
Now that we know what it is used for, let’s examine some of the key properties of Polyethylene. PE is classified as a “thermoplastic” (as opposed to “thermoset”), and the name has to do with the way the plastic responds to heat. Thermoplastic materials become liquid at their melting point (110-130 degrees Celsius in the case of LDPE and HDPE respectively). A major useful attribute about thermoplastics is that they can be heated to their melting point, cooled, and reheated again without significant degradation. Instead of burning, thermoplastics like Polyethylene liquefy, which allows them to be easily [injection molded] and then subsequently recycled. By contrast, thermoset plastics can only be heated once (typically during the injection molding process). The first heating causes thermoset materials to set (similar to a 2-part epoxy) resulting in a chemical change that cannot be reversed. If you tried to heat a thermoset plastic to a high temperature a second time it would simply burn. This characteristic makes thermoset materials poor candidates for recycling.
Different types of Polyethylene exhibit wide variability in their crystalline structures. The less crystalline (the more amorphous) a plastic is, the more it demonstrates a tendency to gradually soften (i.e. they have a wider range between their glass transition temperature and their melting point). Crystalline plastics, by contrast, exhibit a rather sharp transition from solid to liquid.
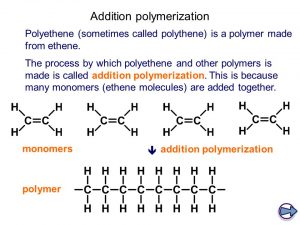
Polyethylene is a homopolymer in that it is composed of a single monomer constituent (in this case ethylene: CH2=CH2).
Why is Polyethylene used so often?
Polyethylene is an incredibly useful commodity plastic. Because of the diversity of PE variants it is incorporated into a wide range of applications. Unless it is required for a specific application, we don’t typically use Polyethylene as part of the design process at Creative Mechanisms. For some projects, a part that will eventually be mass produced in PE can be prototyped with other more prototype-friendly materials like ABS.
PE is not available as a 3D printable material. It can be CNC machined or vacuum formed.
How is PE made?
Polyethylene, like other plastics, starts with the distillation of hydrocarbon fuels (ethane in this case) into lighter groups called “FRACTIONS” some of which are combined with other catalysts to produce plastics (typically via polymerization or polycondensation). You can read about the process in more depth here.
PE for Prototype Development on CNC Machines and 3D Printers:
PE is available in sheet stock, rods, and even specialty shapes in a multitude of variants (LDPE, HDPE etc.), making it a good candidate for subtractive machining processes on a mill or lathe. Colors are usually limited to white and black.
PE is not currently available for FDM or any other 3D printing process (at least not from the two major suppliers: Stratasys and 3D Systems). PE is similar to PP in that it can be difficult to prototype with. You are pretty much stuck with CNC machining or Vacuum forming if you need to use it in your prototype development process.
Is PE toxic?
In solid form, no. In fact, Polyethylene is often used in food handling. It could be toxic if inhaled and/or absorbed into the skin or eyes as a vapor or liquid (i.e. during manufacturing processes). Be careful and closely follow handling instructions for molten polymer in particular.
What are the Disadvantages of Polyethylene?
Polyethylene is generally more expensive than polypropylene (which can be used in similar part applications). PE is the second best choice for living hinges, behind PP at number one.
Common Uses of Polyethylene
Listed below are the top 5 most common uses for Polyethylene. These are the products containing Polyethylene which you are most likely to find already in your home and at the local supermarket.
Sandwich Bags
At some point in our lives, everyone has used sandwich bags for one reason or another. What you may not know is that Polyethylene is used in the manufacturing process of these bags.
The polyethylene is used to make the plastic film that will eventually become the sandwich bags.
It is also used in the sandwich bags cousin, the freezer bag. More of a heavy duty polyethylene plastic is used in the freezer bags, as they need to be able to with stand extreme cold and still be able to protect the items within.
Cling Wrap
Almost every cling wrap you purchase at the supermarket is made from Polyethylene. The Polyethylene combined with other materials helps to make the cling wrap work and keep its hold.
While the cling wrap itself is actually very thin, low density Polyethylene is not used in its production.
Instead, during the manufacturing process the Polyethylene is stretched multiple times to give the cling wrap its normal, thin appearance.
Moisture Barriers
The moisture barriers they use on construction sites and those that are used in crawl spaces under houses are made from Polyethylene.
Low density Polyethylene is not used in the manufacturing of these items, due to the fact that they need the highest quality of Polyethylene available to make sure that the areas are secured from any moisture getting inside.
You can also see non-moisture barriers made from Polyethylene on construction sites, and those are used to keep people out of certain areas or to help protect areas from damaging winds, dirt, or any other material that the workers want to keep off of the site.
Food Packaging
No doubt you have been in the supermarket and found yourself searching for the best pack of ground beef or chicken.
You may notice that there is plastic wrapped around the meat to help keep it fresh before it can be sold and used.
That plastic wrapping is Polyethylene in a low density form. It is used to help make sure that the meat you are purchasing stays fresh until you can get it home and either freeze it or cook it.
The plastic wrapper is tightly fitted onto the packaging so that no other food particles or bacteria can contaminate the meats you are buying.
It can also be used in bakery wrapping to keep bread and other perishable sweet treats from spoiling before they can be sold and used.
You may notice that the bakery bags are a little different from the plastic wraps over your chicken, and that is due to the quality of Polyethylene that is used to make them. However, they both perform the same duty and keep your food fresh and contaminate free.
Coatings
Polyethylene is also used to make the coatings that you see on fruit juice boxes. Though the container is mostly made of out cardboard type material with a small amount of plastic mixed in, the outer coating that keeps the box from falling apart once the liquid has been introduced is the Polyethylene.
It may look like a shiny coating for the box, but it is actually keeping that box tightly together so that kids can enjoy their juice boxes.
It is also used in the wrapping for the straw, and if you buy the juice boxes wrapped instead of in a large box, Polyethylene is also used to make the wrapping for the box.
Most of the time you will see the juice boxes being wrapped when you purchase them from a larger grocery chain.
Almost anything that is either wrapped in plastic or coated in plastic is made from polyethylene.
Polyethylene is made into millions of products every year, most of which we as consumers use on an everyday basis.
And if you are like most people, you did not realize the number of items that can be made from Polyethylene, but it is actually the number one used plastic in the world.
You would be surprised if you looked around at the world today and actually noticed everything that is made from Polyethylene.
Companies are even using it to make cable insulators to keep moisture and animals off of the actual cable wires.
Right now, low density Polyethylene is gaining a lot of ground and is being used in more and more places around the world.
Though it is mainly used in the manufacturing of coatings and cable insulators, it is also being considered for another large Industry.
Manufacturers of plastic toys have been looking into using low density Polyethylene to create their toys.
Polyethylene is also being considered in the manufacturing of more household goods, though some household goods are already using the plastic.
,
Polythene is a type of plastic that is made from the monomer ethylene. It is a versatile material that has a wide range of properties, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Density
The density of polythene is typically between 0.91 and 0.96 grams per cubic centimeter. This means that it is a relatively lightweight material.
Melting point
The melting point of polythene is typically between 110 and 130 degrees Celsius. This means that it can be easily melted and molded into different shapes.
Tensile strength
The tensile strength of polythene is typically between 20 and 30 megapascals. This means that it is a relatively strong material.
Elongation at break
The elongation at break of polythene is typically between 100 and 200%. This means that it is a relatively ductile material.
Impact strength
The impact strength of polythene is typically between 2 and 4 kilojoules per square meter. This means that it is a relatively tough material.
Hardness
The hardness of polythene is typically between 50 and 60 Shore D. This means that it is a relatively hard material.
Toughness
The toughness of polythene is typically between 2 and 4 kilojoules per square meter. This means that it is a relatively tough material.
Chemical resistance
Polythene is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This makes it a good choice for applications where it will be exposed to these chemicals.
Weather resistance
Polythene is resistant to weathering, including sunlight, rain, and snow. This makes it a good choice for applications where it will be exposed to the Elements.
Electrical properties
Polythene is an insulator, meaning that it does not conduct electricity. This makes it a good choice for applications where it will be exposed to electrical current.
Optical properties
Polythene is transparent, meaning that it allows Light to pass through. This makes it a good choice for applications where it is necessary to see through the material.
Biodegradability
Polythene is not biodegradable, meaning that it will not break down over time. This is a disadvantage of polythene, as it can contribute to pollution.
Recyclability
Polythene is recyclable, meaning that it can be reused to make new products. This is an advantage of polythene, as it helps to reduce waste.
Cost
The cost of polythene is relatively low. This makes it a cost-effective material for a variety of applications.
Availability
Polythene is widely available. This makes it a convenient material to use.
Ease of processing
Polythene is easy to process. This makes it a good choice for applications where it is necessary to create complex shapes.
End-use applications
Polythene is used in a wide range of end-use applications, including packaging, construction, and electronics. It is a versatile material that can be used to create a variety of products.
In conclusion, polythene is a versatile material with a wide range of properties. It is a good choice for a variety of applications, including packaging, construction, and electronics.
Polythene is a type of plastic that is made from petroleum. It is a very versatile material and is used in a wide variety of products, including bags, bottles, and food packaging.
Here are some frequently asked questions about polythene:
What are the properties of polythene?
Polythene is a lightweight, strong, and durable material. It is also water-resistant and non-toxic.What are the different types of polythene?
There are two main types of polythene: high-density polythene (HDPE) and low-density polythene (LDPE). HDPE is stronger and more rigid than LDPE. LDPE is more flexible and has a higher melting point than HDPE.How is polythene made?
Polythene is made by heating petroleum and then adding a Catalyst. The catalyst causes the petroleum to break down into smaller Molecules, which are then combined to form polythene.What are the uses of polythene?
Polythene is used in a wide variety of products, including bags, bottles, food packaging, and construction materials.What are the benefits of using polythene?
Polythene is a versatile, durable, and affordable material. It is also non-toxic and can be recycled.What are the drawbacks of using polythene?
Polythene is a non-biodegradable material, which means that it can take hundreds of years to break down in the Environment. It is also a major source of plastic pollution.How can I reduce my use of polythene?
You can reduce your use of polythene by bringing your own reusable bags when you go shopping, choosing products that are not packaged in plastic, and recycling plastic products.What is the future of polythene?
The future of polythene is uncertain. Some experts believe that polythene will eventually be replaced by more sustainable materials, such as bioplastics. Others believe that polythene will continue to be used, but that its production and use will be more environmentally friendly.
Polythene is a type of:
(a) Plastic
(b) Metal
(c) Wood
(d) GlassPolythene is made from:
(a) Petroleum
(b) Coal
(c) Natural gas
(d) All of the abovePolythene is a:
(a) Thermoplastic
(b) Thermoset
(c) Elastomer
(d) None of the abovePolythene is used to make:
(a) Bags
(b) Bottles
(c) Toys
(d) All of the abovePolythene is a:
(a) Good insulator
(b) Good conductor
(c) Neither a good insulator nor a good conductor
(d) Both a good insulator and a good conductorPolythene is a:
(a) Biodegradable material
(b) Non-biodegradable material
(c) Both biodegradable and non-biodegradable material
(d) Neither biodegradable nor non-biodegradable materialPolythene is a:
(a) Recyclable material
(b) Non-recyclable material
(c) Both recyclable and non-recyclable material
(d) Neither recyclable nor non-recyclable materialPolythene is a:
(a) Safe material
(b) Unsafe material
(c) Both safe and unsafe material
(d) Neither safe nor unsafe materialPolythene is a:
(a) Cheap material
(b) Expensive material
(c) Both cheap and expensive material
(d) Neither cheap nor expensive materialPolythene is a:
(a) Durable material
(b) Non-durable material
(c) Both durable and non-durable material
(d) Neither durable nor non-durable material