<<–2/”>a >h2>Preparation of nitrogen
Nitrogen is found in both free and combined states. It occupies 78.07% by volume. Nitrogen can be prepared:
By heating copper in air:
Firstly, air is passed through lime water and then concentrated sulphuric acid to make the air free from carbon dioxide and moistures respectively. The air contains only nitrogen and Oxygen which are passed over the heated copper wire as shown in the figure. Here copper combines with oxygen to make copper oxide and nitrogen gas passes over. This nitrogen can be collected by downward displacement of water.
By burning phosphorous in air:
Nitrogen gas can be prepared by burning phosphorous in air. A crucible with phosphorous is taken and allowed to float on water. Then phosphorous is burnt in crucible is covered with gas jar as shown in figure. The oxygen of the gas jar is consumed during the burning of phosphorous penta oxide is formed. The gas left in the jar is nitrogen.
4P + 5O2 → 2P2O5
By decomposition of compounds containing nitrogen
Like, when dilute solution of ammonium nitrite is heated, nitrogen gas is produced.
NH4NO2→ N2 +2H2O
Principle:
When the solution of sodium nitrite and ammonium chloride is heated they react together and liberate nitrogen gas.
NaNO2 + NH4Cl → NaCl + H2O +N2
Take a mixture of ammonium Chloride and Sodium nitrate in equivalent amount in a round bottom flask. Some water is added to make the solution of the mixture. Then the delivery tube is fitted with a round bottom flask with the help of a cork. The flask is heated gently with a source of heat. After that gas is produced by the reaction of chemicals and is collected in gas jar by downward displacement of water.
Precautions
Ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite should not be used in solid form because ammonium chloride, being a sublimate, sublimes and escape in form of vapour on heating.
Apparatus should be made airtight.
Ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite should be taken in equivalent amount.
Physical Properties
Nitrogen physical properties:
Physical properties of nitrogen is given as,
Nitrogen is a gas without any color, taste and also without any smell which is one of the physical property of nitrogen.
Nitrogen is relatively considered as inert gas which is one of the physical property of nitrogen.
Nitrogen is also considered as the liquid which is similar to water in appearance.
The melting point of the nitrogen is -2100C.
The boiling point of the nitrogen is -195.80C.
Nitrogen contains the two allotropic forms of solid a and b where the transition takes place in between the two forms at the temperature of -2370C.
The vapor density of nitrogen is given as 14which is one of the physical property of nitrogen.
Nitrogen has the soluble property; it is less soluble in water which is one of the physical property of nitrogen.
Chemical Properties
Chemical properties of nitrogen:
The color of indicators is not affected by the nitrogen since it is a neutral gas which is one of the chemical property of nitrogen.
Nitrogen can combine with other Elements and form some compounds under certain temperature which is one of the chemical property of nitrogen..
At high temperature or low temperature nitrogen can form compounds through the biological activity which can act as Catalyst.
In accordance with the oxygen nitrogen forms nitrogen dioxide as well as nitric acid.
When nitrogen is combined with the hydrogen it forms ammonia and with sulfur it form nitrogen sulfide.
Nitrogen is combined with certain metals at higher temperatures which forms the active metals such as lithium and magnesium.
Nitrogen is a non flammable compound which does not support the combustion which is one of the chemical property of nitrogen..
After ionization the energy of nitrogen is given as 1402kJ.mol-1.
The electronegativity of nitrogen due to the Pauling method is given as 3.0.
Common Uses of Nitrogen
This element is present in virtually all pharmacological drugs. In the form of nitrous oxide it is used as an anesthetic. Cryopreservation also uses the gas to conserve egg, blood, sperm and other biological specimens. The CPUs in computers use the gas to keep them from heating up. X-ray detectors also rely on this element.
Nitrogen tanks are also used as paintball gun power sources. These elements have proven to be so effective in this regard they have replaced carbon dioxide. This non-metallic chemical element can be used to fill aircraft and some vehicle tires. The same element is found in military aircraft fuel systems to combat fire hazards. Other common uses for the element are in steel production and in high voltage equipment.
In the latter case, nitrogen is pressurized and dried first. Integrated circuits, diodes, transistors and other electrical components use it too. Nitrogen is present in liquid explosives so they do not explode.
Nitrogen and Living Beings
As stated earlier, the element is present in all living organisms; Plants, animals and people. It is the primary figure in amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. It is also the basis for neurotransmitters, RNA and DNA. The element is also required in plants and is part of chlorophyll pigment. This is what allows plants to change sunlight into energy.
The same element is present in roots, leaves and grains. Plants do not actually take in atmospheric nitrogen. The element is changed into compounds that plants can soak in. The transformation process is called The Nitrogen Cycle.
Uses of Nitrogen in Industries
The element is used in controlling pollution. It is effective in getting rid of unstable organic compounds in liquids. Many industries use it to destroy toxic liquids and vapors in industrial tools. As nitrogen dioxide, the element is vital in the Industrial Sector. It also serves as an oxidation reaction catalyst. Apart from being an oxidizing agent, it can also be used as a flour bleaching agent and rocket fuel.
Liquid Nitrogen
The element assumes this form at -195.5 degree and below. Its uses include refrigerants and cryotherapy. In the latter it is used to take out actinic keratosis, warts and treat other skin disorders.
General Characteristics
This element can be found in the Atmosphere. Nitrogen is also present in other forms. When people think of nitrogen, they immediately associate it with the air. But it is also part of the food they eat every day. Since its discovery, scientists have learned a lot about it. Today nitrogen is commercially available. The most common types are nitrous oxide and supercoolant liquid nitrogen.
This element is the lightest in the nitrogen group. The others are arsenic, antimony and bismuth. Nitrogen can join up with other elements. The Bonds are very effective because nitrogen’s outermost electron shell has few electrons. That is the reason why it is sometimes used as a buffer gas. Since nitrogen makes up 4/5 of the atmosphere, it is pretty common. The element is vital to life, but few animals use the pure kind. Often it is used in the form of amino and nucleic acids.
Discovery
The element was first isolated in 1772. But scientists were aware of it long before that time. In its purest form, nitrogen can be dangerous. It can become an asphyxiant by putting oxygen out of place. This is one of the issues with liquid nitrogen; it turns to gas when exposed to room temperature.
For this reason, proper ventilation is crucial when using it. Decompression sickness usually affects divers that rely on nitrogen. Decompression sickness signs include nitrogen bubbles in the blood. This is due to depressurization.
More about Nitrogen Oxide
The term is applied to the combining of oxygen and nitrogen. The best known variants are nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO). In both instances, one or two oxygen atoms are linked to one nitrogen atom. These oxides have the NOx notation. X symbolizes one or two components of oxygen variables. These elements are generated in engines. According to scientists, too much of these elements in the air causes pollution.
One major cause of pollution are Volatile Organic Compounds (types of chemicals) that join NOx. These two generate smog that dirties the air. That being said, the element has many uses. Scientists are now looking at ways to enhance nitrogen minus these unpleasant elements.
One of the most frequent uses of nitrogen is in Light bulbs. Compared to argon, it is less expensive. Some food packages contain this element to stop oxidation. The element’s inertness is the main reason for its usefulness.
,
Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the Earth’s atmosphere, making up about 78% of the air we breathe. It is also a major component of many Fertilizers and explosives. Nitrogen can be prepared in a number of ways, including liquefaction of air, distillation of liquid air, adsorption of nitrogen, and chemical methods.
Liquefaction of air is the process of cooling air until it turns into a liquid. This can be done by using a variety of methods, such as compression, expansion, and cooling. Once air is liquefied, it can be separated into its component gases, including nitrogen.
Distillation of liquid air is the process of separating the components of liquid air by boiling them at different temperatures. Nitrogen has a boiling point of -195.8 °C, so it can be separated from other gases in liquid air by boiling it off.
Adsorption of nitrogen is the process of attracting nitrogen Molecules to a surface. This can be done by using a variety of materials, such as activated charcoal or silica gel. When nitrogen molecules are adsorbed to a surface, they are removed from the air.
Chemical methods can also be used to prepare nitrogen. One common method is to react ammonia with oxygen to produce nitrogen and water.
The most common method of preparing nitrogen is by liquefaction of air. This process is used to produce large quantities of nitrogen for industrial and commercial purposes. The process begins by compressing air to a high pressure. This increases the temperature of the air, which is then cooled by passing it through a series of heat exchangers. The cooled air is then compressed again, and the process is repeated until the air reaches a temperature of -195.8 °C. At this temperature, the air will liquefy. The liquid air is then distilled to separate the nitrogen from the other gases in the air. The nitrogen is then collected and stored in tanks.
Another method of preparing nitrogen is by adsorption of nitrogen. This process is used to produce small quantities of nitrogen for laboratory and research purposes. The process begins by passing air through a bed of activated charcoal or silica gel. The nitrogen molecules are attracted to the surface of the charcoal or silica gel, and are removed from the air. The nitrogen-rich charcoal or silica gel is then heated, which releases the nitrogen gas. The nitrogen gas is then collected and stored in tanks.
Chemical methods can also be used to prepare nitrogen. One common method is to react ammonia with oxygen to produce nitrogen and water. The reaction is as follows:
2NH3 + 3O2 2N2 + 6H2O
This reaction is carried out in a furnace at a temperature of about 1000 °C. The ammonia and oxygen are mixed together and then heated to the reaction temperature. The nitrogen and water vapor are then produced and collected.
Nitrogen is a very important element in many industrial and commercial applications. It is used in the production of fertilizers, explosives, and other chemicals. It is also used in the food Industry, the medical industry, and the semiconductor industry. Nitrogen is a very versatile element, and it is used in a wide variety of applications.
What is nitrogen?
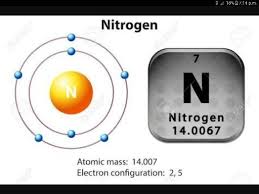
Nitrogen is a chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. It is the most abundant element in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 78.09%. It is a member of the nitrogen group in the periodic table: a group of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements that have a similar chemical behaviour. The atomic nitrogen number is 7, and the atomic mass is 14.006744 u.
What are the properties of nitrogen?
Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas at standard temperature and pressure. It is a member of the nitrogen group in the periodic table: a group of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements that have a similar chemical behaviour. The atomic nitrogen number is 7, and the atomic mass is 14.006744 u.
Nitrogen is a non-Metal and is the most abundant element in the Earth’s atmosphere. It is a relatively inert gas and does not react easily with other elements. However, it can be combined with other elements to form a variety of compounds, including ammonia, nitric acid, and nitrogen oxides.
How is nitrogen prepared?
Nitrogen can be prepared by a variety of methods, including:
- Distillation of liquid air: Liquid air is a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen. When liquid air is distilled, the nitrogen boils at a lower temperature than the oxygen and can be collected separately.
- The Haber process: The Haber process is a Chemical Reaction that combines nitrogen and hydrogen to form ammonia. Ammonia is a valuable industrial chemical that is used in the production of fertilizers, explosives, and other products.
- The Ostwald process: The Ostwald process is a chemical reaction that converts ammonia to nitric acid. Nitric acid is a strong acid that is used in a variety of industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes.
What are the uses of nitrogen?
Nitrogen is a versatile element that has a variety of uses. Some of the most common uses of nitrogen include:
- Fertilizer: Nitrogen is an essential element for plant Growth. It is used in the production of fertilizers, which are used to help plants grow.
- Explosives: Nitrogen is a component of many explosives, including dynamite and TNT.
- Nitric acid: Nitric acid is a strong acid that is used in a variety of industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes.
- Refrigerants: Nitrogen is used as a refrigerant in some refrigerators and freezers.
- Packaging: Nitrogen is used as a packaging gas to protect food and other products from spoilage.
What are the hazards of nitrogen?
Nitrogen is a relatively safe gas, but it can be hazardous in certain situations. Some of the hazards of nitrogen include:
- Asphyxiation: Nitrogen is an asphyxiant, which means that it can displace oxygen in the air and cause suffocation.
- Fire and explosion: Nitrogen can be a fire and explosion hazard when it is mixed with certain other materials.
Health effects: Nitrogen can have a variety of health effects, depending on the exposure level. Some of the health effects of nitrogen exposure include:
Nitrogen narcosis: Nitrogen narcosis is a condition that can occur when people are exposed to high levels of nitrogen. It is characterized by symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and impaired judgment.
- Hypoxia: Hypoxia is a condition that occurs when the body does not have enough oxygen. It can be caused by exposure to low levels of oxygen in the air, such as when people are scuba diving.
- Hyperbaric oxygen toxicity: Hyperbaric oxygen toxicity is a condition that can occur when people are exposed to high levels of oxygen at high pressure. It is characterized by symptoms such as seizures, coma, and death.
What are the safety precautions for working with nitrogen?
When working with nitrogen, it is important to take the following safety precautions:
- Use proper ventilation: Nitrogen is an asphyxiant, so it is important to use proper ventilation when working with it. This will help to ensure that there is enough oxygen in the air to breathe.
- Avoid mixing with other materials: Nitrogen can be a fire and explosion hazard when it is mixed with certain other materials. Be sure to check the MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) for any materials you are working with to see if they are compatible with nitrogen.
- Wear proper personal protective equipment: When working with nitrogen, it is important to wear proper personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, and a respirator. This will help to protect you from
Which of the following is not a method of preparing nitrogen?
(A) Decomposition of ammonium nitrate
(B) Thermal decomposition of ammonia
(C) Combustion of ammonia
(D) Electrolysis of waterWhich of the following is the most common method of preparing nitrogen?
(A) Decomposition of ammonium nitrate
(B) Thermal decomposition of ammonia
(C) Combustion of ammonia
(D) Electrolysis of waterWhat is the chemical formula of ammonium nitrate?
(A) NH4NO3
(B) NH3
(C) N2
(D) NO2What is the chemical formula of ammonia?
(A) NH4NO3
(B) NH3
(C) N2
(D) NO2What is the chemical formula of nitrogen?
(A) N2
(B) NO2
(C) O2
(D) CO2What is the boiling point of nitrogen?
(A) -195.8 °C
(B) -196 °C
(C) -196.1 °C
(D) -196.2 °CWhat is the melting point of nitrogen?
(A) -210 °C
(B) -210.5 °C
(C) -210.8 °C
(D) -211 °CWhat is the density of nitrogen at standard temperature and pressure?
(A) 1.25 g/L
(B) 1.29 g/L
(C) 1.33 g/L
(D) 1.40 g/LWhat is the atomic mass of nitrogen?
(A) 14.006744 u
(B) 14.006745 u
(C) 14.006746 u
(D) 14.006747 uWhat is the number of protons in a nitrogen atom?
(A) 7
(B) 8
(C) 9
(D) 10What is the number of neutrons in a nitrogen atom?
(A) 7
(B) 8
(C) 9
(D) 10What is the number of electrons in a nitrogen atom?
(A) 7
(B) 8
(C) 9
(D) 10What is the chemical symbol for nitrogen?
(A) N
(B) O
(C) C
(D) HWhat is the name of the element nitrogen?
(A) Nitrogen
(B) Oxygen
(C) Carbon
(D) HydrogenWhat is the group number of nitrogen in the periodic table?
(A) 15
(B) 16
(C) 17
(D) 18What is the period number of nitrogen in the periodic table?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5What is the valence electron configuration of nitrogen?
(A) 2s2 2p3
(B) 3s2 3p3
(C) 4s2 4p3
(D) 5s2 5p3What is the electronegativity of nitrogen?
(A) 3.04
(B) 3.44
(C) 3.84
(D) 4.24What is the ionization energy of nitrogen?
(A) 1402 kJ/mol
(B) 1400 kJ/mol
(C) 1398 kJ/mol
(D) 1396 kJ/molWhat is the electron affinity of nitrogen?
(A) -74.8 kJ/mol
(B) -74.6 kJ/mol
(C) -74.4 kJ/mol
(D) -74.2 kJ/molWhat is the standard enthalpy of formation of nitrogen gas?
(A) -46.1 kJ/mol
(B) -46.0 kJ/mol
(C