<<–2/”>a >h2>Preparation of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. The sun and other stars are composed largely of hydrogen. Astronomers estimate that 90% of the atoms in the universe are hydrogen atoms. Hydrogen is a component of more compounds than any other element. Water is the most abundant compound of hydrogen found on earth. Hydrogen is an important part of petroleum, many Minerals, cellulose and starch, sugar, fats, oils, alcohols, acids, and thousands of other substances.
At ordinary temperatures, hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and nonpoisonous gas consisting of the diatomic molecule H2. Hydrogen is composed of three isotopes, and unlike other Elements, these isotopes have different names and chemical symbols: protium, 1H, deuterium, 2H (or “D”), and tritium 3H (or “T”). In a naturally occurring sample of hydrogen, there is one atom of deuterium for every 7000 H atoms and one atom of radioactive tritium for every 1018 H atoms. The chemical properties of the different isotopes are very similar because they have identical electron structures, but they differ in some physical properties because of their differing atomic masses. Elemental deuterium and tritium have lower vapor pressure than ordinary hydrogen. Consequently, when liquid hydrogen evaporates, the heavier isotopes are concentrated in the last portions to evaporate. Electrolysis of heavy water, D2O, yields deuterium. Most tritium originates from nuclear reactions.
Preparation of H2
Elemental hydrogen must be prepared from compounds by breaking chemical Bonds. The most common methods of preparing hydrogen follow.
From Steam and Carbon or Hydrocarbons
Water is the cheapest and most abundant source of hydrogen. Passing steam over coke (an impure form of elemental carbon) at 1000 °C produces a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen known as water gas:
Water gas is as an industrial fuel. It is possible to produce additional hydrogen by mixing the water gas with steam in the presence of a Catalyst to convert the CO to CO2. This reaction is the water gas shift reaction.
It is also possible to prepare a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide by passing hydrocarbons from natural gas or petroleum and steam over a nickel-based catalyst. Propane is an example of a hydrocarbon reactant:
Electrolysis
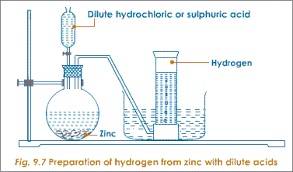
Hydrogen forms when direct current electricity passes through water containing an electrolyte such as H2SO4, as illustrated . Bubbles of hydrogen form at the cathode, and Oxygen evolves at the anode. The net reaction is:
Physical properties :
– Hydrogen is a colorless, odourless and tasteless gas which is sparingly soluble in water.
– Hydrogen is the lightest gas.
– Density: 0.8987 gram per litre
– Boiling point: -253oC
– Melting point: -259oC
– It can be liquefied and solidified at low temperature and high pressure
Chemical properties :
- Action with indicators: It does not show any reaction with litmus and hence is neutral towards litmus paper andother indicators.
- Combustibility:Hydrogen is a inflammable and combustible gas. It is non supporter of combustion.
It gives pale blue flame in air or oxygen to form water. So, hydrogen is also called water gas.
2H2+O2⟶H2O2H2+O2⟶H2O
- Dissociation:Hydrogen is quiet stable to its high bond energy. It dissociates into atomic hydrogen atoms when heated above1730 o.
ZnSO4−→−−−−>1730∘C2ZnO+SO2+O2ZnSO4→>1730∘C2ZnO+SO2+O2
- Reaction with halogen:Hydrogen does not react with halogens at ordinary temperature. But at high temperature in the presence of catalyst, hydrogen react to give their respective halides.
H2+F2⟶2HFH2+F2⟶2HF
H2+Cl2⟶2HClH2+Cl2⟶2HCl
H2+Br2⟶2HBrH2+Br2⟶2HBr
H2+I2⟶2HlH2+I2⟶2Hl
Note: The reactivity order of hydrogen with other halides is: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2.
Reaction with metals: It reduces Metal oxides to metals, when heated.
CuO+H2−→ΔCu+H2OCuO+H2→ΔCu+H2O
ZnO+H2−→ΔZn+H2OZnO+H2→ΔZn+H2O
PbO+H2−→ΔPb+H2OPbO+H2→ΔPb+H2O
Fe2O3+4H2−→Δ3Fe+4H2OFe2O3+4H2→Δ3Fe+4H2O
Action with carbon monoxide: Carbon monoxide reacts with hydrogen at about 430 oC and 200 Atmospheric Pressure in the presence of ZnO and Cr2O3 as a catalyst to give methanol.
\ce{CO2 + 2H2->[{430^{\circ}C}][\ce{ZnO/Cr2O3}] $\underset{\text{Methanol}}{\ce{CH3OH}}\ce{CO2 + 2H2->[{430^{\circ}C}][\ce{ZnO/Cr2O3}] $\underset{\text{Methanol}}{\ce{CH3OH}}
Uses of Hydrogen :
– Hydrogen is used for synthesis of ammonia in Haber’s process.
– Hydrogen is used for the manufacture of ethanol, HCl etc.
– It is used in hydrogenation of oil to produce artificial ghee.
– It is used as a reductant in metallurgical process.
– Liquid hydrogen is used as a fuel in rockets and missiles.
– It is used for filling balloons, study of Atmosphere etc.
,
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, but it is not found in its pure form on Earth. It is usually found in combination with other elements, such as oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen. Hydrogen can be produced from a variety of sources, including natural gas, coal, Biomass/”>Biomass, and water.
The most common method of producing hydrogen is by electrolysis of water. Electrolysis is the process of using an electric current to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process is very efficient and can be used to produce hydrogen from a variety of sources, including water, biomass, and waste.
Another common method of producing hydrogen is by steam reforming of natural gas. Steam reforming is the process of using heat and steam to convert natural gas into hydrogen and carbon monoxide. This process is less efficient than electrolysis, but it is less expensive.
Coal gasification is another method of producing hydrogen. Coal gasification is the process of using heat and pressure to convert coal into a gas mixture that contains hydrogen. This process is less efficient than electrolysis and steam reforming, but it is less expensive.
Pyrolysis of biomass is a promising method of producing hydrogen from renewable Resources. Pyrolysis is the process of heating biomass in the absence of oxygen to produce a gas mixture that contains hydrogen. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources.
Photocatalytic water splitting is another promising method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources. Photocatalytic water splitting is the process of using sunlight to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources.
Biological hydrogen production is another promising method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources. Biological hydrogen production is the process of using bacteria to produce hydrogen from organic matter. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources.
Thermochemical water splitting is another promising method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources. Thermochemical water splitting is the process of using heat to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources.
Direct air capture of hydrogen is a promising method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources. Direct air capture of hydrogen is the process of extracting hydrogen from the air. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources.
Hydrogen from nuclear power is a promising method of producing hydrogen on a large scale. Hydrogen from nuclear power is the process of using nuclear power to produce hydrogen. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen on a large scale.
Hydrogen from RENEWABLE ENERGY is a promising method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources. Hydrogen from renewable energy is the process of using renewable energy to produce hydrogen. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources.
Hydrogen from waste is a promising method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources. Hydrogen from waste is the process of using waste to produce hydrogen. This process is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a cost-effective method of producing hydrogen from renewable resources.
The production of hydrogen from renewable resources is a promising way to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. Hydrogen can be used to power vehicles, generate electricity, and heat homes and businesses. It is a clean and efficient fuel that has the potential to play a major role in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
What is hydrogen?
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, but it is rarely found in its pure form on Earth. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is lighter than air. Hydrogen is highly flammable and can be explosive when mixed with air.
How is hydrogen prepared?
Hydrogen can be prepared by a number of methods, including:
- Electrolysis of water: Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen gas by passing an electric current through it.
- Steam reforming of natural gas: Natural gas is heated with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide gas.
- Coal gasification: Coal is heated with steam and oxygen to produce hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other gases.
- Photolysis of water: Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen gas by using sunlight to excite electrons in water Molecules.
What are the uses of hydrogen?
Hydrogen is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Fuel Cells: Hydrogen fuel cells produce electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen gas.
- Rocket fuel: Hydrogen is used as a rocket fuel because it is very Light and has a high energy content.
- Industry: Hydrogen is used in a variety of industrial processes, such as the production of ammonia and methanol.
- Energy storage: Hydrogen can be used to store energy from renewable sources, such as solar and wind power.
What are the challenges of using hydrogen?
The main challenges of using hydrogen are:
- Hydrogen is highly flammable and can be explosive when mixed with air.
- Hydrogen is difficult to store and transport.
- Hydrogen production is energy-intensive.
- Hydrogen is not currently cost-competitive with other energy sources.
What is the future of hydrogen?
Hydrogen has the potential to play a major role in the future of energy. It is a clean, renewable, and abundant energy source. However, there are a number of challenges that need to be addressed before hydrogen can be widely used. These challenges include the need to develop safe and efficient methods of producing, storing, and transporting hydrogen.
- Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a gas at room temperature. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a flammable gas. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a colorless gas. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a odorless gas. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a tasteless gas. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a very light gas. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a very reactive gas. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a very important gas for industry. True or False?
- Hydrogen is a very important gas for the Environment. True or False?
Answers:
1. True
2. True
3. True
4. True
5. True
6. True
7. True
8. True
9. True
10. True
Here are some additional facts about hydrogen:
- Hydrogen is the simplest element in the periodic table. It has only one proton and one electron.
- Hydrogen is the lightest element in the universe. It is about 1/14th the weight of air.
- Hydrogen is a non-metal. It does not conduct electricity or heat.
- Hydrogen is a gas at room temperature and pressure. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
- Hydrogen is highly flammable. It can explode when mixed with air or oxygen.
- Hydrogen is a renewable resource. It can be produced from water using electrolysis.
- Hydrogen is a clean fuel. It does not produce any harmful emissions when burned.
- Hydrogen is a potential energy source for the future. It could be used to power cars, homes, and businesses.