As far as Elements are concerned, a nonmetal is simply an element that does not display the properties of a Metal. It is not defined by what it is, but by what it is not. It doesn’t look metallic, can’t be drawn into a wire or pounded into shape or bent, doesn’t conduct heat or electricity well, and doesn’t have a high melting or boiling point.
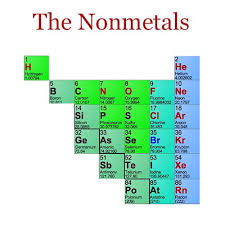
The nonmetals are in the minority on the periodic table, mostly pushed to the right hand side of the periodic table.
The exception is hydrogen, which behaves as a nonmetal at room temperature and pressure and is found on the upper left corner of the periodic table. Under conditions of high pressure, hydrogen is predicted to behave as an alkali metal.
Here’s a look at which elements are nonmetals, how to locate the nonmetals on the table, and their common properties.
LOCATION ON THE NONMETALS ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
The nonmetals are located on the upper right side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are separated from metals by a line that cuts diagonally through the region of the periodic table containing elements with partially filled p orbitals. The halogens and noble gasesare nonmetals, but the nonmetal element group usually is considered to consist of the following elements:
- hydrogen
- carbon
- nitrogen
- Oxygen
- phosphorus
- sulfur
- selenium
The halogen elements are:
- fluorine
- chlorine
- bromine
- iodine
- astatine
- Possibly element 117 (tennessine), although most scientists think this element will behave as a metalloid.
The noble gas elements are:
- helium
- neon
- argon
- krypton
- xenon
- radon
- element 118 – oganesson (predicted to be a liquid, but still a nonmetal)
PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS
Nonmetals have high ionization energies and electronegativities. They are generally poor Conductors of heat and electricity. Solid nonmetals are generally brittle, with little or no metallic luster.
Most nonmetals have the ability to gain electrons easily. Nonmetals display a wide range of chemical properties and reactivities.
SUMMARY OF COMMON PROPERTIES
- High ionization energies
- High electronegativities
- Poor thermal conductors
- Poor electrical conductors
- Brittle solids – not malleable or ductile
- Little or no metallic luster
- Gain electrons easily
- Dull, not metallic-shiny, although they may be colorful
- Lower melting points and boiling point than the metals
COMPARING THE METALS AND NONMETALS
Here’s a comparison of the physical and chemical properties of the metals and nonmetals. These properties apply to the metals in general (alkali metals, alkaline earth, transition metals, basic metals, lanthanides, actinides) and nonmetals in general (nonmetals, halogens, noble gases).
| Metals | Nonmetals | |
| chemical properties | easily lose valence electrons | easily share or gain valence electrons |
| 1-3 electrons (usually) in the outer shell | 4-8 electrons in the outer shell (7 for halogens and 8 for noble gases) | |
| form basic oxides | form acidic oxides | |
| good reducing agents | good oxidizing agents | |
| have low electronegativity | have higher electronegativity | |
| physical properties | solid at room temperature (except mercury) | may be liquid, solid, or gas (noble gases are gases) |
| have metallic luster | do not have metallic luster | |
| good conductor of heat and electricity | poor conductor of heat and electricity | |
| typically malleable and ductile | usually brittle | |
| opaque in a thin sheet | transparent in a thin sheet |
,
Nonmetals are elements that are not metals. They are typically poor conductors of heat and electricity, and they are often brittle and non-lustrous. Nonmetals are found in the right-hand side of the periodic table. Some common nonmetals include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and the noble gases.
Nonmetals are used in a variety of applications, including the production of plastics, Fertilizers, and semiconductors. Nonmetals can also be harmful to human Health, and some are even radioactive. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with nonmetals and to take precautions when handling them.
What are nonmetals?
Nonmetals are elements that are not metals. They are typically poor conductors of heat and electricity, and they are often brittle and non-lustrous. Nonmetals are found in the right-hand side of the periodic table. Some common nonmetals include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and the noble gases.
What are the properties of nonmetals?
Nonmetals are typically poor conductors of heat and electricity. This is because their atoms do not have many free electrons. Free electrons are electrons that are not bound to a particular atom. In metals, there are many free electrons that can move freely around the material. This allows metals to conduct heat and electricity well.
Nonmetals are often brittle and non-lustrous. This is because their atoms are arranged in a way that does not allow them to reflect Light well. Metals, on the other hand, are often shiny because their atoms are arranged in a way that allows them to reflect light well.
Where are nonmetals found on the periodic table?
Nonmetals are found in the right-hand side of the periodic table. This is because their atoms have a high electronegativity. Electronegativity is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons. Atoms with high electronegativities tend to be nonmetals.
What are some common nonmetals?
Some common nonmetals include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and the noble gases. Carbon is the basis for all organic compounds, which are the building blocks of life. Nitrogen is essential for plant Growth. Oxygen is essential for Respiration. Fluorine is the most reactive element. Chlorine is used in bleach and disinfectants. Bromine is used in fire retardants. Iodine is used in iodized salt. The noble gases are very stable and do not react with other elements.
What are some applications of nonmetals?
Nonmetals are used in a variety of applications, including the production of plastics, fertilizers, and semiconductors. Plastics are made from polymers, which are long chains of Molecules. These molecules are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Fertilizers are used to help Plants grow. They are made from nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Semiconductors are materials that conduct electricity when they are given a certain amount of energy. They are used in computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices.
What are the risks associated with nonmetals?
Nonmetals can also be harmful to human health, and some are even radioactive. Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that is produced when carbon is burned incompletely. Nitrogen dioxide is a gas that can cause respiratory problems. Sulfur dioxide is a gas that can cause Acid Rain. Fluoride is a substance that can cause tooth decay. Chlorine is a gas that can be used as a weapon. Bromine is a liquid that can be used as a fire retardant. Iodine is a substance that is used to treat thyroid problems. The noble gases are not harmful to human health, but they can be dangerous if they are inhaled in large amounts.
What are some precautions to take when handling nonmetals?
It is important to be aware of the risks associated with nonmetals and to take precautions when handling them. Some general precautions include:
- Wearing gloves and other protective gear when handling nonmetals.
- Working in a well-ventilated area when handling nonmetals.
- Avoiding contact with skin and eyes.
- Properly disposing of nonmetals.
It is also important to be aware of the specific risks associated with each nonmetal. For example, carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that can be fatal if inhaled. Nitrogen dioxide can cause respiratory problems. Sulfur dioxide can cause acid rain. Fluoride can cause tooth decay. Chlorine can be used as a weapon. Bromine is a liquid that can be used as a fire retardant. Iodine is a substance that is used to treat thyroid problems. The noble gases are not harmful to human health, but they can be dangerous if they are inhaled in large amounts.
Non-metals are elements that are not metals. They are typically poor conductors of heat and electricity, and they are often brittle and break easily. Non-metals are found in the right-hand side of the periodic table.
Here are some frequently asked questions about non-metals:
What are non-metals?
Non-metals are elements that are not metals. They are typically poor conductors of heat and electricity, and they are often brittle and break easily. Non-metals are found in the right-hand side of the periodic table.What are the properties of non-metals?
Non-metals are typically poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are also often brittle and break easily. Non-metals are found in the right-hand side of the periodic table.What are some examples of non-metals?
Some examples of non-metals include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and the noble gases.What are the uses of non-metals?
Non-metals are used in a variety of applications, including:Construction: Non-metals such as concrete, brick, and glass are used in the construction of buildings and other structures.
- Electronics: Non-metals such as silicon and germanium are used in the manufacture of electronic devices.
- agriculture: Non-metals such as nitrogen and phosphorus are used as fertilizers.
Medicine: Non-metals such as carbon and oxygen are used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals.
What are the dangers of non-metals?
Some non-metals, such as fluorine and chlorine, are highly toxic. Others, such as carbon monoxide, can be fatal if inhaled. It is important to take precautions when handling non-metals.What is the future of non-metals?
Non-metals are likely to continue to be used in a variety of applications in the future. As technology advances, new uses for non-metals are likely to be discovered.
Question 1
Which of the following is a non-metal?
(A) Hydrogen
(B) Helium
(C) Lithium
(D) Carbon
Answer
(D) Carbon is a non-metal.
Question 2
Which of the following is a property of non-metals?
(A) They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(B) They are solid at room temperature.
(C) They are brittle and break easily.
(D) They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Answer
(D) Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Question 3
Which of the following is a non-metal that is used in the production of batteries?
(A) Carbon
(B) Sulfur
(C) Oxygen
(D) Nitrogen
Answer
(A) Carbon is a non-metal that is used in the production of batteries.
Question 4
Which of the following is a non-metal that is used in the production of fertilizer?
(A) Nitrogen
(B) Phosphorus
(C) Potassium
(D) Sulfur
Answer
(B) Phosphorus is a non-metal that is used in the production of fertilizer.
Question 5
Which of the following is a non-metal that is used in the production of glass?
(A) Silicon
(B) Carbon
(C) Oxygen
(D) Nitrogen
Answer
(A) Silicon is a non-metal that is used in the production of glass.