Non Metals
As far as Elements are concerned, a nonmetal is simply an element that does not display the properties of a Metal. It is not defined by what it is, but by what it is not. It doesn’t look metallic, can’t be drawn into a wire or pounded into shape or bent, doesn’t conduct heat or electricity well, and doesn’t have a high melting or boiling point.
The nonmetals are in the minority on the periodic table, mostly pushed to the right hand side of the periodic table.
The exception is hydrogen, which behaves as a nonmetal at room temperature and pressure and is found on the upper left corner of the periodic table. Under conditions of high pressure, hydrogen is predicted to behave as an alkali metal.
Here’s a look at which elements are nonmetals, how to locate the nonmetals on the table, and their common properties.
LOCATION ON THE NONMETALS ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
The nonmetals are located on the upper right side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are separated from metals by a line that cuts diagonally through the region of the periodic table containing elements with partially filled p orbitals. 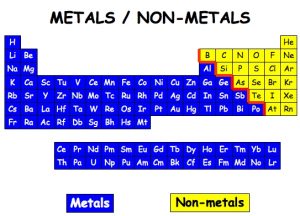
- hydrogen
- carbon
- nitrogen
- Oxygen
- phosphorus
- sulfur
- selenium
The halogen elements are:
- fluorine
- chlorine
- bromine
- iodine
- astatine
- Possibly element 117 (tennessine), although most scientists think this element will behave as a metalloid.
The noble gas elements are:
- helium
- neon
- argon
- krypton
- xenon
- radon
- element 118 – oganesson (predicted to be a liquid, but still a nonmetal)
PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS
Nonmetals have high ionization energies and electronegativities. They are generally poor Conductors of heat and electricity. Solid nonmetals are generally brittle, with little or no metallic luster.
Most nonmetals have the ability to gain electrons easily. Nonmetals display a wide range of chemical properties and reactivities.
SUMMARY OF COMMON PROPERTIES
- High ionization energies
- High electronegativities
- Poor thermal conductors
- Poor electrical conductors
- Brittle solids – not malleable or ductile
- Little or no metallic luster
- Gain electrons easily
- Dull, not metallic-shiny, although they may be colorful
- Lower melting points and boiling point than the metals
COMPARING THE METALS AND NONMETALS
Here’s a comparison of the physical and chemical properties of the metals and nonmetals. These properties apply to the metals in general (alkali metals, alkaline earth, transition metals, basic metals, lanthanides, actinides) and nonmetals in general (nonmetals, halogens, noble gases).
| Metals | Nonmetals | |
| chemical properties | easily lose valence electrons | easily share or gain valence electrons |
| 1-3 electrons (usually) in the outer shell | 4-8 electrons in the outer shell (7 for halogens and 8 for noble gases) | |
| form basic oxides | form acidic oxides | |
| good reducing agents | good oxidizing agents | |
| have low electronegativity | have higher electronegativity | |
| physical properties | solid at room temperature (except mercury) | may be liquid, solid, or gas (noble gases are gases) |
| have metallic luster | do not have metallic luster | |
| good conductor of heat and electricity | poor conductor of heat and electricity | |
| typically malleable and ductile | usually brittle | |
| opaque in a thin sheet | transparent in a thin sheet |
,
Non-metals are elements that do not have the characteristic properties of metals. They are typically poor conductors of heat and electricity, and they are not shiny. Non-metals can be found in all three States of Matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
There are many different types of non-metals, and they can be classified into several groups. The alkali metals are the elements in Group 1 of the periodic table. They are all very reactive and are found in nature as salts. The alkaline earth metals are the elements in Group 2 of the periodic table. They are less reactive than the alkali metals, but they are still very reactive. The carbon group is the elements in Group 14 of the periodic table. They include carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, and lead. The carbon group elements are all non-metals, except for lead, which is a metalloid. The chalcogens are the elements in Group 16 of the periodic table. They include oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium. The chalcogens are all non-metals, except for polonium, which is a metalloid. The halogens are the elements in Group 17 of the periodic table. They include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. The halogens are all non-metals.
The lanthanides are the elements in the lanthanide series of the periodic table. They are all metals, except for promethium, which is a radioactive metalloid. The lanthanides are all very similar to each other, and they are often called the rare earth elements. The metalloids are elements that have properties of both Metals and Non-metals. They are found in the middle of the periodic table, between the metals and the non-metals. The metalloids include boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium.
The noble gases are the elements in Group 18 of the periodic table. They are all very unreactive and are found in nature as gases. The noble gases include helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
The nitrogen group is the elements in Group 15 of the periodic table. They include nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. The nitrogen group elements are all non-metals, except for bismuth, which is a metalloid. The oxygen group is the elements in Group 16 of the periodic table. They include oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium. The oxygen group elements are all non-metals, except for polonium, which is a metalloid. The phosphorus group is the elements in Group 15 of the periodic table. They include phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. The phosphorus group elements are all non-metals, except for bismuth, which is a metalloid. The silicon group is the elements in Group 14 of the periodic table. They include carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, and lead. The silicon group elements are all non-metals, except for lead, which is a metalloid.
Non-metals are an important part of our world. They are used in many different products, including batteries, plastics, and semiconductors. Non-metals are also essential for life. Carbon is the basis of all life on Earth, and oxygen is essential for Respiration. Non-metals are a fascinating and important part of our world.
What are the properties of non-metals?
Non-metals are elements that are not shiny, do not conduct electricity well, and are not good conductors of heat. They are also brittle and break easily.
What are some examples of non-metals?
Some examples of non-metals are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and arsenic.
What are the uses of non-metals?
Non-metals are used in a variety of products, including:
- Electronics: Non-metals are used in the manufacture of semiconductors, which are essential components of electronic devices such as computers, cell phones, and televisions.
- Building materials: Non-metals are used in the manufacture of building materials such as concrete, brick, and glass.
- Fuels: Non-metals are used in the manufacture of fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Pharmaceuticals: Non-metals are used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals such as antibiotics and pain relievers.
What are the dangers of non-metals?
Some non-metals can be dangerous if they are not handled properly. For example, carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that can be released when non-metals are burned. Other non-metals, such as chlorine, can be corrosive and can cause skin and eye irritation.
What are the benefits of non-metals?
Non-metals have a number of benefits, including:
- They are lightweight and easy to work with.
- They are non-conductive, which makes them safe to use around electricity.
- They are resistant to corrosion and can withstand extreme temperatures.
- They are abundant and relatively inexpensive.
What are the challenges of non-metals?
Non-metals also have a number of challenges, including:
- They are brittle and can break easily.
- They are not as strong as metals.
- They are not as good conductors of heat and electricity as metals.
- They can be dangerous if they are not handled properly.
What is the future of non-metals?
The future of non-metals is bright. Non-metals are being used in a growing number of products and applications, and their use is expected to continue to grow in the future. Non-metals are also being used in new and innovative ways, such as in the development of new materials and technologies.
Which of the following is not a metal?
(A) Gold
(B) Silver
(C) Copper
(D) CarbonWhich of the following is a property of metals?
(A) They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(B) They are shiny and have a high luster.
(C) They are ductile and can be easily shaped.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a non-metal?
(A) Hydrogen
(B) Oxygen
(C) Nitrogen
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a property of non-metals?
(A) They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
(B) They are not shiny and do not have a high luster.
(C) They are brittle and cannot be easily shaped.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a metalloid?
(A) Silicon
(B) Germanium
(C) Arsenic
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a property of metalloids?
(A) They have properties of both metals and non-metals.
(B) They are semiconductors.
(C) They are used in the manufacture of transistors and other electronic devices.
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a compound?
(A) Water
(B) Salt
(C) Sugar
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a mixture?
(A) Air
(B) Soil
(C) Concrete
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a pure substance?
(A) Water
(B) Salt
(C) Sugar
(D) None of the above.Which of the following is a heterogeneous mixture?
(A) Air
(B) Soil
(C) Concrete
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a homogeneous mixture?
(A) Water
(B) Salt water
(C) Sugar water
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a solution?
(A) Water
(B) Salt water
(C) Sugar water
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a suspension?
(A) Air
(B) Soil
(C) Concrete
(D) None of the above.Which of the following is a colloid?
(A) Milk
(B) Mayonnaise
(C) Paint
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a physical change?
(A) Water freezing
(B) Water boiling
(C) Water evaporating
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a chemical change?
(A) Wood burning
(B) Iron rusting
(C) Food cooking
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a physical property?
(A) Color
(B) Shape
(C) Size
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a chemical property?
(A) Flammability
(B) Reactivity
(C) Solubility
(D) All of the above.Which of the following is a physical change that can be reversed?
(A) Water freezing
(B) Water boiling
(C) Water evaporating
(D) None of the above.Which of the following is a chemical change that can be reversed?
(A) Wood burning
(B) Iron rusting
(C) Food cooking
(D) None of the above.