<<–2/”>a >h1>Natural Vegetation of India
Forests – Natural Vegetation of India:Types and distribution
types
- Climate, Soil and topographyare the major factors that influence Natural Vegetation of a place.
- The main climatic factors arerainfall and temperature. The amount of annual rainfall has a great bearing on the type of vegetation.
Annual Rainfall | Type of Vegetation |
200 cm or more | Evergreen Rain Forests |
100 to 200 cm | Monsoon Deciduous Forests |
50 to 100 cm | Drier Deciduous or Tropical Savanna |
25 to 50 cm | Dry Thorny Scrub (Semi-arid) |
Below 25 cm | Desert (Arid) |
- Temperature is the major factor in Himalayas and other hilly regions with an elevation of more than 900 metres.
- As the temperature falls with altitude in the Himalayan region the vegetal cover changes with altitude fromtropical to sub-tropical, temperate and finally alpine.
- Soil is an equally determining factor in few regions.Mangrove forests, swamp forests are some of the examples where soil is the major factor.
- Topography is responsible for certain minor types e.g.alpine Flora, tidal forests, etc..
Classification of Natural Vegetation of India
- Classification of Natural Vegetation of India is primarily based on spatial and annual variations in rainfall. Temperature, soil and topography are also considered.
- India’s vegetation can be divided into 5 main types and 16 sub-types as given below.
A. Moist Tropical Forests
- Tropical Wet Evergreen
- Tropical Semi-Evergreen
- Tropical Moist Deciduous
- Littoral and Swamp
B. Dry Tropical Forests
- Tropical Dry Evergreen
- Tropical Dry Deciduous
- Tropical Thorn
C. Montane Sub-tropical Forests
- Sub-tropical broad leaved hill
- Sub-tropical moist hill (pine)
- Sub-tropical dry evergreen
D. Montane Temperate Forests
- Montane Wet Temperate
- Himalayan Moist Temperate
- Himalayan Dry Temperate
E. Alpine Forests
- Sub-Alpine
- Moist Alpine scrub
- Dry Alpine scrub
Forest Type in India | % of Total Area |
| Tropical Moist Deciduous | 37 |
| Tropical Dry Deciduous | 28 |
| Tropical Wet Evergreen | 8 |
| Sub-Tropical Moist Hill | 6 |
| Tropical Semi-Evergreen | 4 |
| Rest below 4 % | |
Moist Tropical Forests
Tropical Wet Evergreen Forests or Rain Forests
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall exceeds 250 cm
- The annual temperature is about 25°-27°C
- The Average annual humidity exceeds 77 per cent and
- The dry season is distinctly short.
Characteristics
- Evergreen: Due to high heat and high humidity, the trees of these forests do not shed their leaves together.
- Mesosphytic:Plants adopted to neither too dry nor too wet type climate.
What are mesophytes?· Unlike hydrophytic plants, such as water lily or pondweed, that grow in saturated soil or water, or xerophytic plants, such as cactus, that grow in extremely dry soil, mesophytes are ordinary plants that exist between the two extremes. · Mesophytic environments are marked by average to hot temperatures and soil that is neither too dry nor too wet. |
- Lofty: The trees often reach 45 – 60 metres in height.
- Thick Canopy: From the air, the tropical rain forest appears like a thick canopy of foliage, broken only where it is crossed by large rivers or cleared for cultivation.
- All plants struggle upwards (mostephiphytes) for sunlight resulting in a peculiar layer arrangement. The entire morphology looks like a green carpet when viewed from above.
- Less undergrowth: The sun Light cannot reach the ground due to thick canopy. The undergrowth is formed mainly of bamboos, ferns, climbers, orchids, etc.
Distribution
- Western side of the Western Ghats (500 to 1370 metres above sea level).
- Some regions in the Purvanchal hills.
- In the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Timber
- Hardwood: The timber of these forests is fine-grained, hard and durable.
- It has high commercial value but it is highly challenging to exploit dueto dense undergrowth, absence of pure stands and lack of transport facilities [Read previous posts on Climatic regions to understand how lumbering Industry works in Equatorial Rainforests (hardwood) and Taiga Climatic (softwood) conditions].
- The important species of these forests aremahogany, mesua, white cedar, jamun, canes, bamboo
Tropical Semi-Evergreen Forests
- They are transitional forests between tropical wet evergreen forests and tropical deciduous forests.
- They are comparatively drier areas compared to tropical wet evergreen forests.
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall is 200-250 cm
- Mean annual temperature varies from 24°C to 27°C
- The relative humidity is about 75 per cent
- The dry season is not short like in tropical evergreen forests.
Distribution
- Western coast
- Assam
- Lower slopes of the Eastern Himalayas
- Odisha and
Characteristics
- The semi-evergreen forests are less dense.
- They are moregregarious [living in flocks or colonies – more pure stands] than the wet evergreen forests.
- These forests are characterized by many species.
- Trees usually havebuttressed trunks with abundant epiphytes.
Buttressed Trunks
- The important species are laurel, rosewood, mesua, thorny bamboo – Western Ghats, white cedar, Indian chestnut, champa, mango, etc. – Himalayan region.
Timber
- Hardwood: Similar to that in tropical evergreen forests except that these forests are less dense withmore pure stands (timber industry here is better than in evergreen forests).
Tropical Moist Deciduous Forests
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall 100 to 200 cm.
- Mean annual temperature of about 27°C
- The average annual relative humidity of 60 to 75 per cent.
- Spring (between winter and summer) and summer are dry.
Characteristics
- The trees drop their leaves during the spring and early summer when sufficient moisture is not available.
- The general appearance is bare in extreme summers (April-May).
- Tropical moist deciduous forests present irregular top storey [25 to 60 m].
- Heavily buttressed trees and fairly complete undergrowth.
- These forests occupy a much larger area than the evergreen forests but large tracts under these forests have been cleared for cultivation.
Distribution
- Belt running along the Western Ghats surrounding the belt of evergreen forests.
- A strip along the Shiwalik range including terai and bhabar from 77° E to 88° E.
- Manipur and Mizoram.
- Hills of eastern Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
- Chota Nagpur Plateau.
- Most of Odisha.
- Parts of West Bengal and
- Andaman and Nicobar islands.
Timber
- These provide valuable timer like
- The main species found in these forests are teak, sal, laurel, rosewood, amla, jamun, bamboo, etc.
- It iscomparatively easy to exploit these forests due to their high degree of gregariousness (more pure stands).
Littoral and Swamp Forests
- They can survive and grow both in fresh as well asbrackish water(The mixture of seawater and fresh water in estuaries is called brackish water and its salinity can range from 0.5 to 35 ppt).
- Occur in and around the deltas, estuaries and creeks prone totidal influences (delta or tidal forests).
- Littoral (relating to or on the shore of the sea or a lake) forests occur at several places along the coast.
- Swamp forests are confined to the deltas of the Ganga, the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Cauvery.
- Dense MANGROVES occur all along the coastline in sheltered estuaries, tidal creeks, backwaters, salt marshes and mudflats. It provides useful fuel wood.
- The most pronounced and the densest is theSunderban in the Ganga delta where the predominant species is Sundri (Heriteera).
Timber
- It provides hard and durable timber which is used for construction, building purposes and making boats.
- The important species found in these forests are Sundri, agar, rhizophora, screw pines, canes and palms, etc.
Dry Tropical Forests
Tropical Dry Evergreen Forests
Distribution
- Along the coasts of Tamil Nadu.
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall of 100 cm [mostly from the north-east Monsoon Winds in October – December].
- Mean annual temperature is about 28°C.
- The mean humidity is about 75 per cent.
- The Growth of evergreen forests in areas of such low rainfall is a bit strange.
Characteristics
- Short statured trees, up to 12 m high, with complete canopy.
- Bamboos and Grasses not conspicuous.
- The important species are jamun, tamarind, neem, etc.
- Most of the land under these forests has been cleared for agriculture orcasuarina plantations.
Casuarina plantation· It resembles feathery conifer in general appearance. · They are rapid-growing, carefree species for sites and climates as varied as coastal sand dunes, high mountain slopes, hot humid tropics, and semi-arid regions. · They have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen. It grows 15 to 25 metres in height on an average.
Casuarina plantation Distribution· Casuarina is the most popular farm Forestry in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Odisha, Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Karnataka. Benefits· Reduces damage in the event of natural calamities. · Line planting in the coastal areas helps in controlling the wind force. · It is also used for tourism promotion in view of its ornamental appearance. · It provides top quality firewood. · The wood is suitable for paper pulp and useful raw material for the manufacture of paper for writing, printing, and wrapping. · It is got some serious medicinal values as well. Wasteland development· The characteristics which make it a suitable species for wasteland development include adaptability to wide range of habitats, fast growth, salt tolerant, drought resistant, ability to reclaim land and stabilize sand dunes. · Intercrops such as groundnut, cucumber, watermelons, sesamum, and pulses can also be raised along with the plantation. |
Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall is 100-150 cm.
Characteristics
- These are similar to moist deciduous forests and shed their leaves in dry season.
- The major difference is that they can grow in areas of comparatively less rainfall.
- They represent a transitional type – moist deciduous on the wetter side and thorn forests on the drier side.
- They have closed but uneven canopy.
- The forests are composed of a mixture of a few species of Deciduous trees rising up to a height of 20 metres.
- Undergrowth: Enough light reaches the ground to permit the growth of grass and climbers.
Distribution
- They occur in an irregular wide strip running from the foot of the Himalayas to Kanniyakumari except in Rajasthan, Western Ghats and West Bengal.
- The important species are teak, axlewood, rosewood, common bamboo,red sanders, laurel, satinwood, etc.
- Large tracts of this forest have been cleared for agricultural purposes.
- These forests have suffer from over grazing, fire, etc.
Tropical Thorn Forests
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall less than 75 cm.
- Humidity is less than 50 per cent.
- Mean temperature is 25°-30°C.
Characteristics
- The trees are low (6 to 10 metres maximum) and widely scattered.
- Acacias and Euphorbias are very prominent.
- The Indian wild date is common. Some grasses also grow in the rainy season.
Distribution
- Rajasthan, south-western Punjab, western Haryana, Kachchh and neighbouring parts of Saurashtra.
- Here they degenerate into desert type in the Thar desert.
- Such forests also grow on the leeside of the Western Ghats covering large areas of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- The important species are neem, babul, cactii, etc.
Montane Sub-Tropical Forests
Sub-tropical Broad-leaved Hill Forests
Climatic conditions
- Mean annual rainfall is 75 cm to 125 cm.
- Average annual temperature is 18°-21°C.
- Humidity is 80 per cent.
Distribution
- Eastern Himalayas to the east of 88°E longitude at altitudes varying from 1000 to 2000 m.
Characteristics
- Forests of evergreen species.
- Commonly found species are evergreen oaks, chestnuts, ash, beech, sals and pines.
- Climbers and epiphytes [a plant that grows non-parasitically on a tree or other plant] are common.
- These forests are not so distinct in the southern parts of the country. They occur only in the Nilgiri and Palni hills at 1070-1525 metres above sea level.
- It is a “stunted rain-forest” and is not so luxuriant as the true tropical evergreen.
- The higher parts of the Western Ghats such as Mahabaleshwar, the summits of the Satpura and the Maikal Range, highlands of Bastar and Mt. Abu in the Aravali Range carry sub-types of these forests.
Sub-tropical Moist Pine Forests
Distribution
- Western Himalayas between 73°E and 88°E longitudes at elevations between 1000 to 2000 metres above sea level.
- Some hilly regions of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Naga Hills and Khasi Hills.
Timber
- Chir or Chilis the most dominant tree which forms pure stands.
- It providesvaluable timber for furniture, boxes and buildings.
- It is also used for producing resin and turpentine.
Sub-tropical Dry Evergreen Forests
Distribution
- Found in the Bhabar, the Shiwaliks and the western Himalayas up to about 1000 metres above sea level.
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall is 50-100 cm (15 to 25 cm in December-March).
- The summers are sufficiently hot and winters are very cold.
Characteristics
- Low scrub forest with small evergreen stunted trees and shrubs.
- Olive, acacia modesta and pistacia are the most predominant species.
Montane Temperate Forests
Montane Wet Temperate Forests
Climatic Conditions
- Grows at a height of 1800 to 3000 m above sea level
- Mean annual rainfall is 150 cm to 300 cm
- Mean annual temperature is about 11°C to 14°C and the
- Average relative humidity is over 80 per cent.
Distribution
- Higher hills of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, in the Eastern Himalayan region.
Characteristics
- These are closed evergreen forests. Trunks have large girth.
- Branches are clothed with mosses, ferns and other epiphytes.
- The trees rarely achieve a height of more than 6 metres.
- Deodar, Chilauni, Indian chestnut, birch, plum, machilus, cinnamomum, litsea, magnolia, blue pine, oak, hemlock, etc. are important species.
Himalayan Moist Temperate Forests
Climatic Conditions
- Annual rainfall varies from 150 cm to 250 cm
Distribution
- Occurs in the temperate zone of the Himalayas between 1500 and 3300 metres.
- Cover the entire length of this mountain range in Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Darjeeling and Sikkim.
Characteristics
- Mainly composed ofconiferous species.
- Species occur in mostly pure strands.
- Trees are 30 to 50 m high.
- Pines, cedars, silver firs, spruce, etc. are most important trees.
- They form high but fairly open forest with shrubby undergrowth including oaks, rhododendrons and some bamboos.
Timber
- It provides fine wood which is of much use for construction, timber and railway sleepers.
Himalayan Dry Temperate Forests
Climatic Conditions
- Precipitation is below 100 cm and is mostly in the form of snow.
Characteristics
- Coniferous forests with xerophytic shrubs in which deodar, oak, ash, olive, etc are the main trees.
Distribution
- Such forests are found in the inner dry ranges of the Himalayas where south-west monsoon is very feeble.
- Such areas are in Ladakh, Lahul, Chamba, Kinnaur, Garhwal and Sikkim.
Alpine Forests
- Altitudes ranging between 2,900 to 3,500.
- These forests can be divided into: (1) sub-alpine; (2) moist alpine scrub and (3) dry alpine scrub.
- The sub-alpine forests occur lower alpine scrub and grasslands.
- It is a mixture of coniferous and broad-leaved trees in which the coniferous trees attain a height of about 30 m while the broad leaved trees reach only 10 m.
- Fir, spruce, rhododendron, etc. are important species.
- The moist alpine scrub is a low evergreen dense growth of rhododendron, birch etc. which occurs from 3,000 metres and extends upto
- The dry alpine scrub is the uppermost limit of scrub xerophytic, dwarf shrubs, over 3,500 metres above sea level and found in dry zone. Juniper, honeysuckle, artemesia etc. are important species.
,
India is a land of diverse landscapes, from the snow-capped Himalayas to the tropical beaches of Goa. This diversity is reflected in the country’s natural vegetation, which includes a wide range of forests, grasslands, deserts, and mangroves.
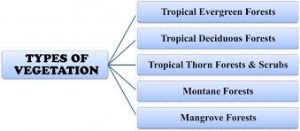
- Tropical Evergreen Forests
Tropical evergreen forests are found in the wettest parts of India, such as the Western Ghats and the Eastern Himalayas. These forests are characterized by their dense canopy of trees, which provides a home for a variety of wildlife, including elephants, tigers, and monkeys.
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
Tropical deciduous forests are found in areas with a more seasonal climate. These forests lose their leaves during the dry season, and then grow new leaves during the wet season. Tropical deciduous forests are home to a variety of animals, including deer, leopards, and birds.
- Thorn Forests
Thorn forests are found in the drier parts of India, such as the Deccan Plateau. These forests are characterized by their thorny trees and shrubs. Thorn forests are home to a variety of animals, including camels, snakes, and lizards.
- Montane Forests
Montane forests are found in the Mountains of India. These forests are characterized by their cool climate and dense vegetation. Montane forests are home to a variety of animals, including snow leopards, Himalayan tahr, and musk deer.
- Scrub Forests
Scrub forests are found in the drier parts of India. These forests are characterized by their low-growing trees and shrubs. Scrub forests are home to a variety of animals, including rabbits, foxes, and hyenas.
- Grasslands
Grasslands are found in the drier parts of India. These areas are characterized by their open, grassy landscape. Grasslands are home to a variety of animals, including cattle, sheep, and antelope.
- Deserts
Deserts are found in the driest parts of India. These areas are characterized by their hot, dry climate and sparse vegetation. Deserts are home to a variety of animals, including camels, snakes, and lizards.
- Mangroves
Mangroves are found along the coasts of India. These forests are characterized by their salt-tolerant trees and shrubs. Mangroves are home to a variety of animals, including crabs, shrimp, and fish.
India’s natural vegetation is a vital part of the country’s ecosystem. It provides habitat for a variety of animals, helps to regulate the climate, and prevents soil erosion. It is important to protect India’s natural vegetation so that it can continue to provide these essential Services.
What is the difference between a forest and a jungle?
A forest is a large area of land covered with trees and other plants. A jungle is a dense forest with a lot of undergrowth.
What are the different types of forests?
There are many different types of forests, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, boreal forests, and coniferous forests.
What are the benefits of forests?
Forests provide many benefits, including:
- Oxygen: Forests produce oxygen, which we need to breathe.
- Water: Forests help to regulate the water cycle.
- Soil: Forests help to prevent soil erosion.
- Climate: Forests help to regulate the climate.
- Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity: Forests are home to a wide variety of plants and animals.
- Recreation: Forests provide a place for recreation, such as hiking, camping, and fishing.
What are the threats to forests?
Forests are threatened by a number of factors, including:
- Deforestation: Deforestation is the clearing of forests for other uses, such as agriculture or development.
- Climate Change: Climate change is causing forests to change in size and composition.
- Fire: Forest fires can destroy large areas of forest.
- Pests and diseases: Pests and diseases can kill trees and other plants in forests.
What can we do to protect forests?
There are many things we can do to protect forests, including:
- Reduce our consumption of products that come from forests, such as paper and wood.
- Support organizations that are working to protect forests.
- Plant trees.
- Recycle paper and wood products.
- Choose products that are made from recycled materials.
- Educate others about the importance of forests.
What is the future of forests?
The future of forests is uncertain. If we do not take steps to protect them, they may disappear altogether. We need to work together to ensure that forests are preserved for future generations.
Which of the following is not a type of natural vegetation in India?
(A) Tropical rainforest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Temperate forest
(D) Alpine vegetationWhich of the following is the most common type of natural vegetation in India?
(A) Tropical rainforest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Temperate forest
(D) Alpine vegetationWhich of the following is the most important type of natural vegetation in India from an economic perspective?
(A) Tropical rainforest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Temperate forest
(D) Alpine vegetationWhich of the following is the most threatened type of natural vegetation in India?
(A) Tropical rainforest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Temperate forest
(D) Alpine vegetationWhich of the following is the most important type of natural vegetation in India from a conservation perspective?
(A) Tropical rainforest
(B) Tropical deciduous forest
(C) Temperate forest
(D) Alpine vegetationWhich of the following is the most common type of tree found in tropical rainforests in India?
(A) Teak
(B) Sal
(C) Bamboo
(D) SandalwoodWhich of the following is the most common type of tree found in tropical deciduous forests in India?
(A) Teak
(B) Sal
(C) Bamboo
(D) SandalwoodWhich of the following is the most common type of tree found in temperate forests in India?
(A) Oak
(B) Pine
(C) Spruce
(D) FirWhich of the following is the most common type of tree found in alpine vegetation in India?
(A) Oak
(B) Pine
(C) Spruce
(D) FirWhich of the following is the most important type of animal found in tropical rainforests in India?
(A) Tiger
(B) Elephant
(C) Rhinoceros
(D) LeopardWhich of the following is the most important type of animal found in tropical deciduous forests in India?
(A) Tiger
(B) Elephant
(C) Rhinoceros
(D) LeopardWhich of the following is the most important type of animal found in temperate forests in India?
(A) Musk deer
(B) Snow leopard
(C) Red panda
(D) Himalayan tahrWhich of the following is the most important type of animal found in alpine vegetation in India?
(A) Musk deer
(B) Snow leopard
(C) Red panda
(D) Himalayan tahrWhich of the following is the most important type of bird found in tropical rainforests in India?
(A) Hornbill
(B) Peacock
(C) Kingfisher
(D) StorkWhich of the following is the most important type of bird found in tropical deciduous forests in India?
(A) Hornbill
(B) Peacock
(C) Kingfisher
(D) StorkWhich of the following is the most important type of bird found in temperate forests in India?
(A) Snow cock
(B) Monal
(C) Kalij pheasant
(D) Blood pheasantWhich of the following is the most important type of bird found in alpine vegetation in India?
(A) Snow cock
(B) Monal
(C) Kalij pheasant
(D) Blood pheasantWhich of the following is the most important type of fish found in tropical rainforests in India?
(A) Mahseer
(B) Catla
(C) Rohu
(D) CarpWhich of the following is the most important type of fish found in tropical deciduous forests in India?
(A) Mahseer
(B) Catla
(C) Rohu
(D) CarpWhich of the following is the most important type of fish found in temperate forests in India?
(A) Trout
(B) Salmon
(C) Perch
(D) PikeWhich of the following is the most important type of fish found in alpine vegetation in India?
(A) Trout
(B) Salmon
(C) Perch
(D) PikeWhich of the following is the most important type of insect found in tropical rainforests in India?
(A) Butterfly
(B) Moth
(C) Beetle
(D) AntWhich of the following is the