<<–2/”>a >a href=”https://exam.pscnotes.com/irrigation/”>Irrigation and Hydropower of Bihar
Irrigation is being practiced there since past chemical analysis back to Kautilya, World Health Organization lived in Patliputra (now Patna), that was the capital of the mighty Mauryan empire (400 BC). Kautilya had ordered down the principles on Precipitation and irrigation in his renowned book Kautilya Arthasashtra. In Bihar the history of irrigation are going to be derived long back but one may notice the systematic written documents from the primary British quantity exclusively. unit canals, Teur canals, thermoplastic canal, Dacca Canal, Triveni canal and Kharagpur Irrigation Works unit of measurement variety of the earliest milestones on the path of scientific development of water Resources at intervals the State of Bihar.
Bihar’s extraordinary economic process in recent years has raised expectations of continuous high Growth rates in future. If this record ought to be sustained, then agricultural growth will need to play an important half. Agricultural development depends, in turn, on increasing irrigation and Cropping intensity. And for a state with ninety six of the farmers classified as little and marginal, the most focus ought to air developing and maintaining minor irrigation Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE within the state. This was the premise for conducting this study, following an on the spot request from the Minor Water Resources Department, Government of Bihar. The study focuses on the steps required to reorganise and strengthen the department to achieve its irrigation intensity targets throughout the twelfth and thirteenth five Year established periods (2012-22).
Bihar irrigation schemes unit of measurement sometimes classified into three classes: a) Major and medium schemes – surface schemes irrigating over a combine of,000 hectares; b) Minor surface schemes – diversion or reservoir schemes irrigating however a combine of,000 hectares; c) Life schemes – tubewell or little stream elevate irrigation schemes. There are a unit presently twenty seven major and 163 medium completed irrigation schemes, and another nineteen major and thirty one medium schemes below construction at intervals the state. There are also regarding forty,000 minor surface irrigation works, of that 747 unit of measurement formally recognized as schemes and so the rest unit of measurement ahars2 (small tanks). There unit of measurement a combine of,074 stream lift-irrigation schemes, 5,791 deep tubewells, about 600,000 shallow tubewells and regarding four hundred,000 exocrine gland wells used for irrigation. Bihar’s gross seeded irrigated area of around 5 hundredth is comparatively low as compared to ninety fifth in region, sixty seven in Bihar, and hour for country as a complete. The standard groundwater exploitation is thirty ninth, indicating Associate in Nursing oversize undeveloped potential. The visionary programme of Water Resources Department (WRD) of Bihar indicates that the ultimate word irrigation potential of the state is 10.7 million angular distance, out of that 5.3 million angular distance are going to be through major and medium irrigation comes. However, till the year a combine of005 created potential is two.61 million and actual utilization is barely one.6 million angular distance. Thereby, half the potential fields unit of measurement still rainfed. sadly, seventy six of North Bihar Population and seventy 3 of region is below constant threat of floods. in line with the visionary programme of WRD, associate calculable Rs1500 crores worth of property and many lives unit of measurement lost every year as a results of floods; the programme planned to realize, among several things,
- a) Water to any or all likely irrigable fields by 2025,
- b) Complete flood country by 2025,
- c) Reclamation of water logged area by 2025, and
- d) to create positive democratic irrigation management transfer of whole command area
The Water and Land Management Institute (WALMI), based in Patna, could be a full pledged field based institute. it completely was started in 1987 with the support from USAID, below the Indo-US Water Resources, Management and training Project. As a vicinity of this project, WALMI took the lead in initiating the action research project in Paliganj area of unit command area. In Bihar, this was the first step towards democratic irrigation management in major Canal Irrigation systems.
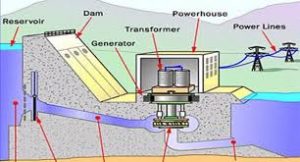
Power might be a important demand for socio Economic Development. economic process depends on accessibility of adequate, reliable and quality power at competitive rate. Bihar is on its path of progress but its property growth is suffering as results of non accessibility of adequate power. The per capita power consumption at intervals the state is around 100 units against the all country Average of approx. 700 units. The total place in capability of generation in Bihar is around 600 MW against the standard demand of 2500 MW and peak demand of 3000 MW. The state has access to 1846 MW as well as capability allocation from central sectors generating stations.
Power system in Bihar is predominant by thermal power generation and so the contribution of Hydro Power is barely baseball game. Thus on use the available renewal offer of energy, Govt. of Bihar is esurient and committed to encourage speedy development of hydro power at intervals the State at the earliest. The key objective of the policy is as below.
- To enhance the overall generation capability of the state as well as Hydro power
- To obtain best thermal – hydro generation mixture of 60:40 magnitude relation
- To encourage the participation of freelance Power Producers by providing them best policy frame work, and support.
Depending upon place in capability, the hydro comes unit of measurement classified as under:
Micro Hydro comes with place in capability below 3 MW
Mini hydro comes with place in capability from 3 MW to 25MW
Medium hydro comes with place in capability over 25MW and upto 100 MW and
Big hydro comes with place in capability on the way aspect 100 MW.
At present Bihar State electricity Power Corporation (BHPC), (A Govt. of Bihar Enterprise), registered below Company Act 1956 is in control of development of hydro power comes at intervals the state. below Bihar State Hydro-Power Policy -2012, BHPC square measure the Nodal Agency on behalf of, Govt. of Bihar for notifying hydropower locations, tantalizing proposals, examining the techno-commercial usefulness of comes (under the horizon of the State), its method, transference govt. approvals, approving technical proposals and look physical progress of the work. The technical appraisal for the comes below the horizon of Central Govt. square measure done by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) as per provision of Indian Electricity Act. 2003.
Small electricity power units square measure got wind at Kataiya, Daulatpur, Thumha, Singheshwar Bazar, Kariapatti, Jadia, Parsa (all in Supaul district), Manhara and Malhanwa (Saharsa district) and Satokhar (Madhepura). The total place in capability of future electricity power stations in Bihar square measure 650 mw, a significant push for a sector that has not so far reached its full potential within the State.
The place in capability of this electricity stations vary from highest twenty MW at Kataiya electricity power station to Shrikhinda station in Rohtas district that generates exclusively zero.7 mw.
The Government has in addition best-known five places for fixing pumped-storage electricity power stations in Kaimur district with the whole place in capability of 2,970 mw. The pumped-storage power comes is also established at Hathiadah-Durgawati, Telharkund, Sinafadar, Panchgotia and Kohira.,
Irrigation and Hydropower in Bihar
Irrigation is the artificial application of water to land to assist in the growing of crops. It is one of the most important agricultural practices in Bihar, where the state’s economy is heavily dependent on agriculture. Irrigation helps to increase crop yields, improve crop quality, and extend the growing season.
Bihar has a long history of irrigation, dating back to the ancient Mauryan Empire. The first major irrigation project in Bihar was the construction of the Son Canal in the 17th century. The canal was built to irrigate the Gangetic Plain, and it remains one of the most important irrigation systems in the state.
In the 20th century, the government of Bihar built a number of large-scale irrigation projects, including the Kosi Barrage and the Gandak Barrage. These projects have helped to increase the amount of land that is irrigated in Bihar, and they have also helped to improve the efficiency of irrigation.
Irrigation is essential for the agricultural economy of Bihar. The state’s main crops, such as rice, wheat, and sugarcane, all require irrigation to grow. Without irrigation, these crops would not be able to grow in Bihar’s hot, dry Climate.
Irrigation also helps to improve the Quality Of Life in Bihar. By increasing crop yields, irrigation helps to reduce POVERTY and hunger. It also helps to improve the Environment by reducing Soil erosion and Water Pollution.
Hydropower is the generation of electricity from the power of moving water. It is a RENEWABLE ENERGY source that has a number of advantages over fossil fuels, such as coal and oil. Hydropower is a clean Source Of Energy that does not produce greenhouse gases. It is also a reliable source of energy, as the water cycle is constantly replenishing the supply of water.
Bihar has a significant potential for hydropower development. The state has a number of rivers that are suitable for hydropower projects. The most important river for hydropower in Bihar is the Ganges River. The Ganges River has a number of tributaries that are also suitable for hydropower projects.
The government of Bihar has been promoting the development of hydropower in the state. A number of hydropower projects have been built in Bihar in recent years. These projects have helped to increase the state’s electricity generation capacity and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
Hydropower is a valuable resource for Bihar. It is a clean, reliable, and renewable source of energy. The government of Bihar should continue to promote the development of hydropower in the state.
Irrigation and hydropower are both important for the development of Bihar. Irrigation helps to increase crop yields and improve the quality of life. Hydropower is a clean, reliable, and renewable source of energy. The government of Bihar should continue to promote the development of both irrigation and hydropower in the state.
What is irrigation?
Irrigation is the artificial application of water to land to assist in the growing of crops.
What is hydropower?
Hydropower is the conversion of the energy of falling water into electricity.
What are the benefits of irrigation?
Irrigation can increase crop yields, improve crop quality, and extend the growing season. It can also help to control pests and diseases, and reduce soil erosion.
What are the challenges of irrigation?
Irrigation can be expensive, and it can require a lot of water. It can also be difficult to manage irrigation systems, and they can be prone to problems such as leaks and waterlogging.
What are the different types of irrigation systems?
There are many different types of irrigation systems, including surface irrigation, Sprinkler Irrigation, and Drip Irrigation.
What is surface irrigation?
Surface irrigation is the most common type of irrigation. It involves flooding the land with water from a canal or ditch.
What is sprinkler irrigation?
Sprinkler irrigation involves spraying water onto the land from a series of sprinklers.
What is drip irrigation?
Drip irrigation involves delivering water directly to the roots of Plants through a Network of small pipes.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type of irrigation system?
The advantages and disadvantages of each type of irrigation system vary depending on the specific circumstances. For example, surface irrigation is a relatively inexpensive system, but it can be wasteful of water. Sprinkler irrigation is more efficient than surface irrigation, but it can be more expensive to install and maintain. Drip irrigation is the most efficient type of irrigation, but it can also be the most expensive to install and maintain.
What are the environmental impacts of irrigation?
Irrigation can have a number of environmental impacts, including water pollution, soil erosion, and Salinization.
What are the social impacts of irrigation?
Irrigation can have a number of social impacts, including the displacement of people, the loss of traditional livelihoods, and the conflict over water resources.
What are the future trends in irrigation?
The future trends in irrigation are likely to be driven by a number of factors, including the increasing demand for food, the need to conserve water, and the need to reduce the environmental impacts of irrigation.
Which of the following is not a major river in Bihar?
(A) Ganga
(B) Yamuna
(C) Son
(D) NarmadaWhich of the following is the capital of Bihar?
(A) Patna
(B) Ranchi
(C) Jamshedpur
(D) GayaWhich of the following is the largest city in Bihar?
(A) Patna
(B) Ranchi
(C) Jamshedpur
(D) GayaWhich of the following is the Official Language of Bihar?
(A) Hindi
(B) Urdu
(C) English
(D) BengaliWhich of the following is the chief minister of Bihar?
(A) Nitish Kumar
(B) Lalu Prasad Yadav
(C) Ram Vilas Paswan
(D) Tejashwi YadavWhich of the following is the Literacy rate in Bihar?
(A) 63.8%
(B) 70.9%
(C) 77.7%
(D) 84.1%Which of the following is the population of Bihar?
(A) 104,099,198
(B) 110,389,216
(C) 116,789,234
(D) 123,189,252Which of the following is the GDP of Bihar?
(A) $117.7 billion
(B) $124.1 billion
(C) $130.5 billion
(D) $136.9 billionWhich of the following is the agricultural land in Bihar?
(A) 36,000 square kilometers
(B) 40,000 square kilometers
(C) 44,000 square kilometers
(D) 48,000 square kilometersWhich of the following is the forest cover in Bihar?
(A) 7,000 square kilometers
(B) 8,000 square kilometers
(C) 9,000 square kilometers
(D) 10,000 square kilometersWhich of the following is the mineral resources in Bihar?
(A) Coal, iron Ore, limestone, bauxite, mica
(B) Coal, iron ore, limestone, bauxite, graphite
(C) Coal, iron ore, limestone, bauxite, feldspar
(D) Coal, iron ore, limestone, bauxite, quartzWhich of the following is the industries in Bihar?
(A) Steel, cement, textiles, sugar, paper
(B) Steel, cement, textiles, sugar, fertilizer
(C) Steel, cement, textiles, sugar, chemicals
(D) Steel, cement, textiles, sugar, pharmaceuticalsWhich of the following is the tourism in Bihar?
(A) Patna, Bodh Gaya, Rajgir, Nalanda, Vaishali
(B) Patna, Gaya, Rajgir, Nalanda, Vaishali
(C) Patna, Ranchi, Jamshedpur, Gaya, Vaishali
(D) Patna, Ranchi, Jamshedpur, Gaya, BhagalpurWhich of the following is the Education in Bihar?
(A) There are 10 universities in Bihar.
(B) There are 12 universities in Bihar.
(C) There are 14 universities in Bihar.
(D) There are 16 universities in Bihar.Which of the following is the health in Bihar?
(A) There are 10 medical colleges in Bihar.
(B) There are 12 medical colleges in Bihar.
(C) There are 14 medical colleges in Bihar.
(D) There are 16 medical colleges in Bihar.Which of the following is the Sports in Bihar?
(A) Cricket, football, hockey, kabaddi, wrestling
(B) Cricket, football, hockey, volleyball, wrestling
(C) Cricket, football, hockey, badminton, wrestling
(D) Cricket, football, hockey, tennis, wrestlingWhich of the following is the culture in Bihar?
(A) Maithili, Bhojpuri, Magahi, Angika, Urdu
(B) Maithili, Bhojpuri, Magahi, Angika, Hindi
(C) Mait