<–2/”>a >The Global Positioning System consists of 24 satellites, that circle the globe once every 12 hours, to provide worldwide position, time and velocity information. GPS makes it possible to precisely identify locations on the earth by measuring distance from the satellites. GPS allows you to record or create locations from places on the earth and help you navigate to and from those places.
GPS satellites circle the Earth twice a day in a precise orbit. Each satellite transmits a unique signal and orbital parameters that allow GPS devices to decode and compute the precise location of the satellite. GPS receivers use this information and trilateration to calculate a user’s exact location. Essentially, the GPS receiver measures the distance to each satellite by the amount of time it takes to receive a transmitted signal. With distance measurements from a few more satellites, the receiver can determine a user’s position.
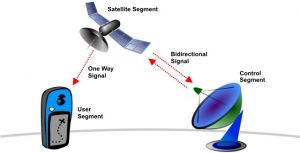
GPS System has three segments:-
Space Segment
The space segment consists of a nominal constellation of 24 operating satellites that transmit one-way signals that give the current GPS satellite position and time. The space segment consists of 24 satellites circling the earth at 12,000 miles in altitude. This high altitude allows the signals to cover a greater area. The satellites are arranged in their orbits so a GPS receiver on earth can always receive a signal from at least four satellites at any given time.
Control Segment
AF flight control officer The control segment consists of worldwide monitor and control stations that maintain the satellites in their proper orbits through occasional command maneuvers, and adjust the satellite clocks. It tracks the GPS satellites, uploads updated navigational data, and maintains Health and status of the satellite constellation.
User Segment
receiver The user segment consists of the GPS receiver equipment, which receives the signals from the GPS satellites and uses the transmitted information to calculate the user’s three-dimensional position and time.,
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a wide variety of users. It is maintained by the United States government and is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver.
GPS satellites are placed in orbit around the Earth at an altitude of approximately 12,550 miles. Each satellite carries a precise atomic clock and a radio transmitter. The satellites broadcast signals that contain the time and their position in orbit. GPS receivers use these signals to calculate their own position, speed, and time.
GPS receivers are available in a variety of sizes and shapes. Some are small enough to be carried in a pocket, while others are large enough to be mounted on a vehicle or boat. GPS receivers are used for a variety of purposes, including navigation, tracking, and surveying.
GPS accuracy is determined by a number of factors, including the number of satellites in view, the receiver’s antenna quality, and the amount of interference. In general, GPS receivers can achieve an accuracy of within 10 meters. However, in ideal conditions, GPS receivers can achieve an accuracy of within 1 meter.
GPS security is a concern for both the government and the public. The government is concerned about the possibility of GPS being used by terrorists or other hostile actors. The public is concerned about the possibility of their location being tracked without their knowledge or Consent.
The GPS future is bright. GPS is already being used in a variety of new and innovative ways. For example, GPS is being used to develop self-driving cars and to monitor the Environment. As GPS technology continues to improve, it is likely to be used in even more ways in the future.
Here are some additional details about each of the subtopics:
- Introduction to GPS: The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a wide variety of users. It is maintained by the United States government and is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver.
- GPS satellites: GPS satellites are placed in orbit around the Earth at an altitude of approximately 12,550 miles. Each satellite carries a precise atomic clock and a radio transmitter. The satellites broadcast signals that contain the time and their position in orbit. GPS receivers use these signals to calculate their own position, speed, and time.
- GPS signals: GPS signals are broadcast by GPS satellites at a frequency of 1.57542 GHz. The signals are modulated with a pseudorandom noise (PRN) code that is unique to each satellite. The PRN code is used to identify the satellite and to prevent interference from other signals.
- GPS receivers: GPS receivers use the signals from GPS satellites to calculate their own position, speed, and time. The receiver first locks onto the signals from four or more satellites. Once the signals are locked, the receiver uses the PRN codes to calculate its position, speed, and time.
- GPS applications: GPS is used for a variety of purposes, including navigation, tracking, and surveying. Navigation is the most common use of GPS. GPS receivers are used in cars, boats, and airplanes to provide directions and track their progress. Tracking is another common use of GPS. GPS receivers are used to track the location of vehicles, people, and assets. Surveying is a less common use of GPS. GPS receivers are used to measure distances and elevations.
- GPS accuracy: GPS accuracy is determined by a number of factors, including the number of satellites in view, the receiver’s antenna quality, and the amount of interference. In general, GPS receivers can achieve an accuracy of within 10 meters. However, in ideal conditions, GPS receivers can achieve an accuracy of within 1 meter.
- GPS security: GPS security is a concern for both the government and the public. The government is concerned about the possibility of GPS being used by terrorists or other hostile actors. The public is concerned about the possibility of their location being tracked without their knowledge or consent.
- GPS future: The GPS future is bright. GPS is already being used in a variety of new and innovative ways. For example, GPS is being used to develop self-driving cars and to monitor the environment. As GPS technology continues to improve, it is likely to be used in even more ways in the future.
What is GPS?
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth.
How does GPS work?
GPS works by using a Network of satellites that orbit the Earth. These satellites transmit signals that are received by GPS receivers. The receivers use these signals to calculate their position, speed, and time.
How accurate is GPS?
GPS is very accurate. The Average accuracy of GPS is about 10 meters. However, in ideal conditions, GPS can be accurate to within a few centimeters.
What are the benefits of using GPS?
There are many benefits to using GPS. GPS can be used for navigation, tracking, and timing. It can also be used for a variety of other applications, such as surveying, mapping, and search and rescue.
What are the limitations of using GPS?
There are a few limitations to using GPS. One limitation is that GPS can be blocked by tall buildings or Mountains. Another limitation is that GPS can be affected by interference from other electronic devices.
What are some common GPS errors?
There are a few common GPS errors. One error is called “positional dilution of precision” (PDOP). PDOP is caused by the geometry of the satellites in the GPS constellation. When the satellites are not in a favorable position, PDOP can cause the GPS receiver to be less accurate. Another error is called “multipath.” Multipath is caused by the GPS signal bouncing off of objects before it reaches the receiver. This can cause the receiver to calculate a false position.
How can I improve the accuracy of my GPS?
There are a few things you can do to improve the accuracy of your GPS. One thing you can do is to use a GPS receiver with a higher number of channels. More channels means that the receiver can track more satellites, which can improve accuracy. Another thing you can do is to use a GPS receiver that is designed for high accuracy. These receivers typically have more features and are more expensive than standard GPS receivers.
What are some tips for using GPS safely?
There are a few tips you can follow to use GPS safely. One tip is to always be aware of your surroundings. When you are using GPS, it is easy to become distracted by the device. Make sure you are aware of your surroundings and that you are not walking into traffic or other hazards. Another tip is to use a GPS receiver that is designed for outdoor use. These receivers are typically more durable and can withstand the Elements. Finally, make sure you have a backup plan in case your GPS fails. Carry a map and compass with you and know how to use them.
What are some of the most common GPS applications?
Some of the most common GPS applications include navigation, tracking, and timing. Navigation is the most common use for GPS. GPS can be used to find your way around unfamiliar areas. Tracking is another common use for GPS. GPS can be used to track the location of people, vehicles, or assets. Timing is another common use for GPS. GPS can be used to time events or to measure distances.
1. What is the Global Positioning System (GPS)?
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth.
2. How does GPS work?
GPS works by using a network of satellites that orbit the Earth. These satellites transmit signals that are received by GPS receivers. The receivers use these signals to calculate their position, speed, and time.
3. How many satellites are in the GPS constellation?
There are currently 31 satellites in the GPS constellation.
4. What is the accuracy of GPS?
The accuracy of GPS depends on a number of factors, including the number of satellites in view, the receiver’s location, and the environment. In general, GPS can provide accuracy to within a few meters.
5. What are some of the benefits of using GPS?
GPS has many benefits, including:
- Navigation: GPS can be used to navigate to a specific location.
- Tracking: GPS can be used to track the movement of people or objects.
- Timing: GPS can be used to accurately measure time.
- Surveying: GPS can be used to survey land and measure distances.
- Mapping: GPS can be used to create maps and charts.
6. What are some of the limitations of using GPS?
GPS has some limitations, including:
- Signal blockage: GPS signals can be blocked by buildings, mountains, and other objects.
- Jamming: GPS signals can be jammed by intentional interference.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of GPS can be affected by a number of factors, including the number of satellites in view, the receiver’s location, and the environment.
7. What are some of the Applications of GPS?
GPS has many applications, including:
- Navigation: GPS is used in a variety of navigation devices, including car navigation systems, handheld GPS units, and aviation navigation systems.
- Tracking: GPS is used to track the movement of people, vehicles, and other assets.
- Timing: GPS is used to accurately measure time in a variety of applications, including Sports, timing events, and scientific research.
- Surveying: GPS is used to survey land and measure distances.
- Mapping: GPS is used to create maps and charts.
- agriculture: GPS is used in agriculture to track the movement of Livestock, monitor crop Growth, and apply fertilizer and pesticides.
- Construction: GPS is used in construction to survey land, track the movement of equipment, and monitor progress.
- Transportation: GPS is used in transportation to track the movement of vehicles, monitor traffic conditions, and provide directions.
- Public safety: GPS is used by law enforcement, fire departments, and emergency medical Services to track the movement of personnel and vehicles, monitor traffic conditions, and provide directions.
- Recreation: GPS is used by hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts to navigate, track their progress, and find their way back to their starting point.
8. What is the future of GPS?
The future of GPS is bright. GPS is constantly being improved, and new applications are being developed all the time. GPS is likely to become even more ubiquitous in the future, as it becomes an essential part of our lives.