Horticulture-2/”>Horticulture sector of Gujarat
The term “horticulture” comprises the cultivation of fruits and vegetables, ornamental flowers, medicinal and aromatic Plants and their post-harvest management.
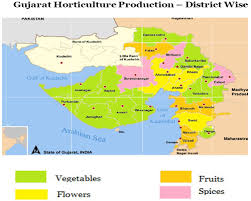
Gujarat has a total geographical area of 19.6 M ha of which about 9.7 M ha is utilized for agricultural purposes. It is about 49% of the total area of the state are under cultivation. Out of the total geographical area, the area covered under command area is about 3.8 Million ha. Rain fed area of the state is about 6.6 Million ha. Average land holding of Gujarat is 2.03ha compared to 1.16ha of total of India. The area under Irrigation is about 33% of the net area sown, while rest of area is cultivated under rain-fed conditions. Thus, there is large area dependence on rain in the state. Horticulture is a priority sector in agriculture by virtue of it’s vast potential in improving the Socio – economic conditions of the farmers. The horticulture sector is supplier for large number of agro-based industries, which has high avenues for generation of skill full EMPLOYMENT and self-employment opportunities both in rural and urban areas. Gujarat has a wide variety of Soil, rainfall pattern, temperature regimes and irrigation availability. The major fruit crops grown in Gujarat are Banana, Mango, Citrus, Papaya and Sapota. In the year 2013-14 the productivity of fruit crops is estimated at 21.18 MT/ Hectare. The major vegetables grown in Gujarat are Onion, Garlic, Potato, Brinjal, Tomato, Okra and Cucurbits. In the year 2013-14, the average productivity of vegetables is estimated at 19.90 MT/Hectare.
Gujarat state mainly produces spices viz. Cumin, Fennel, and Garlic. The State enjoys monopoly in seed spices. Isabgul is prominent medicinal crop grown in the State. Area under flowers like; Rose, Lily and Marigold is increasing day by day in the State. The cultivation of medicinal plants like; Allovera, Sena, Gugal is scattered in the state.
Gujarat has taken a lead in the sector of establishing Greenhouses by producing high value flowers like; Dutch Roses, Gerberas and Carnation and Vegetable Crops like; Capsicum, Khira, Cucumber and Tomato. The state is in leading position in Onion, Potato, Banana and Papaya. The State also introduced new horticulture crops like; Cashew Nut, Pamaroza, Sweet Orange and medicinal crops. The Climate is favourable for development of Alphanso mango in South Gujarat and Kesar in Junagadh areas. Date palm in Kutch is monopoly crop in country. Besides, Banana, Lime, Ber, Sapota, Coconut have also occupied area in the State. Horticulture in Gujarat, today, has become a sustainable and viable venture for the small and marginal farmers. It is a matter of satisfaction that their food consumption levels and household income have increased. Gujarat in the overall horticulture production of the country, which was ranked at eighth positions in 2011-12, has jumped to the fifth spot in the 2012-13, increased almost 8%. The maximum production was in fruits and flowers.
Mission for integrated development of horticulture During 12th Plan 2012-17, the central Government launched the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture to integrated all the government initiatives (MIDH) having following components: National Horticulture Mission (NHM), Horticulture Mission for North East &Himalayan States (HMNEH), National Bamboo Mission (NBM), Central Sector Scheme of National Horticulture Board (NHB), Coconut Development Board (CDB) and Central Institute for Horticulture (CIH) for holistic development of sector.
Soil Health Card A scheme of “Soil Health Card” has been initiated to provide farmers status on soil nutrient of their soil and recommendation on appropriate dosage of nutrient to be applied for improving soil health and its fertility.
Government Authorities
- Agriculture and Co-operation Department, Government of Gujarat
The Agriculture & Co-operation Department of Gujarat Govt. takes care of agriculture and related matters in its charge like horticulture, soil conservation, Dairy development, Animal Husbandry, and formation of policies / schemes in co-operative activities as well as implementation, monitoring and supervision.
- Gujarat Agro Industries Corporation Limited
Gujarat Agro Industries Corporation Ltd.(GAIC) was set up in the year 1969, under the Companies Act-1956, with the objective of promoting agricultural activities and development of Agro Based Industries in the State of Gujarat.
- National Horticulture Board
National Horticulture Board (NHB) was set up by the Government of India in 1984. NHB implements various schemes under overall supervision and guidance of the Board of Directors of NHB as well as the Department of Agriculture & Co-operation, Ministry of Agriculture, Govt. of India.
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
A Centrally Sponsored Scheme of MIDH has been launched for the holistic development of horticulture in the country during 12th five year plan. The scheme, which has taken take off from 2014-15, integrates the on-going schemes of National Horticulture Mission, Horticulture Mission for North East & Himalayan States, National Bamboo Mission, National Horticulture Board, Coconut Development Board and Central Institute for Horticulture, Nagaland.
Floriculture
Floriculture, too, has emerged as a new farming business in Gujarat, with area under cultivation almost doubling to 12,534 hectare in 2009-10, compared to 6,956 hectare in 2004-05.
The State, which is actively promoting cultivation of rose, marigold, mogra and lily, produced 95,185 tonnes of flowers in 2009-10. The State now has 165 green-houses for floriculture that defy the vagaries of Nature impacting floriculture.
The area under spices has increased from 3.58 lakh hectare to 4.96 lakh hectare, with a lion’s share of cumin (3.11 lakh ha).
,
The horticulture sector of Gujarat is a major contributor to the state’s economy. The sector is responsible for the production of a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, flowers, spices, nuts, oilseeds, and other agricultural products.
Gujarat is one of the leading producers of mangoes in the world. The state also produces a significant amount of bananas, grapes, pomegranates, oranges, apples, guavas, litchis, chikoos, and papayas. In addition to fruits, Gujarat is also a major producer of vegetables, such as tomatoes, onions, potatoes, cauliflowers, cabbages, brinjals, green chilies, spinach, cucumbers, carrots, and beans.
The state is also home to a thriving floriculture Industry. Gujarat is a major producer of roses, jasmines, marigolds, lilies, orchids, chrysanthemums, sunflowers, lotuses, and gladioli. The state’s spices are also in high demand, and Gujarat is a major producer of turmeric, ginger, garlic, chili powder, cumin, coriander, fenugreek, mustard, red chili, black pepper, cardamom, and cinnamon.
Gujarat is also a major producer of nuts, such as almonds, cashews, pistachios, walnuts, peanuts, hazelnuts, Brazil nuts, macadamia nuts, and pecans. The state is also a major producer of oilseeds, such as groundnuts, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, rapeseed, mustard, cottonseed, soybeans, coconuts, and palms.
In addition to the major agricultural products mentioned above, Gujarat also produces a variety of other agricultural products, such as medicinal plants, aromatic plants, fiber crops, ornamental plants, mushrooms, honey, beekeeping products, silk, fish, and flowers.
The horticulture sector of Gujarat is a major contributor to the state’s economy. The sector provides employment to millions of people and generates billions of rupees in revenue each year. The sector is also a major source of Foreign Exchange for the state.
The horticulture sector of Gujarat is facing a number of challenges, including Climate Change, water scarcity, pests and diseases, and labor shortages. However, the sector is also making progress in addressing these challenges. For example, the State Government is investing in research and development to develop new varieties of crops that are resistant to pests and diseases. The government is also working to improve irrigation Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE and to provide training to farmers on modern agricultural practices.
The horticulture sector of Gujarat has a bright future. The sector is well-positioned to benefit from the growing demand for fruits, vegetables, flowers, spices, nuts, oilseeds, and other agricultural products. The sector is also well-positioned to benefit from the government’s efforts to improve the infrastructure and productivity of the agricultural sector.
What is horticulture?
Horticulture is the science and art of cultivating plants, including the production of fruits, vegetables, flowers, ornamental plants, and herbs.
What are the different types of horticulture?
There are many different types of horticulture, including:
- Fruit and vegetable production: This involves growing fruits and vegetables for human consumption.
- Ornamental horticulture: This involves growing plants for their beauty, such as flowers, trees, and shrubs.
- Landscape horticulture: This involves designing and maintaining landscapes, such as parks, gardens, and golf courses.
- Floriculture: This involves growing flowers for commercial purposes.
- Medicinal horticulture: This involves growing plants for their medicinal properties.
- Urban horticulture: This involves growing plants in urban areas, such as on rooftops, in parks, and in vacant lots.
What are the benefits of horticulture?
Horticulture has many benefits, including:
- It provides food for people and animals.
- It helps to improve air quality.
- It can be used to create beautiful landscapes.
- It can be a Source Of Income for farmers and businesses.
- It can provide jobs for people in rural areas.
- It can help to reduce Stress and anxiety.
- It can promote physical activity.
- It can help people to connect with nature.
What are the challenges of horticulture?
Horticulture also has some challenges, including:
- It can be difficult to grow crops in certain climates.
- Pests and diseases can damage crops.
- Weather conditions can damage crops.
- Labor costs can be high.
- The market for horticultural products can be volatile.
- There is a lot of competition in the horticultural industry.
What is the future of horticulture?
The future of horticulture looks bright. The global demand for horticultural products is increasing, and there is a growing interest in Sustainable Agriculture. Horticulture can play a role in addressing many of the world’s challenges, such as Food Security, climate change, and POVERTY.
What are some of the latest trends in horticulture?
Some of the latest trends in horticulture include:
- The use of vertical farming to grow crops in urban areas.
- The use of hydroponics to grow crops without soil.
- The use of LED lights to grow crops indoors.
- The use of robots to automate tasks in horticulture.
- The use of drones to monitor crops and apply pesticides.
- The use of blockchain technology to track the provenance of horticultural products.
What are some of the most important issues facing the horticulture sector?
Some of the most important issues facing the horticulture sector include:
- The need to increase productivity.
- The need to reduce costs.
- The need to improve quality.
- The need to meet the growing demand for horticultural products.
- The need to address the challenges of climate change.
- The need to ensure the sustainability of the horticulture sector.
Which of the following is not a type of horticulture?
(A) Floriculture
(B) Olericulture
(C) Pomiculture
(D) Horticulture sector of GujaratWhich of the following is the most important crop in Gujarat?
(A) Cotton
(B) Groundnut
(C) Wheat
(D) HorticultureWhich of the following is not a benefit of horticulture?
(A) It provides jobs
(B) It increases food security
(C) It helps to conserve water
(D) It pollutes the EnvironmentWhich of the following is the most important fruit crop in Gujarat?
(A) Mango
(B) Banana
(C) Grapes
(D) AppleWhich of the following is the most important vegetable crop in Gujarat?
(A) Tomato
(B) Onion
(C) Potato
(D) CauliflowerWhich of the following is the most important spice crop in Gujarat?
(A) Turmeric
(B) Chili
(C) Coriander
(D) GingerWhich of the following is the most important medicinal plant in Gujarat?
(A) Aloe vera
(B) Ashwagandha
(C) Turmeric
(D) GingerWhich of the following is the most important forest product in Gujarat?
(A) Timber
(B) Bamboo
(C) Honey
(D) LacWhich of the following is the most important animal product in Gujarat?
(A) Milk
(B) Meat
(C) Eggs
(D) FishWhich of the following is the most important marine product in Gujarat?
(A) Fish
(B) Shrimp
(C) Crab
(D) Oyster