<<–2/”>a >p style=”text-align: center;”>The Greenhouse Effect
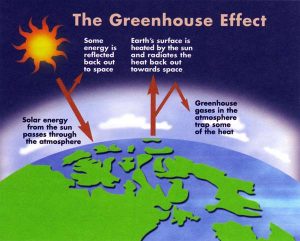
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that insulates the Earth . Incoming solar radiations are absorbed and reemitted back from the Earth’s surface as infrared energy, greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the Atmosphere prevent some of this heat from escaping into space, instead reflecting the energy back to further warm the surface. Human activities that produce GHGs (anthropogenic) amplify the greenhouse effect. Anthropogenic GHG emissions are modifying the Earth’s energy balance between incoming solar radiation and the heat released back into space, resulting in Climate change. Gases such as CO2 , NO2 , CFCs (chloro fluorocarbons) allow sun rays to pass through them but then absorb and reradiate the heat back towards the earth. These are therefore termed as Green House Gases.
The amount of Solar Energy absorbed or radiated by Earth is modulated by the atmosphere and depends on its composition. Greenhouse gases—such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane—occur naturally in small amounts and absorb and release heat energy more efficiently than abundant atmospheric gases like nitrogen and Oxygen. Small increases in carbon dioxide concentration have a large effect on the climate system.
Mazor Green House gases are:-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)- 0.038%
Water Vapor (H20) -0-4%
Methane (CH4) -trace amount
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) -trace amount
Ozone (O3) -trace amount
Nitrogen oxides(NO, NO2, N2O)- trace amount
Mitigation is achieved by reducing both the energy intensity of GDP and the carbon intensity of energy used.Mazor Mitigation strategies are:-
- Improved supply and distribution efficiency; fuel switching from coal to gas; nuclear power; renewable heat and power (hydropower, solar, wind, geothermal and bioenergy); combined heat and power; early applications of carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS) (e.g. storage of removed CO2from natural gas); CCS for gas, Biomass/”>Biomass and coal-fired electricity generating facilities; advanced nuclear power; advanced RENEWABLE ENERGY, including tidal and Wave energy, concentrating solar, and solar photovoltaics
- More fuel-efficient vehicles; hybrid vehicles; cleaner diesel vehicles; biofuels; modal shifts from road transport to rail and public transport systems; non-motorised transport (cycling, walking); land-use and transport planning; second generation biofuels; higher efficiency aircraft; advanced electric and hybrid vehicles with more powerful and reliable batteries
- Efficient lighting and daylighting; more efficient electrical appliances and heating and cooling devices; improved cook stoves, improved insulation; passive and active solar design for heating and cooling; alternative refrigeration fluids, recovery and recycling of fluorinated gases; integrated design of commercial buildings including technologies, such as intelligent meters that provide feedback and control; solar photovoltaics integrated in buildings
- More efficient end-use electrical equipment; heat and power recovery; material recycling and substitution; control of non-CO2 gas emissions; and a wide array of process-specific technologies; advanced Energy Efficiency; CCS for cement, ammonia, and iron manufacture; inert electrodes for aluminium manufacture
- Improved crop and grazing land management to increase Soil carbon storage; restoration of cultivated peaty soils and degraded lands; improved rice cultivation techniques and Livestock and manure management to reduce CH4 emissions; improved nitrogen fertiliser application techniques to reduce N2O emissions; dedicated energy crops to replace fossil fuel use; improved energy efficiency; improvements of crop yields
- Afforestation; reforestation; forest management; reduced deforestation; harvested wood product management; use of Forestry products for bioenergy to replace fossil fuel use; tree species improvement to increase biomass productivity and Carbon Sequestration; improved remote sensing technologies for analysis of vegetation/soil carbon sequestration potential and mapping land-use change
- Landfill CH4 recovery; waste incineration with energy recovery; composting of organic waste; controlled wastewater treatment; recycling and waste minimisation; biocovers and biofilters to optimise CH4 oxidation
,
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When sunlight hits the Earth’s atmosphere, some of the energy is reflected back to space, and some of it is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which warms the planet.
The main greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Human activities are increasing the levels of these gases in the atmosphere, which is causing the greenhouse effect to become stronger. This is leading to Climate Change, which is a long-term change in the Earth’s climate.
Climate change is already having a significant impact on the planet. It is causing sea levels to rise, Glaciers to melt, and extreme weather events to become more common. These changes are having a devastating impact on people and Ecosystems around the world.
There are a number of things that can be done to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and reduce the Impact Of Climate Change. These include:
- Reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and switching to renewable energy sources
- Improving energy efficiency
- Reducing deforestation
- Protecting and restoring forests
- Investing in sustainable agriculture
- Reducing food waste
- Changing our transportation habits
- Making our homes and businesses more energy-efficient
Climate change is a serious problem, but it is not too late to take action. By working together, we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect our planet for future generations.
Ocean Acidification is a serious problem that is caused by the increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. When carbon dioxide dissolves in the ocean, it forms carbonic acid. This acid can harm marine life, coral reefs, and other ecosystems.
Deforestation is the clearing of forests for other uses, such as agriculture, development, or logging. Deforestation can lead to a number of problems, including climate change, soil erosion, and Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity loss.
Air Pollution is the contamination of the air by harmful substances, such as particulate matter, ozone, and sulfur dioxide. Air pollution can cause a number of Health problems, including respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
Water Pollution is the contamination of water by harmful substances, such as sewage, industrial waste, and agricultural runoff. Water pollution can cause a number of health problems, as well as damage to ecosystems.
Land degradation is the decline in the quality of land, which can be caused by a number of factors, such as deforestation, overgrazing, and soil erosion. Land degradation can lead to a number of problems, such as food insecurity, POVERTY, and conflict.
Biodiversity loss is the decline in the variety of life on Earth. Biodiversity loss can be caused by a number of factors, such as habitat loss, overexploitation, and climate change. Biodiversity loss can lead to a number of problems, such as ecosystem collapse, food insecurity, and climate change.
Overpopulation is a condition in which a Population exceeds the carrying capacity of its Environment. Overpopulation can lead to a number of problems, such as resource depletion, pollution, and Environmental Degradation.
Overconsumption is the excessive use of Resources, such as food, water, energy, and materials. Overconsumption can lead to a number of problems, such as resource depletion, pollution, and environmental degradation.
Poverty is a state of deprivation or lack of resources. Poverty can lead to a number of problems, such as hunger, Malnutrition, disease, and lack of Education.
Inequality is the unequal distribution of wealth, income, and opportunity. Inequality can lead to a number of problems, such as poverty, crime, and social unrest.
Conflict is a state of disagreement or hostility between two or more parties. Conflict can lead to a number of problems, such as violence, death, and destruction.
Governance is the act of governing or controlling a country, state, or organization. Good Governance is essential for Sustainable Development.
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes. Technology can be used to solve environmental problems, such as climate change, pollution, and deforestation.
Finance is the management of Money and other assets. Finance can be used to support sustainable development projects.
Education is the process of Learning and acquiring knowledge. Education is essential for raising awareness about environmental issues and promoting sustainable development.
Awareness is the state of being conscious or aware of something. Awareness is essential for taking action to address environmental issues.
Action is the process of doing something. Action is essential for solving environmental problems and achieving sustainable development.
We can all play a role in addressing global environmental issues. By working together, we can create a more sustainable future for our planet.
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s climate system observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere. The term is frequently used interchangeably with the term climate change, though the latter refers to both human- and naturally produced warming and the effects it has on our planet. It is most commonly measured as the Average increase in Earth’s global surface temperature.
What are the causes of global warming?
The primary cause of global warming is human activity, primarily the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. When these fuels are burned, they release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which causes the planet to warm.
Other human activities that contribute to global warming include deforestation, agriculture, and industrial processes. Deforestation removes trees, which absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Agriculture releases methane, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. Industrial processes also release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
What are the effects of global warming?
Global warming is already having a significant impact on our planet. The average global temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius since the pre-industrial period. This may not seem like much, but it is already having a noticeable impact on our planet.
The effects of global warming include rising sea levels, melting glaciers, more extreme weather events, and changes in plant and animal life. Rising sea levels are caused by the melting of glaciers and ice sheets. This is causing coastal flooding and erosion. Melting glaciers are also causing changes in the flow of rivers and streams.
More extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, are becoming more common due to global warming. These events can cause widespread damage and loss of life. Changes in plant and animal life are also being observed due to global warming. Some species are moving to new areas in order to find suitable habitats. Others are facing extinction due to changes in their environment.
What can we do to mitigate global warming?
There are a number of things that we can do to mitigate global warming. These include reducing our reliance on fossil fuels, investing in renewable energy sources, and improving energy efficiency. We can also make changes to our lifestyles, such as driving less, eating less meat, and recycling more.
Reducing our reliance on fossil fuels is one of the most important things that we can do to mitigate global warming. Fossil fuels are the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions. We can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels by using renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. We can also improve energy efficiency by making our homes and businesses more energy-efficient.
Investing in renewable energy sources is another important way to mitigate global warming. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, do not produce greenhouse gases. We can invest in renewable energy sources by installing solar panels on our homes or by buying renewable energy from our utility company.
Improving energy efficiency is another way to mitigate global warming. Energy efficiency means using less energy to do the same things. We can improve energy efficiency by making our homes and businesses more energy-efficient. We can do this by weatherizing our homes, using energy-efficient appliances, and driving more fuel-efficient cars.
Making changes to our lifestyles is another way to mitigate global warming. We can reduce our impact on the environment by driving less, eating less meat, and recycling more. We can also choose to buy products that are made from recycled materials.
By taking these steps, we can help to mitigate global warming and protect our planet for future generations.
Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
(A) Carbon dioxide
(B) Methane
(C) Water vapor
(D) OxygenWhich of the following is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere?
(A) Carbon dioxide
(B) Methane
(C) Water vapor
(D) Nitrous oxideThe greenhouse effect is caused by the presence of which of the following gases in the atmosphere?
(A) Greenhouse gases
(B) Ozone
(C) Water vapor
(D) All of the aboveThe greenhouse effect is beneficial because it:
(A) Traps heat in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm enough for life.
(B) Causes the Earth to cool, making it more hospitable to life.
(C) Has no effect on the Earth’s temperature.Human activities are increasing the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which is causing the Earth’s temperature to rise. This is known as:
(A) Global warming
(B) Climate change
(C) The greenhouse effectThe main cause of global warming is the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These fuels release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which traps heat and causes the Earth’s temperature to rise.
Other human activities that contribute to global warming include deforestation, agriculture, and industrial processes.
The effects of global warming are already being felt around the world, in the form of rising sea levels, more extreme weather events, and changes in plant and animal life.
Global warming is a serious threat to the planet and its inhabitants. It is important to take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of global warming.
Some of the things that can be done to reduce greenhouse gas emissions include:
(A) Using renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
(B) Improving energy efficiency.
(C) Reducing deforestation.
(D) All of the aboveSome of the things that can be done to mitigate the effects of global warming include:
(A) Building sea walls to protect coastal areas from rising sea levels.
(B) Developing drought-resistant crops.
(C) Restoring forests.
(D) All of the above