Geographical location of Bihar:-
Introduction:-
Bihar is a land locked state lying in the eastern part of India although the outlet to the sea through the port of Kolkata is not far away. Bihar lies mid-way between the humid West Bengal in the east and the sub humid Uttar Pradesh in the west which provides it with a transitional position in respect of Climate, economy and culture. It is bounded by Nepal in the north and by Jharkhand in the south. The Bihar plain is divided into two unequal halves by the river Ganga which flows through the middle from west to east.
Located in the Eastern part of India, Bihar is the 13th largest state of the country and constitutes only 2.86 % of the total land of India. On 15 November 2000, the southern part of Bihar was split to form the state of Jharkhand. Bihar is divided into 37 districts and has Patna as its capital. Bihar has a total area of 94,163 sq. km. and is located between 21°-58′-10″ N ~ 27°-31′-15″ N latitude and between 82°-19′-50″ E ~ 88°-17′-40″ E longitude. The elevation above sea level stands to 173 Feet.The location of Bihar is strategic. It is located in the eastern part of the country, which lies in the middle of the humid West Bengal and sub-humid Uttar Pradesh. The place enjoys close proximity to Nepal. There is Jharkhand in the South as well. The state of Bihar is fortunate to have river, Ganga running just in the middle of it from west to east. That is what makes the place even more significant. The river, Ganga is considered as one of the holy rivers of India since ages. This has made the state of Bihar preserve its rich historical culture in terms of religion much intensely as compared to other states. India’s largest Mountains, the Himalayan Mountains are to the north of Bihar. If one goes to the south, one can find Chota Nagpur plateau. However, it has been a part of Jharkhand, which was in Bihar until the year 2000.
Geographical Structure of Bihar:-
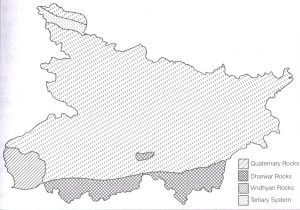
The Geographical Structure of Bihar is embedded with younger geological structure in the North by Dharwarian rocks and older in the South by quaternary rocks. As far as the physiological structure is concern, Bihar is consists of Terai in the North-West, Gangetic Plain in the centre and Plateau in the Southern region.
Geology of Bihar:-
The Geology of Bihar corresponds the balance picture of the term geology because it is consists of younger (Tertiary Period) and older formation of rock (Pre-Cambrian period), and the plain was formed by filling up of a vast trough by the heavy loads of detritus carried by swiftly flowing rivers down the Southern slopes of newly uplifted Himalayas.
List of rocks found in geographical land area of Bihar:-
- Dharwar Rock:-
- Found in the South-Eastern part of Bihar like Munger, Jamui, and Nawada.
- They are made up of Quartzite, phyllite, Gneiss, Schist and slate.
- Region is dominated by mica-schists
- Vindhyan Rock:-
- Found in South- Western part of Bihar in between Kaimur district and
Sone river valley in Rohtas District.
- They are made up of sandstone, quartzite, limestone, dolomites and shale.
- Tertiary Rock:-
- Found in Himalayan terai region of Bihar.
- Formed by up warping of sediments deposited in Tethys Sea between Eurasian plate and Indian plate.
- Quaternary Rock:-
- Found in down warped section between Himalayas and Chhotanagpur Plateau
- They are made up of sandstones, alluvium, conglomerate, coarse gravel etc.
Physiographical Division of Bihar:-
Bihar is divided into three physiographic units on the basis of physical and structural conditions:-
- Shiwalik Range
- Bihar Plain
- Southern Plateau Region.
Shiwalik Range:-
This range shadows the state from Northern part of West Champaran district over an area 32 km long and 6-8 km wide and it is divided into sub-divided into three parts on the basis of variation:
- Ramanagar Doon
- Someshwar Range
- Harha Valley
Bihar Plain:-
The plains of Bihar, adjoining Nepal, are drained by a number of rivers that have their catchments in the steep and geologically nascent Himalayas. Kosi, Gandak, Burhi Gandak, Bagmati, Kamla Balan, Mahananda and Adhwara Group of rivers originates in Nepal, carry high discharge and very high sediment load and drops it down in the plains of Bihar. About 65% of catchments area of these rivers falls in Nepal/Tibet and only 35% of catchments area lies in Bihar. Plains of north Bihar have recorded the highest number of floods during the last 30 years. In the years 1978, 1987, 1998, 2004 and 2007 Bihar witnessed high magnitudes of flood. The total area affected by floods has also increased during these years. Flood of 2004 demonstrates the severity of flood problem when a vast area of 234908 Sq Km was badly affected by the floods of Bagmati, Kamla & Adhwara groups of rivers causing loss of about 800 human lives, even when Ganga, the master drain was flowing low. It is located between Northern Mountains and Southern Plateau region which is bounded by 150m contour line in the North as well as in the South. This plain is sub-divided into two parts on the basis of characteristics:
- Northern Plain: It is located in East & West Champaran (Terai area with higher elevation), and Chaurs of Samastipur, Begusarai, Saharsa and Kathihar districts. Region is drained by Saryu, Gandak, Burhi Gandak, Bagmati, Kamla-Balan, Kosi and Mahanadi and their tributaries.
- Southern Plain: It is narrow than northern plain of Bihar and triangular in shape because many hills are located in this region such as hills of Gaya, Rajgir, Giriak, Bihar Sharif, Sheikhpura, Jamalpur and Kharagpur hills.
Southern Plateau Region:-
It is located between Kaimur districts in the West to Banka in the East. It is made up of hard rock’s like gneiss, schist and granite. This region blessed with many conical hills which are made up of batholim like Pretshil, Ramshila and Jethian hill.
,
Bihar is a state in northeastern India. It is the 3rd most populous state in India, with over 100 million inhabitants. The state is bordered by Uttar Pradesh to the west, Jharkhand to the south, West Bengal to the east, Nepal to the north, and the Indian state of Sikkim to the northeast.
The capital of Bihar is Patna, which is also the largest city in the state. Other major cities include Gaya, Bhagalpur, Muzaffarpur, Darbhanga, and Purnia.
Bihar is a landlocked state with a tropical savanna climate. The Average temperature ranges from 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit) in winter to 38 degrees Celsius (100 degrees Fahrenheit) in summer. The state receives an average annual rainfall of 1,000-1,500 mm (39-59 inches).
The Official Language of Bihar is Hindi, but Urdu, Maithili, Bhojpuri, Magahi, Angika, and Tharu are also spoken in the state. The majority of the Population is Hindu, followed by Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, and Jains.
Bihar is a unitary parliamentary constitutional republic. The head of state is the Governor, who is appointed by the President of India. The head of government is the Chief Minister, who is elected by the members of the Legislative Assembly.
The currency of Bihar is the Indian rupee. The time zone is UTC+5:30. The Internet TLD is .in and the calling code is +91.
Bihar is a land of rich history and culture. The state is home to many ancient temples, including the Mahabodhi Temple, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Bihar is also the birthplace of Gautama Buddha, the founder of Buddhism-2/”>Buddhism.
The economy of Bihar is based on agriculture, manufacturing, and Services. The state is a major producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, and milk. Bihar is also home to a number of industrial units, including steel mills, power Plants, and chemical factories.
Bihar is a developing state with a number of challenges. The state has a high rate of POVERTY and illiteracy. The Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE in Bihar is also underdeveloped. However, the state has made significant progress in recent years. The government has implemented a number of development programs, which have helped to improve the lives of the people of Bihar.
Bihar is a beautiful and diverse state with a rich history and culture. The state has a lot to offer visitors, including ancient temples, historical sites, and natural beauty.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about Bihar:
What is Bihar known for?
Bihar is known for its rich history and culture, as well as its natural beauty. The state is home to many ancient temples and monuments, as well as a variety of wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.What is the capital of Bihar?
The capital of Bihar is Patna.What is the population of Bihar?
The population of Bihar is over 100 million people.What is the language spoken in Bihar?
The official language of Bihar is Hindi, but there are also many other languages spoken in the state, including Urdu, Bengali, and Maithili.What is the religion of the people of Bihar?
The majority of the people of Bihar are Hindu, but there are also significant Muslim, Christian, and Sikh minorities.What is the economy of Bihar like?
The economy of Bihar is based on agriculture, manufacturing, and services. The state is a major producer of rice, wheat, and sugar cane.What are some of the challenges facing Bihar?
Some of the challenges facing Bihar include poverty, illiteracy, and Corruption. The state has also been affected by violence and terrorism.What are some of the opportunities for Bihar?
Some of the opportunities for Bihar include its rich natural Resources, its young population, and its strategic location. The state has also made significant progress in recent years in improving its infrastructure and Education system.What is the future of Bihar?
The future of Bihar looks bright. The state has the potential to become a major economic and social force in India. With continued Investment in education, infrastructure, and healthcare, Bihar can achieve its full potential and become a model for other developing countries.
Sure, here are some MCQs about Bihar without mentioning the topic of geographical location:
Bihar is a state in which of the following regions of India?
(A) Northern India
(B) Eastern India
(C) Central India
(D) Western IndiaBihar is bordered by which of the following states?
(A) Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Nepal
(B) Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Nepal
(C) Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Nepal
(D) Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, and NepalThe capital of Bihar is:
(A) Patna
(B) Ranchi
(C) Bhubaneswar
(D) KolkataThe official language of Bihar is:
(A) Hindi
(B) English
(C) Urdu
(D) BengaliThe population of Bihar is approximately:
(A) 100 million
(B) 120 million
(C) 140 million
(D) 160 millionThe Literacy rate in Bihar is approximately:
(A) 60%
(B) 70%
(C) 80%
(D) 90%The main religion in Bihar is:
(A) Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism
(B) Islam
(C) Christianity
(D) SikhismThe main crops grown in Bihar are:
(A) Rice, wheat, sugarcane, and maize
(B) Rice, wheat, Cotton, and jute
(C) Rice, wheat, tea, and coffee
(D) Rice, wheat, millet, and sorghumThe main industries in Bihar are:
(A) Agriculture, textiles, and mining
(B) Agriculture, steel, and cement
(C) Agriculture, Software, and IT
(D) Agriculture, tourism, and hospitalityThe main tourist attractions in Bihar are:
(A) The Mahabodhi Temple, the Nalanda University, and the Rajgir Hills
(B) The Taj Mahal, the Red Fort, and the Qutub Minar
(C) The Gateway of India, the Marine Drive, and the Juhu Beach
(D) The Charminar, the Golconda Fort, and the Qutb Shahi Tombs
I hope these MCQs were helpful!