<–2/”>a >Enlightenment and Industrial revolution
Emergence and Background
Beginning of geographical discoveries and direct sea routes opened new avenues of Trade and Commerce. It formed the bedrock of Industrial revolution as mismatch between demand and supply led to new innovative ways of enhancing production.
Second factor was emergence of capitalist ideology. Profit making became the core of all economic activities in Europe. Capitalists financed the voyages of sailors in search of new markets and new sources of raw material. New industries were also financed by capitalists.
New inventions were made which enhanced productivity many fold. Invention of Steam Power, Use of Mechanical Power instead of Man and Animal power changed the way production was done Hargreaves’s spinning mill, improvement of Arkwright and Crompton over that spinning mill. Invention of steam engine led to birth of Cotton Jenny, a much improved cotton weaver.
Factory production arrived as new mode of production as community or home workshop production failed to meet burgeoning demands.
Colonial quests led to discoveries of new cheap sources of raw materials and profitable dumping markets for finished products.
Faster means of Communication, commoditification of labor with introduction of wage System, development of new sources of energy like coal, new durable materials like steel were the other supporting factors for the rise of Industrial Revolution.
Industrial Revolution in Britain
A number of factors contributed to Britain’s role as the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution. For one, it had great deposits of coal and iron Ore, which proved essential for industrialization. Additionally, Britain was a politically stable Society, as well as the world’s leading colonial power, which meant its colonies could serve as a source for raw materials, as well as a marketplace for manufactured goods.
As demand for British goods increased, merchants needed more cost-effective methods of production, which led to the rise of mechanization and the factory system.
There were many conducive factors. Britain had adequate capital which was accumulated through colonialism Disappearance of serfdom and ‘enclosure movement’ provided huge surplus agricultural labor which looked for EMPLOYMENT and became source of cheap labor. (As Industrialization started, land became valuable commodity. Big landlords started snatching the land of small farmers and this was termed as ‘enclosure movement’). Britain was also rich with natural Resources. Iron and coal proved twin pillars of Industrial Revolution and Britain was lucky to have them in close proximity. Britain also had a stable Polity unlike Europe. It also had a strong navy – a symbol of military might. Inventions, capitalist ideology and communication were other factors.
Salient Features of Industrial Revolution
- First feature is that, Britain was the epicenter of this revolution in 1750.
- Secondly, it started from textile sector. Britain used to spent huge wealth on import of foreign clothes like Dhaka Muslin, Calicut Calico and so on leading to huge forex drain. So, textile industries became a natural choice to start with.
- It was also a revolution in Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE which was necessary for spread of it. Railways, steam boats (reduced dependence on wind sails with heavier load), Macadamized roads (pucca roads named after its inventor Macadam), new form of communication like telegraph and penny post (now it was possible to send post in a mere penny) etc lead to new Globalization/”>Globalization-3/”>Globalization.
- It gave birth to ideology of mercantilism which viewed world resources as limited and merchants vied for each other in a ‘zero-sum game’
- A process of new globalization started in which colonies were integrated in a highly subservient manner.
- It also affected agriculture. Cropping patterns were changed. Staple Food Crops were replaced with Cash Crops like cotton, indigo, tea, opium etc.
Impact of Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution also had certain other fallouts which were not expected. There was also opposition to these new developments. Luddite movement was such an even which was a movement launched by workers who attacked machines as they feared that machines will replace manpower. This and other movements forced Industrialists to give a serious consideration to worker’s condition
- I. Social Impact – new urban centers (like Manchester, Leeds), slums, nuclear family, Urbanization, exploitation of Women and children, new class formation
- II. Economic Impact – birth of capitalism, transnational trade, cheap goods, ruin of handicrafts
- III. Political Impact – colonialism gets a new fillip, new division of countries as developed and und-developed, Europeanization of different parts of world, reforms movement like Chartist Movement started. Unions also began to form. New movements like – Socialism, Marxism also trace their roots to Industrial Revolution. Child labor laws were formed as exploitation of children increased.
,
The Enlightenment was a philosophical movement that emphasized reason and individualism over tradition and superstition. It began in Europe in the 17th century and spread to other parts of the world in the 18th century. The Enlightenment had a profound impact on the development of modern society, and its ideas continue to influence our thinking today.
One of the key ideas of the Enlightenment was that people should use their reason to question authority and tradition. This led to a number of important scientific and technological advances, as well as to the development of new political and social ideas.
Another key idea of the Enlightenment was that people are born with certain natural rights, such as the right to life, Liberty, and property. These rights are not granted by governments, but are inherent in all human beings. This idea helped to inspire the American Revolution and the French Revolution, as well as many other movements for social and political change.
The Enlightenment also emphasized the importance of individualism. This meant that people should be free to think for themselves and to make their own choices. It also meant that people should be tolerant of others, even if they have different beliefs or opinions.
The Enlightenment was a time of great intellectual and social ferment. Its ideas helped to shape the modern world, and they continue to be relevant today.
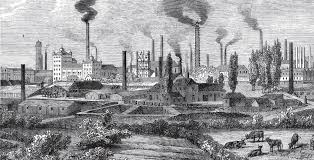
The Industrial Revolution was a period of rapid social and economic change that began in Great Britain in the late 18th century and spread to other parts of the world in the 19th century. The Industrial Revolution was characterized by the development of new technologies, such as the steam engine and the power loom, which led to the rise of factories and mass production.
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on society. It led to the Growth of cities, as people moved from rural areas to find work in factories. It also led to the development of new Social Classes, such as the factory owners and the factory workers.
The Industrial Revolution also had a significant impact on the Environment. The burning of coal and other fossil fuels led to Air Pollution, and the dumping of industrial waste into rivers and streams led to Water Pollution.
The Industrial Revolution was a time of great change, and it had both positive and negative effects. It led to economic growth and Technological Progress, but it also led to social unrest and environmental problems.
The Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution were two of the most important events in human history. They had a profound impact on the way we live, work, and think. The ideas of the Enlightenment continue to influence our thinking today, and the technologies of the Industrial Revolution have changed the way we live our lives.
The Renaissance
The Renaissance was a period of European history from the 14th to the 17th century, marking the transition from the Middle Ages to the Modern Age. It was a time of great change and innovation in art, literature, science, and philosophy.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What was the Renaissance?
The Renaissance was a period of European history from the 14th to the 17th century, marking the transition from the Middle Ages to the Modern Age. It was a time of great change and innovation in art, literature, science, and philosophy.
- Who were some of the key figures of the Renaissance?
Some of the key figures of the Renaissance include Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Raphael, Donatello, Botticelli, Titian, William Shakespeare, Miguel de Cervantes, Galileo Galilei, Nicolaus Copernicus, and Francis Bacon.
- What were some of the major achievements of the Renaissance?
Some of the major achievements of the Renaissance include the development of new artistic techniques, the rediscovery of classical texts, and the advancement of scientific knowledge.
- What was the impact of the Renaissance on the world?
The Renaissance had a profound impact on the world, shaping the development of art, literature, science, and philosophy for centuries to come.
Short Answers
- The Renaissance was a time of great change and innovation in Europe.
- Some of the key figures of the Renaissance include Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Raphael, Donatello, Botticelli, Titian, William Shakespeare, Miguel de Cervantes, Galileo Galilei, Nicolaus Copernicus, and Francis Bacon.
- Some of the major achievements of the Renaissance include the development of new artistic techniques, the rediscovery of classical texts, and the advancement of scientific knowledge.
- The Renaissance had a profound impact on the world, shaping the development of art, literature, science, and philosophy for centuries to come.
The Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a period of European history from the 16th to the 18th century, during which new ideas and knowledge in physics, astronomy, biology, chemistry, and mathematics were rapidly developed.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What was the Scientific Revolution?
The Scientific Revolution was a period of European history from the 16th to the 18th century, during which new ideas and knowledge in physics, astronomy, biology, chemistry, and mathematics were rapidly developed.
- Who were some of the key figures of the Scientific Revolution?
Some of the key figures of the Scientific Revolution include Nicolaus Copernicus, Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, Isaac Newton, and Francis Bacon.
- What were some of the major achievements of the Scientific Revolution?
Some of the major achievements of the Scientific Revolution include the development of the heliocentric model of The Solar System, the discovery of the laws of motion, and the development of the scientific method.
- What was the impact of the Scientific Revolution on the world?
The Scientific Revolution had a profound impact on the world, shaping the development of science, technology, and society for centuries to come.
Short Answers
- The Scientific Revolution was a time of great change and innovation in science.
- Some of the key figures of the Scientific Revolution include Nicolaus Copernicus, Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, Isaac Newton, and Francis Bacon.
- Some of the major achievements of the Scientific Revolution include the development of the heliocentric model of The Solar System, the discovery of the laws of motion, and the development of the scientific method.
- The Scientific Revolution had a profound impact on the world, shaping the development of science, technology, and society for centuries to come.
The following are multiple choice questions about the Enlightenment and Industrial Revolution:
The Enlightenment was a period of intellectual and philosophical change that began in the 17th century and lasted until the 19th century. It was characterized by a focus on reason, science, and progress. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Enlightenment?
(A) A focus on reason
(B) A focus on science
(C) A focus on tradition
(D) A focus on progressThe Industrial Revolution was a period of rapid social and economic change that began in Great Britain in the late 18th century and spread to other parts of Europe and North America in the 19th century. It was characterized by the development of new technologies, such as the steam engine, and the rise of factories. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the Industrial Revolution?
(A) The development of new technologies
(B) The rise of factories
(C) The growth of cities
(D) The decline of agricultureThe Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on the world. Which of the following is NOT an impact of the Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution?
(A) The rise of Democracy
(B) The rise of capitalism
(C) The rise of socialism
(D) The rise of CommunismThe Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution were both important events in world history. However, they were also very different events. Which of the following is NOT a difference between the Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution?
(A) The Enlightenment was a period of intellectual and philosophical change, while the Industrial Revolution was a period of social and economic change.
(B) The Enlightenment was primarily concerned with ideas, while the Industrial Revolution was primarily concerned with technology.
(C) The Enlightenment had a global impact, while the Industrial Revolution was primarily limited to Europe and North America.
(D) The Enlightenment had a positive impact on the world, while the Industrial Revolution had a negative impact on the world.The Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution were both important events in world history. However, they were also very complex events. Which of the following is NOT a complexity of the Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution?
(A) The Enlightenment was not a monolithic movement; there were many different Enlightenment thinkers with different ideas.
(B) The Industrial Revolution was not a smooth process; there were many ups and downs along the way.
(C) The Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution had both positive and negative impacts on the world.
(D) The Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution are still being debated by historians today.
The correct answers are:
1. (C)
2. (D)
3. (D)
4. (D)
5. (A)