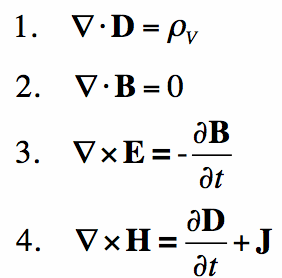<<–2/”>a >a href=”https://exam.pscnotes.com/electromagnetic-wave/”>Electromagnetic Wave
Electromagnetic Wave are waves composed of undulating electrical fields and magnetic fields. The different kinds of Electromagnetic Waves, such as Light and radio waves, form the electromagnetic spectrum. All electromagnetic waves have the same speed in a vacuum, a speed expressed by the letter c (the speed of light) and equal to about 186,000 miles (or 300,000 kilometers) per second. Electromagnetic Wave transport energy, due to oscillating electric and magnetic fields, Electromagnetic Waves are called electromagnetic radiation, light, or photons.
Maxwell‘s equations predicts the existence of electromagnetic waves that travel with speed of light c =1/ μ ? . The reason is due to the fact that a changing electric field produces a Magnetic Field and vice versa, and the coupling between the two fields leads to the generation of electromagnetic waves.
Four Maxwell equations are:-
In 1887, Heinrich Hertz generated and detected electromagnetic waves in his lab. The waves radiated from a transmitter circuit and were detected in a receiver circuit. Hertz used the fact that electrical circuits have resonant frequencies just like mechanical systems do.
A stationary charge produces an electric field.
A charge moving at constant speed produces electric and magnetic fields.
A charge that is accelerated will produce variable electric and magnetic fields. These are electromagnetic waves.,
Electromagnetic waves are waves of energy that travel through the universe. They are made up of an electric field and a magnetic field that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of travel. Electromagnetic waves can travel through the vacuum of space, and they can also travel through matter.
There are many different types of electromagnetic waves, each with its own wavelength and frequency. The different types of electromagnetic waves are classified into the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuum of all possible wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. The different types of electromagnetic waves are listed below, in order of increasing wavelength:
- Gamma rays
- X-rays
- Ultraviolet light
- Visible light
- Infrared light
- Microwaves
- Radio waves
The properties of electromagnetic waves depend on their wavelength. Longer wavelengths have lower frequencies and lower energies, while shorter wavelengths have higher frequencies and higher energies.
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and the highest energies. They are produced by nuclear reactions, such as those that occur in stars. X-rays have shorter wavelengths than gamma rays, but they still have high energies. They are produced by high-energy electrons colliding with matter. Ultraviolet light has shorter wavelengths than X-rays, but it still has high energies. It is produced by the sun and other hot objects. Visible light has wavelengths that are visible to the Human Eye. It is produced by many different sources, including the sun, fire, and light bulbs. Infrared light has longer wavelengths than visible light. It is produced by hot objects, such as the human body. Microwaves have even longer wavelengths than infrared light. They are used in microwave ovens and radar. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths of all electromagnetic waves. They are used in radio and television broadcasting.
Electromagnetic waves are used in many different technologies. They are used in Communication, such as radio, television, and cell phones. They are also used in medicine, such as X-rays and MRIs. And they are used in science, such as astronomy and particle physics.
Electromagnetic waves are a fundamental part of the universe. They are responsible for many of the phenomena that we see and experience every day. They are also a powerful tool that we can use to understand the universe and our place in it.
Here are some additional details about each type of electromagnetic wave:
- Gamma rays: Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and the highest energies of all electromagnetic waves. They are produced by nuclear reactions, such as those that occur in stars. Gamma rays can be harmful to living things, but they are also used in medicine to treat cancer.
- X-rays: X-rays have shorter wavelengths than gamma rays, but they still have high energies. They are produced by high-energy electrons colliding with matter. X-rays are used in medicine to diagnose diseases and in Industry to inspect materials.
- Ultraviolet light: Ultraviolet light has shorter wavelengths than X-rays, but it still has high energies. It is produced by the sun and other hot objects. Ultraviolet light can cause sunburn and skin cancer, but it is also used in medicine to treat certain skin conditions.
- Visible light: Visible light has wavelengths that are visible to the human eye. It is produced by many different sources, including the sun, fire, and light bulbs. Visible light is essential for life on Earth, as it is used by Plants to photosynthesize and by animals to see.
- Infrared light: Infrared light has longer wavelengths than visible light. It is produced by hot objects, such as the human body. Infrared light is used in remote controls, night vision goggles, and heat-seeking missiles.
- Microwaves: Microwaves have even longer wavelengths than infrared light. They are used in microwave ovens and radar. Microwaves are also used in telecommunications and in some medical applications.
- Radio waves: Radio waves have the longest wavelengths of all electromagnetic waves. They are used in radio and television broadcasting. Radio waves are also used in navigation, astronomy, and meteorology.
Electromagnetic waves are a fascinating and important part of the universe. They are responsible for many of the phenomena that we see and experience every day. They are also a powerful tool that we can use to understand the universe and our place in it.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that travels through space and matter in the form of waves. They are made up of electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other and to the direction of travel of the wave.
What are the different types of electromagnetic waves?
There are many different types of electromagnetic waves, each with its own wavelength and frequency. The most common types of electromagnetic waves are radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What are the characteristics of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves have a number of characteristics, including wavelength, frequency, speed, and energy. The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is the number of waves that pass a given point in a given amount of time. The speed of an electromagnetic wave is the speed at which it travels through space. The energy of an electromagnetic wave is related to its frequency.
What are some of the uses of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves have a wide variety of uses, including radio, television, radar, microwave ovens, lasers, and medical imaging.
What are some of the dangers of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves can be harmful to human Health if they are absorbed in high doses. The most common health effects of exposure to electromagnetic waves are cancer, reproductive problems, and neurological problems.
How can I protect myself from the dangers of electromagnetic waves?
There are a number of ways to protect yourself from the dangers of electromagnetic waves, including:
- Using a hands-free device when talking on a cell phone
- Keeping your cell phone away from your body when you are not using it
- Avoiding using cordless phones
- Unplugging appliances when you are not using them
- Keeping your distance from power lines and other sources of electromagnetic radiation
What is the future of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are a rapidly evolving field, with new discoveries being made all the time. The future of electromagnetic waves is likely to be one of continued innovation and progress.
Which of the following is not a type of electromagnetic wave?
(A) Radio waves
(B) Microwaves
(C) Infrared waves
(D) X-raysWhich of the following is the longest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation?
(A) Radio waves
(B) Microwaves
(C) Infrared waves
(D) Visible lightWhich of the following is the shortest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation?
(A) Radio waves
(B) Microwaves
(C) Infrared waves
(D) Gamma raysElectromagnetic waves are produced by the vibration of electric and magnetic fields.
(A) True
(B) FalseElectromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light.
(A) True
(B) FalseElectromagnetic
waves can be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe frequency of an electromagnetic wave is inversely proportional to its wavelength.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe energy of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its frequency.
(A) True
(B) FalseRadio waves are used for communication, television, and radar.
(A) True
(B) FalseMicrowaves are used for cooking, radar, and telecommunications.
(A) True
(B) FalseInfrared waves are used for night vision, remote controls, and heat therapy.
(A) True
(B) FalseVisible light is used for vision, Photosynthesis, and lasers.
(A) True
(B) FalseUltraviolet light is used for tanning, sterilization, and photography.
(A) True
(B) FalseX-rays are used for medical imaging, security, and crystallography.
(A) True
(B) FalseGamma rays are used for cancer treatment, industrial radiography, and astronomy.
(A) True
(B) False