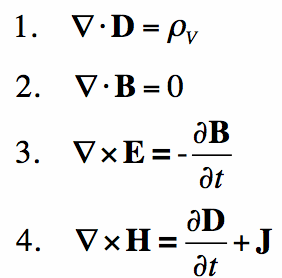Current Electricity
Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge through a conducting medium with respect to time. It is caused by drift of free electrons through a conductor to a particular direction.Charges in motion constitute an electric current. Such currents occur naturally in many situations. Lightning is one such phenomenon in which charges flow from the clouds to the earth through the Atmosphere, sometimes with disastrous results. The flow of charges in lightning is not steady, but in our everyday life we see many devices where charges flow in a steady manner. A torch and a cell-driven clock are examples of such devices. Conventionally, the direction of current is taken as the direction in which a positive charge moves. The electrons move in the opposite direction.
The current is the rate of flow of charge through a surface area placed perpendicular to the direction of flow. If charge ?q flows in time ?t, the Average current is defined as :
q I av = ———– t
Ohm’s Law:-
A basic law regarding flow of currents was discovered by G.S. Ohm in 1828. Imagine a conductor through which a current I is flowing and let V be the potential difference between the ends of the conductor. Then Ohm‘s law states that :- V? Ior, V = R I
Resistance and Resistivity :-Resistivity ? is an intrinsic property of a material and directly proportional to the total resistance R, an extrinsic quantity that depends on the length and cross-sectional area of a resistor.
The resistivity of a material is found to be dependent on the temperature. Different materials do not exhibit the same dependence on temperatures. Over a limited range of temperatures, that is not too large, the resistivity of a metallic conductor is approximately given by, ?(T) = ?(0) [1 + ? (T– T(0) )]
Series and Parallel circuits Resistance
A series circuit is a circuit in which resistors are arranged in a chain, so the current has only one path to take. The current is the same through each resistor. The total resistance of the circuit is found by simply adding up the resistance values of the individual resistors:
equivalent resistance of resistors in series : R = R1 + R2 + R3 + …
A parallel circuit is a circuit in which the resistors are arranged with their heads connected together, and their tails connected together. The current in a parallel circuit breaks up, with some flowing along each parallel branch and re-combining when the branches meet again. The voltage across each resistor in parallel is the same.
The total resistance of a set of resistors in parallel is found by adding up the reciprocals of the resistance values, and then taking the reciprocal of the total:
equivalent resistance of resistors in parallel: 1 / R = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3 +… Krichoff Rules:-
Kirchhoff’s junction rule states that the algebraic sum of the currents at any branch point or junction in a circuit is zero. Symbolically, we may write , below, as the sum of n currents flowing into a junction:
Kirchhoff’s second rule states that the algebraic sum of the potential changes around any complete loop in the Network is zero. Again we may write , symbolically ,as the sum of the potential changes:
Moving Charge and Magnetism
Magnetism is a phenomenon produced by the motion of electric charge, which results in attractive and repulsive forces between objects.
A magnet is any piece of material that has the property of attracting iron (or steel). Magnetite, also known as lodestone, is a naturally occurring rock that is a magnet. This natural magnet was first discovered in a region known as magnesia and was named after the area in which it was discovered. Magnetism may be naturally present in a material or the material may be artificially magnetized by various methods.
Magnets may be permanent or temporary. After being magnetized, a permanent magnet will retain the properties of magnetism indefinitely. A temporary magnet is a magnet made of soft iron, that is usually easy to magnetize; however, temporary magnets lose most of their magnetic properties when the magnetizing cause is discontinued. Permanent magnets are usually more difficult to magnetize, but they remain magnetized. Materials which can be magnetized are called ferromagnetic materials.
The force exerted on a charged particle by a Magnetic Field is given by the vector cross product: F = q ( v x B ) F = force (vector) q = charge on the particle (scalar) v = velocity of the particle relative to field (vector) B = magnetic field (vector)
Electromagnetic Wave are waves composed of undulating electrical fields and magnetic fields. The different kinds of Electromagnetic Waves, such as Light and radio waves, form the electromagnetic spectrum. All electromagnetic waves have the same speed in a vacuum, a speed expressed by the letter c (the speed of light) and equal to about 186,000 miles (or 300,000 kilometers) per second. Electromagnetic Wave transport energy, due to oscillating electric and magnetic fields, Electromagnetic Waves are called electromagnetic radiation, light, or photons.
Maxwell‘s equations predicts the existence of electromagnetic waves that travel with speed of light c =1/ μ ? . The reason is due to the fact that a changing electric field produces a magnetic field and vice versa, and the coupling between the two fields leads to the generation of electromagnetic waves.
The Biot-Savart law asserts that the magnetic field dB due to an element dl carrying a steady current i at a point P at a distance r from the current element is:
Four Maxwell equations are:-
In 1887, Heinrich Hertz generated and detected electromagnetic waves in his lab. The waves radiated from a transmitter circuit and were detected in a receiver circuit. Hertz used the fact that electrical circuits have resonant frequencies just like mechanical systems do.
A stationary charge produces an electric field.
A charge moving at constant speed produces electric and magnetic fields.
A charge that is accelerated will produce variable electric and magnetic fields. These are electromagnetic waves.,
Electricity and magnetism are two of the fundamental forces of nature. They are closely related, and together they form the basis of electromagnetism.
Electrostatics/”>Electrostatics is the study of electric charges at rest. Electric charges are of two types, positive and negative. Like charges repel each other, while unlike charges attract each other. Electric fields are created by electric charges. The electric field at a point is a measure of the force that would be exerted on a unit positive charge placed at that point.
Electric potential is the energy per unit charge possessed by a point charge in an electric field. The electric potential at a point is equal to the work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point.
Electric circuits are networks of electrical components that are used to control the flow of electric current. Electric current is the flow of electric charge. It is measured in amperes. Electric resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms. Electric inductance is the property of an electric circuit that opposes any change in the current flowing through it. It is measured in henrys. Electric capacitance is the property of an electric circuit that stores electric charge. It is measured in farads.
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electric current in a conductor by a changing magnetic field. Electromagnetic waves are waves that are produced by the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields. They travel at the speed of light.
Magnetism is the property of a material that attracts or repels other materials. Magnetic fields are created by moving electric charges. Magnetic materials are materials that are attracted to magnets. Magnetic domains are small regions within a magnetic material where the magnetic field is aligned. Magnetic flux is the total magnetic field passing through a surface. Magnetic permeability is a measure of how easily a material can be magnetized. Magnetic susceptibility is a measure of how strongly a material is magnetized. Magnetic hysteresis is the property of a magnetic material that retains some of its magnetization after the external magnetic field is removed.
Electromagnets are devices that use electricity to create a magnetic field. Permanent magnets are materials that have a permanent magnetic field. Electric motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Generators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Transformers are devices that transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another. Inductors are devices that store energy in a magnetic field. Capacitors are devices that store energy in an electric field. Resistors are devices that resist the flow of electric current.
Circuits are networks of electrical components that are used to control the flow of electric current. Circuit analysis is the study of how electric circuits work. Circuit design is the process of designing electric circuits. Circuit theory is the study of the mathematical properties of electric circuits.
Electronics is the study of the behavior and application of electrons. Electrical engineering is the field of engineering that deals with the design, construction, and operation of electrical systems. Electromagnetism is the study of the relationship between electricity and magnetism.
Electricity and magnetism are two of the most important forces in the universe. They are used in a wide variety of applications, from powering our homes and businesses to providing the technology for Communication and transportation.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about the topics of light, Sound, and waves:
Light
- What is light?
Light is a form of energy that travels in waves. It is made up of tiny particles called photons. - What are the different types of light?
There are two main types of light: visible light and invisible light. Visible light is the light that we can see with our eyes. Invisible light includes ultraviolet light, infrared light, and X-rays. - How does light travel?
Light travels in waves. The waves of light are very small, and they can travel through empty space. - What are the properties of light?
The properties of light include its wavelength, frequency, and speed. The wavelength of light is the distance between two peaks of a wave. The frequency of light is the number of waves that pass a point in a given amount of time. The speed of light is the speed at which light travels. - What are some examples of light?
Some examples of light include sunlight, candlelight, and light from a flashlight.
Sound
- What is sound?
Sound is a form of energy that travels in waves. It is made up of tiny vibrations that travel through the air. - What are the different types of sound?
There are two main types of sound: audible sound and inaudible sound. Audible sound is the sound that we can hear with our ears. Inaudible sound includes ultrasonic sound and infrasonic sound. - How does sound travel?
Sound travels in waves. The waves of sound are very small, and they can travel through air, water, and solid objects. - What are the properties of sound?
The properties of sound include its frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. The frequency of sound is the number of waves that pass a point in a given amount of time. The wavelength of sound is the distance between two peaks of a wave. The amplitude of sound is the height of a wave. - What are some examples of sound?
Some examples of sound include music, speech, and the sound of an animal.
Waves
- What is a wave?
A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium. The medium can be a solid, liquid, or gas. - What are the different types of waves?
There are two main types of waves: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves are waves that require a medium to travel through. Electromagnetic waves are waves that can travel through empty space. - How do waves travel?
Waves travel by transferring energy from one point to another. The energy is transferred by the motion of the particles in the medium. - What are the properties of waves?
The properties of waves include their wavelength, frequency, and speed. The wavelength of a wave is the distance between two peaks of a wave. The frequency of a wave is the number of waves that pass a point in a given amount of time. The speed of a wave is the speed at which the wave travels. - What are some examples of waves?
Some examples of waves include water waves, sound waves, and light waves.
Sure, here are some MCQs without mentioning the topic Electricity and Magnetism:
Which of the following is not a property of electricity?
(A) It can be generated by friction.
(B) It can be conducted through metals.
(C) It can be stored in batteries.
(D) It can be used to create light.Which of the following is not a property of magnetism?
(A) It can be attracted to iron.
(B) It can be used to create a magnetic field.
(C) It can be used to create electricity.
(D) It can be used to create a compass.What is the difference between electricity and magnetism?
(A) Electricity is a flow of electrons, while magnetism is a force that attracts or repels objects.
(B) Electricity is a force that attracts or repels objects, while magnetism is a flow of electrons.
(C) Electricity and magnetism are the same thing.
(D) Electricity and magnetism are two different forces that are not related to each other.What is a circuit?
(A) A circuit is a path that electricity flows through.
(B) A circuit is a device that converts electricity into another form of energy.
(C) A circuit is a device that stores electricity.
(D) A circuit is a device that generates electricity.What is a conductor?
(A) A conductor is a material that allows electricity to flow through it.
(B) A conductor is a material that does not allow electricity to flow through it.
(C) A conductor is a material that stores electricity.
(D) A conductor is a device that generates electricity.What is an insulator?
(A) An insulator is a material that allows electricity to flow through it.
(B) An insulator is a material that does not allow electricity to flow through it.
(C) An insulator is a material that stores electricity.
(D) An insulator is a device that generates electricity.What is a battery?
(A) A battery is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
(B) A battery is a device that stores electrical energy.
(C) A battery is a device that generates electrical energy.
(D) A battery is a device that conducts electricity.What is a Generator?
(A) A generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(B) A generator is a device that stores electrical energy.
(C) A generator is a device that generates electrical energy.
(D) A generator is a device that conducts electricity.What is a transformer?
(A) A transformer is a device that converts electrical energy from one voltage to another.
(B) A transformer is a device that stores electrical energy.
(C) A transformer is a device that generates electrical energy.
(D) A transformer is a device that conducts electricity.What is a light bulb?
(A) A light bulb is a device that converts electrical energy into light energy.
(B) A light bulb is a device that stores electrical energy.
(C) A light bulb is a device that generates electrical energy.
(D) A light bulb is a device that conducts electricity.
I hope these MCQs are helpful!