Education, education Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE and policy of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh has many institutes of higher education along with numerous primary and secondary schools. The government also implements Fee Reimbursement Scheme for the economically backwards sections of the state.
The regional and Official Language of Andhra Pradesh is Telugu. Other linguistic groups in the state include speakers of Urdu and Hindi. Andhra Pradesh Education is offered through a number of institutes spread across the state. In order to improve the Literacy rate among the masses and enhance the standard of education, the government of Andhra Pradesh has launched numerous projects and schemes. In Andhra Pradesh the education system is of 10+2 system before joining under graduation. First standard to Tenth standard classes are conducted by the School Education under the administration of the School Education Department and finally the Tenth Class (S.S.C.) Public examination at state level is conducted by the Board of Secondary Education, Hyderabad. After this two year Intermediate Education under the administration of the Board of Intermediate Education,AP,Hyderabad.
School Education
This state operates many state-run, as well as private schools, and this is the way state education is offered here. Government offers assistance to some private schools. Government schools include Mandal Praja Parishad, Zilla Parishad (ZP) or Municipal Schools. Classes taught as part of school education are primary classes, upper primary classes, secondary classes and high school classes. In order to bring an improvement in scenario related to education in state, government facilitates primary level education permeating all Society levels. Primary level education is offered free by the State Government for all students. As a result of all these initiatives, rate of literacy has increased substantially in past few years. Andhra Pradesh schools are either affiliated to CBSE or Central Board of Secondary Education or ICSE or state board.
Higher Education
For higher education facilities available in country, Andhra Pradesh is a highly sought after state. Quality education is offered to students coming not only from this state but different parts of the country. Some major institutions that offer high quality advanced education are NIT Warangal, Central University of Hyderabad, and SPA Vijayawada. These institutions are also renowned for conducting research work in various fields. Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University(s) (JNTU), Indian School of Business (ISB) and International Institute of Information Technology (IIIT) are some institutions that have gained a lot of acclaim globally for imparting high standard education to students.
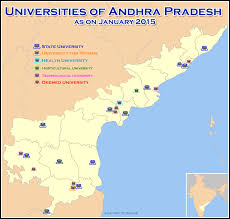
Universities in Andhra Pradesh
Highly experienced, and knowledgeable professors and lecturers have been offering their Services in Universities located in the state of Andhra Pradesh. Curriculum offered in Universities is updated and comprises of latest happenings in respective fields. In order to pursue higher education, students come to Andhra Pradesh Universities from all over the country and also from various offshore destinations. After completing studies from these colleges and institutions, students studying here can dream about a great future in their chosen field. Placements are also provided by many Universities by inviting some top notch companies for campus recruitments. Free scholarships are also offered by many Andhra Universities for students who excel in studies that help them to complete their studies without any hitch.
Some Distinguished Universities in this state are
- University of Hyderabad
- Andhra University
- Dravidian University
- B. R. Ambedkar Open University
Education policy of Andhra Pradesh
The Department of School Education is the largest among the 200 departments in the State. The department focuses on primary and secondary education and arranges to train teachers. The objectives of the Department of School Education are:
- Provide access to primary education for all children in the age group of 5-15 years.
- Ensure the enrollment of children in schools.
- Ensure that the children do not discontinue primary education.
- Maintain quality standards in education within the State.
- Provide mid-day meals to children in primary and upper primary schools that fall under the government, local bodies and aided managements.
- Provide free text books to children of classes I to V studying in the schools under the government, local bodies and aided managements.
- Provide free text books to all the children of classes VI to X belonging to Backward Classes (BC), Scheduled Caste (SC.) and Scheduled Tribe (ST.) studying in the schools under the government, local bodies and aided managements
- Provide training to the teachers to help them upgrade their knowledge and skills, thereby ensure quality in teaching.
The Department of Higher Education deals with matters relating to education at various levels in the State. The Higher Education Department in the State deals with higher education i.e., college education, technical education and universities. Objectives of the department are development of Undergraduate and Post graduate education, Increasing Access to Higher Education, encouraging private participation in the expansion of Collegiate Education, development of infrastructure in Government Colleges, ensuring maintenance of high standards of education in colleges.
Higher education is a tool for social progress. It cannot be viewed as an end in itself. The Government cannot promote a throwback to diehard attitudes of obscurantism and too many stagnant concepts. Society has to change positively as the world changes and adapts itself. Higher education must aim at the comprehensive development of the new generation.
- Confirm with the latest knowledge about various aspects of human life and to provide guidance and Leadership .
- Growing youth in traditional moral and intellectual characteristics and values as a cultured and enlightened young conductor to build strength.
Mission of the Department:
- Development of Undergraduate and Post Graduate Education.
- Increasing Access to Higher Education.
- Objectives in Higher Education for the under privileged sections of the society and Women, particularly in rural areas.
- Encouraging private participation in the expansion of Collegiate Education
- Development of infrastructure in Government Colleges.
,
Education in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh is a state in southern India. It is the seventh-largest state in India by area and the eighth-most populous state with over 85 million inhabitants. The state is bordered by Telangana to the north, Odisha to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the east, Karnataka to the south, Tamil Nadu to the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal to the east. The official language of Andhra Pradesh is Telugu.
The education system in Andhra Pradesh is divided into three levels: primary, secondary, and higher education. Primary education is compulsory for all children aged 6 to 14 years. Secondary education is for students aged 14 to 18 years. Higher education is for students aged 18 years and above.
The state government of Andhra Pradesh is responsible for the development and management of education in the state. The Department of School Education is responsible for the development and management of primary and secondary education. The Department of Higher Education is responsible for the development and management of higher education.
The state government of Andhra Pradesh has been making significant investments in education in recent years. The state has been building new schools, colleges, and universities. The state has also been providing scholarships and financial assistance to students.
The education system in Andhra Pradesh has been improving in recent years. The state has been ranked among the top states in India in terms of education. The state has also been ranked among the top states in India in terms of literacy rate.
Education infrastructure in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh has a well-developed education infrastructure. The state has a large number of schools, colleges, and universities. The state also has a number of research institutions and think tanks.
The state government of Andhra Pradesh has been making significant investments in education infrastructure in recent years. The state has been building new schools, colleges, and universities. The state has also been providing scholarships and financial assistance to students.
The education infrastructure in Andhra Pradesh is of good quality. The schools, colleges, and universities in the state are well-equipped with modern facilities. The teachers in the state are well-qualified and experienced.
Education policy in Andhra Pradesh
The education policy of Andhra Pradesh is designed to provide quality education to all children in the state. The policy aims to make education accessible to all children, irrespective of their social, economic, or religious background. The policy also aims to improve the quality of education in the state.
The education policy of Andhra Pradesh is implemented by the Department of School Education and the Department of Higher Education. The Department of School Education is responsible for the implementation of the policy at the primary and secondary levels. The Department of Higher Education is responsible for the implementation of the policy at the higher education level.
The education policy of Andhra Pradesh has been successful in achieving its objectives. The state has made significant progress in improving the quality of education in recent years. The state has also made significant progress in increasing access to education for all children.
Andhra Pradesh State Council of Higher Education
The Andhra Pradesh State Council of Higher Education (APSCHE) is a statutory body established by the Government of Andhra Pradesh in 1974. The APSCHE is responsible for the promotion and coordination of higher education in the state.
The APSCHE has the following functions:
- To advise the government on matters relating to higher education;
- To promote and coordinate higher education in the state;
- To establish and maintain institutions of higher education;
- To provide financial assistance to institutions of higher education;
- To regulate the admission of students to institutions of higher education;
- To conduct examinations for students of institutions of higher education;
- To award degrees and diplomas to students of institutions of higher education;
- To undertake research in higher education;
- To publish journals and other publications on higher education;
- To organize conferences and seminars on higher education;
- To provide consultancy services on higher education;
- To undertake any other activity that may be conducive to the promotion and development of higher education in the state.
The APSCHE is headed by a Chairman who is appointed by the Governor of Andhra Pradesh. The Chairman is assisted by a Vice-Chairman and a Registrar. The APSCHE has a Governing Council which consists of the Chairman, Vice-Chairman, Registrar, and other members nominated by the government.
The APSCHE has its headquarters in Hyderabad. The APSCHE has regional offices in Visakhapatnam, Vijayawada, and Tirupati.
Andhra Pradesh Open University
The Andhra Pradesh Open University (APOU) is a public university established by the Government of Andhra Pradesh in 1982. The APOU is the largest open university in India.
The APOU has the following objectives:
- To provide opportunities for higher education to all sections of society, irrespective of their age, sex, caste, creed, or religion;
- To promote lifelong
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about education in general:
What is education?
Education is the process of facilitating Learning, or the acquisition of knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, and habits. Educational methods include storytelling, discussion, teaching, training, and directed research. Education frequently takes place under the guidance of educators, but learners may also educate themselves. Education can take place in formal or informal settings and any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts may be considered educational. The methodology of teaching is called pedagogy.What are the different types of education?
There are many different types of education, including formal education, informal education, and non-formal education. Formal education is the most common type of education and it takes place in schools, colleges, and universities. Informal education is education that takes place outside of formal settings, such as through family, friends, or the media. Non-formal education is a type of education that is not as structured as formal education, but it is still more structured than informal education.What are the benefits of education?
There are many benefits to education, including improved job prospects, higher earnings, and better Health. Education can also help people develop critical thinking skills, become more civically engaged, and live longer, healthier lives.What are the challenges of education?
There are many challenges to education, including POVERTY, lack of access to education, and poor quality of education. Poverty can prevent people from accessing education, as they may not be able to afford the costs of education or they may not have the time to attend school. Lack of access to education is a problem in many parts of the world, as there are not enough schools or teachers to meet the demand for education. Poor quality of education is a problem in some countries, as schools may not have the Resources or the qualified teachers to provide a good education.What is the future of education?
The future of education is uncertain, but it is likely that there will be a number of changes in the way that education is delivered. Some of the changes that are likely to occur include the use of technology in education, the increasing importance of lifelong learning, and the need for education to be more flexible and responsive to the needs of the economy.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about education infrastructure:
What is education infrastructure?
Education infrastructure is the physical facilities that are used for education, such as schools, colleges, and universities. Education infrastructure also includes the equipment and technology that is used in education, such as computers, projectors, and whiteboards.What are the benefits of good education infrastructure?
Good education infrastructure can help to improve the quality of education, as it can provide students with access to the resources and technology that they need to learn. Good education infrastructure can also help to attract and retain qualified teachers, as it can provide them with a safe and comfortable working Environment.What are the challenges of education infrastructure?
One of the challenges of education infrastructure is the cost of building and maintaining schools and other educational facilities. Another challenge is the lack of access to education infrastructure in some parts of the world. This can be due to poverty, lack of resources, or political instability.What is the future of education infrastructure?
The future of education infrastructure is uncertain, but it is likely that there will be a number of changes in the way that education is delivered. Some of the changes that are likely to occur include the use of technology in education, the increasing importance of lifelong learning, and the need for education to be more flexible and responsive to the needs of the economy.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about education policy:
What is education policy?
Education policy is a set of laws, regulations, and guidelines that govern the education system in a country or state. Education policy can be used to achieve a variety of goals, such as improving the quality of education, increasing access to education, and reducing inequality in education.What are the different types of education policy?
There are many different types of education policy, including curriculum policy, teacher policy, and school finance policy. Curriculum policy is concerned with the content of education, such as what subjects are taught and how they are taught. Teacher policy is concerned with the qualifications and training of teachers. School finance policy is concerned with how Money is allocated to schools.What are the benefits of good education policy?
Good education policy can help to improve the quality of education, increase access to education, and reduce inequality in education. Good education policy can also help to attract and retain qualified teachers, as it can provide them with a safe and comfortable working environment.What are the challenges of education policy?
One of the challenges of education policy is the difficulty of achieving consensus on what constitutes good education policy. Another challenge is the difficulty of implementing education policy,
Sure. Here are some MCQs without mentioning the topic Education, education infrastructure and policy of Andhra Pradesh:
Which of the following is not a type of education?
(A) Formal education
(B) Informal education
(C) Non-formal education
(D) All of the aboveWhich of the following is not a goal of education?
(A) To develop the mind
(B) To prepare for EMPLOYMENT
(C) To instill values
(D) To make people happyWhich of the following is not a factor that affects education?
(A) The economy
(B) The government
(C) The family
(D) The weatherWhich of the following is not a right of all children?
(A) The right to education
(B) The right to food
(C) The right to health
(D) The right to a good timeWhich of the following is not a responsibility of all parents?
(A) To provide their children with education
(B) To provide their children with food
(C) To provide their children with health care
(D) To provide their children with a good timeWhich of the following is not a role of the government in education?
(A) To provide funding for education
(B) To set standards for education
(C) To regulate education
(D) To provide entertainment for studentsWhich of the following is not a role of teachers in education?
(A) To teach students
(B) To grade students
(C) To discipline students
(D) To entertain studentsWhich of the following is not a role of students in education?
(A) To learn
(B) To do their homework
(C) To take tests
(D) To have funWhich of the following is not a type of school?
(A) Elementary school
(B) Middle school
(C) High school
(D) DisneylandWhich of the following is not a type of teacher?
(A) Elementary school teacher
(B) Middle school teacher
(C) High school teacher
(D) Disneyland teacher
I hope these MCQs are helpful!