East West division of Himalayas
Kashmir Himalayas Kumaon Himalayas Nepal Himalayas Sikkim Himalaya Assam Himalayas
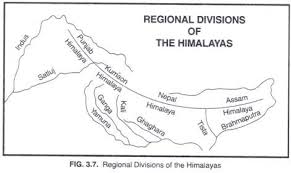
( Punjab Himalayas ) < [ satlaj – kali] < [ Kali – Kosi] < [ Kosi – Teesta] < [ Teesta- Dihang]
[ Indus – sutlaj] (Brahmaputra)
Classification of Himalayas on the basis of Geographic Location
- Punjab Himalayas / Kashmir Himalaya / Himachal Himalaya→ Between the Indus and Sutlej
- Kumaon Himalayas→ Between Sutlej and Kali rivers
- Nepal Himalayas→ Between Kali and Tista rivers
- Assam Himalayas→ Between Tista and Dihang rivers
Kashmir Himalayas
- Karakoram , ladakh , Zaskar , Pir panjal , Dhaula dhar
- Kashmir Himalayas also known as Punjab Himalayas and Himachal Himalayas .
- Zozila pass situated between Kashmir and ladakh .
- In this region have many vallelies , Dun and lakes .
- The general elevation falls westwards.
- All the major rivers of Indus river system flow through Punjab Himalayas.
Kumaon Himalayas
- Kumaon Himalayas is Located in uttarakhand .
- The middle Himalayas discontinuous ranges are present between Great Himalayas and shiwalik – in western side called as Garwal Himalayas and in eastern side its called as Kumaon Himalayas .
- There are many peaks in this region like Nanda devi , Kamet , Badirinath , Kedarnath , Gangotri ( sourse of ganga) all peaks are found in southern side of Great Himalayas .
- After deposition lakes becomes dry .When lakes are dry it called as Tal and that dry lakes are very fertile so some cities are developed on these dry lakes like – Nainital , Bhimtal etc.
Nepal Himalayas
- Nepal Himalayas are the tallest section in all over the ranges in Himalayas .
- Higher peaks in Nepal himalayas –
- IN Great Himalayas—– Dhaulagiri , Annapurna , Mansalu , Evert , Makalu ( or kanchanjanga) .
- Kathmandu valley – There are many river sources , which cross to tibet region and meets India.
- Like Kali river ,Karnali river comes through India , Nepal border and meet into India called Ganga river.
- Gandak aries in Nepal near Kathmandu
- Kosi pass from Nepal and meet india in Bihar its also known as sorrow of bihar.
Sikkim Himalayas
- It’s a very small range Kosi to Teesta river.
- Peak : kanchanjanga
- Teesta is originated near kanchanjanga.
- There is a very important pass that is ‘Jelep la pass’. This pass is a trijunction of India- China- Bhuta.
Assam Himalayas
- Himalayas narrower .
- Lesser Himalayas close to great Himalayas. Because the shiwalik rangae are almost disappear in this region of Himalayas .
- There are important peaks like – Namcha Barwa , Kula kangrl.
- There is a pass also knoen as Diphu pass ,that pass is located on the India , China , Myanmar trijunction .
- Bengal Duar’s :- called Gateways of Himalayas, in this region uplifted in sudden way and it is very narrow.
- Duar’s are hilly , weightier regions and High rainfall. Tea cultivation happened In this regions.
“Duns” formation
- Dunis a valley between the Himalayan foothills and the Siwalik Range to the south .
- After lakes are dry out when river find weak rocks to cut across the mountain . dry rivers are called DUNS .
- Dehradun between Shiwaliks and Masoorie range.
Karewas ( of Kashmir)
- Karewas in Kashmir valley are some 367 meters thick.
- Flat-topped terraces of Kashmir valley on flanks of Pir panjal. This region are very fertile . this fertile land are made up of clay , sand from old deltaic fans.
- Now a days in this fertile land are use for cultivation of Apple , Saffron , Rice (stable food of kashmie).
Significance of Himalayas for India
| Strategic significance | Acts as a natural frontier of India with other countries (China, Pakistan, Afghanistan) |
| Climatic significance | Prevent further northward movement of summer monsoon and also prevent cold northern winds from Siberia to enter into India |
| Agricultural significance | Rivers from Himalayas deposits a lot of sediment on its foothold, from which are formed India’s most fertile agricultural grounds known as Northern plains |
| Economic significance | Huge hydro-electric power potential of Himalayan rivers + Himalayan timber + Himalayan Herbs & Medicinal Plants |
| Tourism Significance | Comprises of Large ecological Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity, natural views & hill stations |
The East-West division of the Himalayas is a geographical division of the mountain range that runs along the northern border of India and Nepal. The eastern Himalayas are located in the Indian states of Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland, while the western Himalayas are located in the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Jammu and Kashmir. The two regions are separated by the Indus River.
The eastern Himalayas are characterized by their high peaks, deep valleys, and dense forests. The western Himalayas are lower in elevation and have a more arid Climate. The two regions are home to a diverse range of plant and animal life.
The East-West division of the Himalayas is important for a number of reasons. First, it is a major physical barrier between India and China. Second, it is a source of water for millions of people in both countries. Third, it is home to a number of important cultural and religious sites.
The East-West division of the Himalayas is also a major tourist destination. The region is home to a number of popular trekking and mountaineering destinations, as well as a number of beautiful lakes and temples.
Geography
The East-West division of the Himalayas is a major mountain range that runs along the northern border of India and Nepal. The eastern Himalayas are located in the Indian states of Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland, while the western Himalayas are located in the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Jammu and Kashmir. The two regions are separated by the Indus River.
The eastern Himalayas are characterized by their high peaks, deep valleys, and dense forests. The western Himalayas are lower in elevation and have a more arid climate. The two regions are home to a diverse range of plant and animal life.
Climate
The climate of the East-West division of the Himalayas varies depending on the elevation. The eastern Himalayas are located in the tropical climate zone, while the western Himalayas are located in the temperate climate zone. The eastern Himalayas receive more rainfall than the western Himalayas.
The Average temperature in the eastern Himalayas ranges from 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit) in the winter to 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit) in the summer. The average temperature in the western Himalayas ranges from 5 degrees Celsius (41 degrees Fahrenheit) in the winter to 25 degrees Celsius (77 degrees Fahrenheit) in the summer.
The East-West division of the Himalayas is home to a diverse range of plant and animal life. The eastern Himalayas are home to a number of tropical plants and animals, such as tigers, elephants, and rhinoceroses. The western Himalayas are home to a number of temperate plants and animals, such as snow leopards, yaks, and blue sheep.
Culture and religion
The East-West division of the Himalayas is home to a diverse range of cultures and religions. The eastern Himalayas are home to a number of Buddhist cultures, such as the Tibetan and Bhutanese cultures. The western Himalayas are home to a number of Hindu cultures, such as the Punjabi and Kashmiri cultures.
Tourism
The East-West division of the Himalayas is a major tourist destination. The region is home to a number of popular trekking and mountaineering destinations, as well as a number of beautiful lakes and temples. Some of the most popular tourist destinations in the East-West division of the Himalayas include:
- Mount Everest: The highest mountain in the world, Mount Everest is located in the eastern Himalayas.
- Kanchenjunga: The third highest mountain in the world, Kanchenjunga is located in the eastern Himalayas.
- Annapurna: The tenth highest mountain in the world, Annapurna is located in the western Himalayas.
- Nanda Devi: The seventh highest mountain in the world, Nanda Devi is located in the western Himalayas.
- Lake Tso Moriri: A beautiful lake located in the western Himalayas, Lake Tso Moriri is a popular tourist destination.
- Hemis Monastery: A Buddhist monastery located in the western Himalayas, Hemis Monastery is a popular tourist destination.
- Leh Palace: A palace located in the western Himalayas, Leh Palace is a popular tourist destination.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Himalayas, without mentioning the topic of East-West division:
What are the Himalayas?
The Himalayas are a mountain range in Asia that separates the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. They are the highest mountain range in the world, and include Mount Everest, the highest mountain on Earth.How did the Himalayas form?
The Himalayas formed as a result of the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates. The Indian plate is moving northward at a rate of about 4 centimeters per year, and is slowly colliding with the Eurasian plate. This collision has been happening for millions of years, and has resulted in the uplift of the Himalayas.What are the effects of the Himalayas on the climate?
The Himalayas have a significant effect on the climate of Asia. They block the flow of moisture from the Indian Ocean to the Tibetan Plateau, which results in a dry climate on the plateau. The Himalayas also cause the Indian monsoon, a seasonal wind that brings heavy rains to India.What are the effects of the Himalayas on the Environment?
The Himalayas are home to a wide variety of plants and animals. The mountain range is also a major source of water for many countries in Asia. The Himalayas are facing a number of environmental threats, including deforestation, Climate Change, and pollution.What are the cultural and historical significance of the Himalayas?
The Himalayas have been a major cultural and historical region for centuries. The mountain range is home to many different cultures, and has been a major trade route for centuries. The Himalayas are also a sacred place for many religions, including Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism, Buddhism-2/”>Buddhism, and Jainism.What are the challenges facing the Himalayas today?
The Himalayas are facing a number of challenges today, including deforestation, climate change, and pollution. Deforestation is a major problem in the Himalayas, as trees are cut down for timber and fuel. Climate change is also a major threat to the Himalayas, as it is causing Glaciers to melt and sea levels to rise. Pollution is also a problem in the Himalayas, as air and Water Pollution are caused by human activities.What are the efforts being made to protect the Himalayas?
There are a number of efforts being made to protect the Himalayas. These efforts include reforestation, Climate Change Mitigation, and pollution control. Reforestation is the process of planting trees to replace those that have been cut down. Climate change mitigation is the process of reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow the rate of climate change. Pollution control is the process of reducing air and water pollution.
Sure, here are some MCQs on the topics of the Himalayas, without mentioning the topic of the East-West division of the Himalayas:
The Himalayas are located in which continent?
(A) Asia
(B) Africa
(C) North America
(D) South AmericaThe Himalayas are the highest mountain range in the world. Which of the following is the highest mountain in the Himalayas?
(A) Mount Everest
(B) K2
(C) Kanchenjunga
(D) DhaulagiriThe Himalayas are a major source of water for many countries in Asia. Which of the following rivers originates in the Himalayas?
(A) The Ganges
(B) The Indus
(C) The Brahmaputra
(D) The YangtzeThe Himalayas are a major tourist destination. Which of the following is a popular tourist destination in the Himalayas?
(A) The Taj Mahal
(B) The Great Wall of China
(C) The Potala Palace
(D) The Everest Base CampThe Himalayas are a major source of biodiversity. Which of the following animals is found in the Himalayas?
(A) The snow leopard
(B) The red panda
(C) The Himalayan tahr
(D) The blue sheepThe Himalayas are a major source of hydroelectric power. Which of the following countries is a major producer of hydroelectric power from the Himalayas?
(A) India
(B) China
(C) Nepal
(D) BhutanThe Himalayas are a major source of natural Resources. Which of the following Natural Resources is found in the Himalayas?
(A) Coal
(B) Iron Ore
(C) Copper
(D) GoldThe Himalayas are a major barrier to transportation. Which of the following is a major transportation challenge in the Himalayas?
(A) Building roads
(B) Building railways
(C) Building Airports
(D) Building bridgesThe Himalayas are a major source of environmental challenges. Which of the following is an environmental challenge in the Himalayas?
(A) Deforestation
(B) Soil erosion
(C) Air Pollution
(D) Water pollutionThe Himalayas are a major source of cultural and religious significance. Which of the following is a major cultural and religious site in the Himalayas?
(A) The Taj Mahal
(B) The Great Wall of China
(C) The Potala Palace
(D) The Everest Base Camp