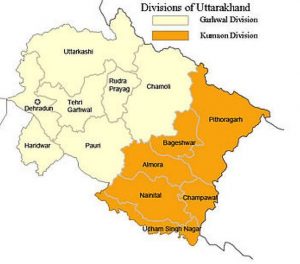
Divisions of Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand is divided into two administrative divisions.:
- Garhwal division
- Kumaon division
Listing of divisions and districts:
| Garhwal | · Chamoli · Dehradun · Haridwar · Pauri Garhwal · Rudraprayag · Tehri Garhwal · Uttarkashi | ||||||||
| Kumaon | · Almora · Bageshwar · Champawat · Pithoragarh · Nainital · Udham Singh Nagar | ||||||||
| Garhwal Division, Uttarakhand | |||||||||
| |||||||||
,
Uttarakhand is a state in India that was formed in 2000 by carving out the Himalayan hill regions of the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the west, Nepal to the east, China to the northeast, and Uttar Pradesh to the south. Uttarakhand is a popular tourist destination, known for its natural beauty, including the Himalayas, the Ganges River, and the Kedarnath Temple.
The state is divided into four divisions: Garhwal, Kumaon, Haridwar, and Dehradun.
Garhwal is the largest division in Uttarakhand, covering an area of 29,400 square kilometers. The capital of Garhwal is Srinagar. The division is home to the Garhwal Himalayas, which are part of the greater Himalayan mountain range. The Garhwal Himalayas are home to several peaks over 7,000 meters, including Nanda Devi, the second-highest peak in India. The division is also home to the Ganges River, which flows through the Garhwal Himalayas and is considered sacred by Hindus.
Kumaon is the second-largest division in Uttarakhand, covering an area of 23,000 square kilometers. The capital of Kumaon is Nainital. The division is home to the Kumaon Himalayas, which are part of the greater Himalayan mountain range. The Kumaon Himalayas are home to several peaks over 7,000 meters, including Nanda Devi, the second-highest peak in India. The division is also home to the Ganges River, which flows through the Kumaon Himalayas and is considered sacred by Hindus.
Haridwar is a district in the Garhwal division of Uttarakhand. The city of Haridwar is located on the banks of the Ganges River. Haridwar is a popular Hindu pilgrimage site, and is considered to be one of the holiest cities in India. The city is home to several temples and shrines, including the Har Ki Pauri, which is a ghat (riverbank) where Hindus believe that the Ganges River descends from heaven.
Dehradun is the capital of Uttarakhand. The city is located in the Doon Valley, which is a popular tourist destination. Dehradun is home to several universities, including the University of Dehradun and the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee. The city is also home to several temples and shrines, including the Tapkeshwar Mahadev Temple and the Mansa Devi Temple.
Uttarakhand is a beautiful and diverse state with a rich history and culture. The state is home to a variety of natural attractions, including the Himalayas, the Ganges River, and the Kedarnath Temple. Uttarakhand is also home to a number of historical and cultural sites, including the Haridwar and Dehradun.
What is Uttarakhand?
Uttarakhand is a state in northern India. It was formed on November 9, 2000, by carving out the Himalayan hill regions of the erstwhile state of Uttar Pradesh. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the west, Nepal to the east, China’s Tibet Autonomous Region to the north, and Uttar Pradesh to the south.
What is the capital of Uttarakhand?
The capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun. It is located in the Doon Valley, at an elevation of 700 meters (2,300 feet). Dehradun is a major educational and tourist destination.
What are the major cities of Uttarakhand?
The major cities of Uttarakhand are Dehradun, Haridwar, Rishikesh, Mussoorie, Nainital, Almora, and Pithoragarh.
What is the population of Uttarakhand?
The population of Uttarakhand is 10,116,752 (2011 census). The majority of the population is Hindu, followed by Muslim, Sikh, and Christian.
What is the language spoken in Uttarakhand?
The Official Language of Uttarakhand is Hindi. However, there are many other languages spoken in the state, including Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, and Bhoti.
What is the economy of Uttarakhand?
The economy of Uttarakhand is based on agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing. The main agricultural products are rice, wheat, sugarcane, and maize. The main tourist attractions are the Himalayas, the temples of Haridwar and Rishikesh, and the lakes of Nainital and Almora. The main manufacturing industries are textiles, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
What are the major challenges facing Uttarakhand?
The major challenges facing Uttarakhand are POVERTY, illiteracy, Unemployment, and Environmental Degradation. The state also faces the threat of natural disasters, such as Earthquakes and landslides.
What are the hopes and aspirations of the people of Uttarakhand?
The people of Uttarakhand hope for a better future for their state. They hope for more jobs, better Education, and better healthcare. They also hope for a more sustainable Environment.
Sure, here are some MCQs about Uttarakhand without mentioning the topic Divisions of Uttarakhand:
Uttarakhand is a state in northern India. It was formed on November 9, 2000, by carving out the Himalayan hill regions of Uttar Pradesh. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the northwest, China to the northeast, Nepal to the east, Uttar Pradesh to the south, and Madhya Pradesh to the southwest. The capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun.
Uttarakhand is a popular tourist destination, known for its Mountains, forests, and temples. The state is home to several national parks, including Jim Corbett National Park, Rajaji National Park, and Nanda Devi National Park.
The official language of Uttarakhand is Hindi. However, several other languages are spoken in the state, including Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, and Bhoti.
The economy of Uttarakhand is based on agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing. The state is a major producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, and potatoes.
Uttarakhand is a beautiful state with a rich history and culture. It is a popular tourist destination, and its economy is based on agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing.
Here are some MCQs about the geography of Uttarakhand:
The highest mountain in Uttarakhand is Nanda Devi. It is located in the Garhwal Himalayas and has an elevation of 7,816 meters (25,646 feet).
The largest river in Uttarakhand is the Ganges. It originates in the Garhwal Himalayas and flows through the state before entering the plains of India.
The capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun. It is located in the Doon Valley in the Garhwal Himalayas.
The population of Uttarakhand is approximately 10 million people. The majority of the population is Hindu, followed by Muslim and Sikh.
The Climate of Uttarakhand varies from temperate to alpine. The temperature ranges from 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit) in the winter to 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit) in the summer.
Here are some MCQs about the history of Uttarakhand:
The history of Uttarakhand can be traced back to the 6th century BC. The region was ruled by several different dynasties, including the Guptas, the Kushans, and The Palas.
In the 12th century, the region was conquered by the Gurjara-Pratiharas. The Gurjara-Pratiharas were a powerful dynasty that ruled over much of northern India.
In the 13th century, the region was invaded by the Mongols. The Mongols were a nomadic people from Central Asia who conquered much of Asia.
In the 16th century, the region was conquered by the Mughals. The Mughals were a powerful dynasty that ruled over much of India.
In the 18th century, the region was ruled by the Gorkhas. The Gorkhas were a Nepalese people who conquered much of the Himalayas.
In the 19th century, the region was ruled by the British. The British were a colonial power that ruled over much of India.
In 1947, India gained independence from the British. The region of Uttarakhand was part of the state of Uttar Pradesh.
In 2000, the state of Uttarakhand was formed. The state was carved out of the Himalayan hill regions of Uttar Pradesh.
Here are some MCQs about the culture of Uttarakhand:
The culture of Uttarakhand is a mix of Hindu, Muslim, and Sikh traditions.
The people of Uttarakhand are known for their hospitality and their love of music and dance.
The cuisine of Uttarakhand is based on rice, wheat, and lentils.
The festivals of Uttarakhand include Holi, Diwali, and Dussehra.
The art and architecture of Uttarakhand is influenced by Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism and Buddhism-2/”>Buddhism.