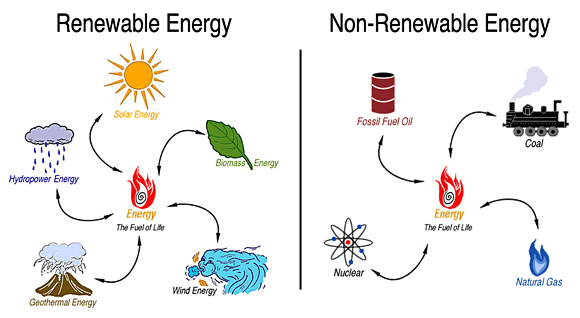
Conventional and Non Conventional Sources of Energy
Main Sources of Energy:
The sources of energy are of following types:
- Conventional Sources of Energy:
These sources of energy are also called non renewable sources. These sources of energy are in limited quantity except hydro-electric power.
(a) Coal and Lignite:
Coal is the major Source Of Energy. Coal deposits in India are 148790 million tonnes. Total lignite reserves found at Neyveli are 3300 million tonnes. In 1950-51, annual production of coal was 32 million tonnes. In 2005-06, annual production of coal was 343 million tonnes.
Lignite production was 20.44 million tonnes in 2005-06. According to an estimate, coal reserves in India would last about 130 years. India is now the fourth largest coal producing country in the world. Coal deposits are mainly found in Orissa, Bihar, Bengal and Madhya Pradesh. It provides EMPLOYMENT to 7 lakh workers.
(b) Oil and Natural Gas:
In India it is found in upper Assam, Mumbai High and in Gujarat. The Resources of oil are small in India.
In 1950-51, the total production of oil in India was 0.3 million tonnes. It increased to 32.4 million tonnes in 2000-01. Despite tremendous increase in oil production. India still imports 70% of has oil requirements from abroad. In 1951, there was only one oil refinery in Assam.
After independence 13 such refineries were set up in public sector and their refining capacity was 604 lakh tonnes. After implementation of Economic Reforms, private refineries are also engaged in oil refining. As per current rate of consumption, oil reserves in India may last about 20 to 25 years.
Electricity
There are three main sources of power generation:
- Thermal Power
- Hydro-electric power
- Nuclear Power
- Thermal Power:
It is generated in India at various power stations with the help of coal and oil. It has been a major source of electric power. In 2004-05, its share in total installed capacity was 70 percent.
- Hydro electric Power:
It is produced by constructing Dams over overflowing rivers. For example Bhakra Nangal Project, Damodor Valley Project and Hirakund Project etc. In 1950-51, installed capacity of hydro-electricity was 587.4 MW and in 2004-05, it was 19600 MW.
- Nuclear Power:
India has also developed nuclear power. Nuclear Power Plants use uranium as fuel. This fuel is cheaper than coal. India has nuclear power plants at Tarapur, Kota (Rajasthan) Kalapakam (Chennai) Naroura (UP). Its supply accounts for only 3 percent of the total installed capacity.
POWER FROM NON CONVENTIONAL ENERGY
India is one of the fastest growing countries in terms of energy consumption. Currently, it is the fifth largest consumer of energy in the world, and will be the third largest by 2030. At the same time; the country is heavily dependent on fossil sources of energy for most of its demand. This has necessitated the country to start aggressively pursuing alternative energy sources – solar, wind, biofuels, small hydro and more.
India‘s wind power potential has been assessed at 48500 MW. The current technical potential is estimated at about 13 000 MW, assuming 20% grid penetration, which would increase with the augmentation of grid capacity in potential states. The state-wise gross and technical potentials are given below India is implementing the world’s largest wind resource assessment program comprising wind monitoring, wind mapping and complex terrain projects.
- Hydro Energy
Hydro Power is the largest RENEWABLE ENERGY resource being used for the generation of electricity. The 50,000 MW hydro initiatives have been already launched and are being vigorously pursued with DPRs for projects of 33,000 MW capacity already under preparation. Harnessing hydro potential speedily will also facilitate Economic Development of States, particularly North-Eastern States, Sikkim, Uttaranchal, Himachal Pradesh and J&K, since a large proportion of our hydro power potential islocated in these States. In India, hydro power projects with a station capacity of up to 25 megawatt (MW) each fall under the category of small hydro power (SHP).
India is a solar rich country. India is a country near the equator – which means that given its geographical location, it is subject to a large amount of solar radiation throughout the year. India is also, according to area, the 7th largest country in the world.
The Average solar radiation received by most parts of India range from about 4 to 7 kilowatt hours per meter square per day, with about 250-300 sunny days in a year. As can be seen from the solar radiation map above, the highest annual solar radiation is received by Rajasthan (desert area) and the lowest by the North eastern states of India.
- Biomass/”>Biomass energy
Globally, India is in the fourth position in generating power through biomass and with a huge potential, is poised to become a world leader in the utilization of biomass. Biomass power projects with an aggregate capacity of 773.3 MW through over 100 projects have been installed in the country. For the last 15 years, biomass power has become an Industry attracting annual Investment of over Rs. 1,000 billion, generating more than 09 billion unit of electricity per year. More than 540 million tons of crop and plantation residues are produced every year in India and a large portion is either wasted, or used inefficiently.
- E) Energy from Wastes: The rising piles of garbage in urban areas caused by rapid Urbanization and industrialization throughout India represent another source of nonconventional energy. An estimated 50 million tones of solid waste and approximately 6,000 million cubic meters of liquid waste are generated annually in the urban areas of India. Good potential exists for generating approximately 2,600 MW of power from urban and municipal wastes and approximately 1,300 MW from industrial wastes in India. A total of 48 projects with aggregate capacity of about 69.62 MWeq have been installed in the country thereby utilising only 1.8% of the potential that exists.
- F) Biofuels: The GOI recently mandated the blending of 10 percent fuel ethanol in 90 percent gasoline. This mandate as created an approximately 3.6 billionliter demand for fuel ethanol in blend mandate to the entire country. This significant demand Growth creates a tremendous manufacturing opportunity for the fuel ethanol industry seeking to expand its investments internationally
,
Hydropower
Hydropower is a form of energy that harnesses the power of moving water to generate electricity. It is the most widely used renewable energy source in the world, accounting for about 16% of global electricity generation.
There are three main types of hydropower: run-of-river, pumped-storage, and storage. Run-of-river hydropower uses the natural flow of a river to generate electricity. Pumped-storage hydropower uses two reservoirs, one at a higher elevation than the other. During periods of low demand, electricity is used to pump water from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir. During periods of high demand, the water is released from the upper reservoir, driving a turbine to generate electricity. Storage hydropower uses a reservoir to store water during periods of low demand and release it during periods of high demand.
Hydropower has a number of advantages over other forms of energy. It is a renewable energy source, meaning that it will never run out. It is also a low-carbon energy source, meaning that it does not contribute to Climate change. Hydropower is also a reliable energy source, as it can be generated 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
However, hydropower also has some disadvantages. One of the biggest disadvantages is that it can have a significant impact on the Environment. Dams can disrupt the flow of rivers, which can impact fish populations and other wildlife. Dams can also cause flooding and erosion.
Another disadvantage of hydropower is that it can be expensive to build and maintain. Dams are large and complex structures, and they require regular maintenance to ensure that they are safe and operating properly.
Despite its disadvantages, hydropower is a valuable source of energy. It is a renewable, low-carbon, and reliable source of energy. However, it is important to carefully consider the environmental and social impacts of hydropower projects before they are built.
Non-conventional sources of energy
Non-conventional sources of energy are those that do not come from traditional sources such as coal, oil, or natural gas. These sources include solar energy, wind energy, Geothermal Energy, biomass energy, Wave energy, Tidal energy, and Ocean Thermal Energy conversion (OTEC).
Solar energy is the most abundant source of energy on Earth. It can be used to generate electricity, heat water, and power vehicles. Wind energy is another clean and renewable source of energy. Wind turbines can be used to generate electricity, and wind farms can be built in many parts of the world. Geothermal energy is heat that comes from the Earth’s interior. It can be used to generate electricity, heat homes and businesses, and provide hot water. Biomass energy is energy that comes from plants and other organic materials. It can be used to generate electricity, produce heat, and make transportation fuels. Wave energy is the energy of ocean waves. It can be used to generate electricity, power desalination plants, and provide transportation. Tidal energy is the energy of ocean tides. It can be used to generate electricity, power desalination plants, and provide transportation. OTEC is a technology that uses the temperature difference between the surface and deep ocean waters to generate electricity.
Non-conventional sources of energy have a number of advantages over traditional sources of energy. They are renewable, meaning that they will never run out. They are also low-carbon, meaning that they do not contribute to Climate Change. Non-conventional sources of energy are also becoming more affordable as technology improves.
However, non-conventional sources of energy also have some disadvantages. They can be intermittent, meaning that they do not always produce energy. They can also be difficult to store. Additionally, some non-conventional sources of energy, such as wind and solar energy, can have a visual impact on the landscape.
Despite their disadvantages, non-conventional sources of energy are an important part of the future of energy. They are clean, renewable, and low-carbon, and they have the potential to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
What is hydro power?
Hydro power is a form of energy that harnesses the power of moving water. It is a renewable energy source that can be used to generate electricity, pump water, and grind grain.
How does hydro power work?
Hydro power works by using the force of moving water to turn a turbine. The turbine is connected to a Generator, which produces electricity. The amount of electricity that can be generated depends on the size of the turbine and the amount of water that is flowing.
What are the benefits of hydro power?
Hydro power is a renewable energy source that does not produce greenhouse gases. It is also a reliable source of energy, as the amount of water that is available for hydropower generation is relatively constant.
What are the drawbacks of hydro power?
Hydro power can have a negative impact on the environment. The construction of dams can disrupt the flow of rivers and streams, which can harm fish and other wildlife. Dams can also displace people who live in the area.
What is non-conventional energy?
Non-conventional energy is a term used to describe energy sources that are not commonly used, such as solar power, wind power, and geothermal power. Non-conventional energy sources are often considered to be renewable energy sources, as they do not produce greenhouse gases.
What are the benefits of non-conventional energy?
Non-conventional energy sources are renewable and do not produce greenhouse gases. They can also help to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
What are the drawbacks of non-conventional energy?
Non-conventional energy sources can be expensive to develop and install. They can also be intermittent, meaning that they do not always produce power when it is needed.
What is the future of energy?
The future of energy is likely to be a mix of conventional and non-conventional energy sources. As non-conventional energy sources become more affordable and efficient, they are likely to play a larger role in our energy mix.
Which of the following is not a non-conventional source of energy?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear EnergyWhich of the following is the most common source of energy in the world?
(A) Coal
(B) Oil
(C) Natural gas
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the cleanest source of energy?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the most expensive source of energy?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the most reliable source of energy?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the most sustainable source of energy?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the most environmentally friendly source of energy?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the most efficient source of energy?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the most widely used source of energy in the United States?
(A) Coal
(B) Oil
(C) Natural gas
(D) Nuclear energyWhich of the following is the most likely source of energy to replace fossil fuels in the future?
(A) Solar energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Hydro power
(D) Nuclear energy