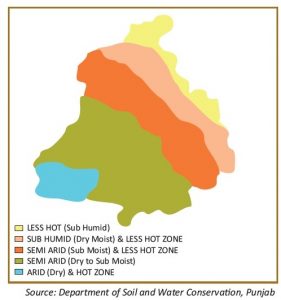
Climate of Punjab:-
Introduction:-
Climate can be defined as the Average weather experienced by a region over a period of time. There are various deciding factors for climatic changes like Precipitation, temperature, clouds, wind and sunshine. Climate governs the various factors like Economic Development, clothing, food habits, cultural and social living of the region.
Punjab is situated in the North-Eastern part of India. The Punjab Climate is determined by the extreme hot and extreme cold conditions. The region lying near the foot hills of Himalayas receive heavy rainfall whereas the region lying at a distant from the hills, the rainfall is scanty and the temperature is high. Punjab Climate comprises of three seasons. They are the summer months that spans from mid April to the end of June. The rainy season in Punjab is from the months of early July to end of September. The winter season in Punjab is experienced during the months of early December to the end of February. The transitional Seasons in Punjab are the post monsoon season and the post winter season. Summer in Punjab actually commences from mid April. But the temperature starts rising from February onwards. The summer months are followed by the rainy seasons. Generally, the rainy season in Punjab begins in the first weeks of July. It ranges from 250mm to 1000mm. The agriculture of the state highly depends on the rains. The monsoon is brought by the monsoonal winds blowing over the Bay of Bengal. The winter season in Punjab is mostly experienced in the month of January, when the temperature falls to 5 degree in the night and it is around 12 degree in the morning. The post monsoonal transitional season remains quite fair and dry. In the post winter transitional season, hail storms and brief showers occur which causes damage to the crops. During the end of the March, the wind becomes dry. The Punjab Climate has been a great factor in contributing to the economy of the state.
Climate of Punjab is tropical , semi arid, hot and subtropical monsoon type with cold winter and hot summer. State experience four seasons Cold Season from November to March, hot season from April to June, Monsoon season from last week of June to the first week of September and post monsoon or transition season from Sept till beginning of November. Hot season i.e April to June weather is relatively dry and uncomfortable. Weather tends to be humid during July –September due to increased moisture contents in the air, However these months are comfortable due reduced day temperature.
Seasons:-
Punjab state experiences three main seasons. They are:
- Hot Season (mid-April to the end of June)
- Rainy Season ( early July to the end of September)
- Cold Season (early December to the end of February)
Apart from these three main seasons, the state also experiences transitional seasons like:
- Pre-summer season (Mar to mid of April): This is the period of transition between winter and summer season.
- Post-monsoon season (Sep to Nov end). This is the period of transition between monsoon and winter season.
Summer Season:-
The area starts experiencing mild hot temperature from February month. However, actual summer season commences from mid of April. The area experiences pressure variations during summer months. The Atmospheric Pressure of the region remains at 987 mili bars during February month and it touches 970 mili bars in June.
Rainy Season:-
Monsoon brings joy to the agriculture field as it is the time when farmers become very busy. Monsoon in the state begins in first week of July and it is the monsoon currents generated in Bay of Bengal which brings rain in the region.
Winter Season:-
Temperature variation is minimal in January month. The mean night and day temperature fall to 5oC and 12oC respectively. Winter season in northern part are blight for the poor who cannot arrange for protection against cold climate. However, the wealthy people thoroughly enjoy winter climate.
Post-Monsoon Transitional Season:-
Monsoon begins to reduce by the second week of September. This brings in a gradual change in climate and temperature. The period between October and November is the transitional period between monsoon and winter seasons. Weather during this period is generally fair and dry.
Post-Winter Transitional Season:-
The effect of winter season diminishes by the first week of March. Hot summer season commences from mid April. This period is marked by occasional showers with hail storm and squalls which causes extensive damage to crops. The winds remain dry and warm during the last week of March commencing the harvest period.
Temperature:-
The geographical and sub-tropical latitudinal location of Punjab makes large variation in temperature from month to month. Even though only limited region experience temperature below 0o C, ground frost is commonly found in majority of the areas in winter season. The temperature rises gradually with high presence of moisture and overcast sky. However, the rise in temperature is steep when sky is clear and moisture content is very less in air.
The mid May and June months records the maximum temperature. The temperature remains above 40oC in the entire region during this period. Ludhiana recorded the highest maximum temperature at 46.1oC with Patiala and Amritsar recording 45.5o C. The maximum temperature during the summer months in Ludhiana remains above 41o C for a duration of one and a half months. These areas experience lowest temperature during the January month. The sun rays are oblique during these months and the Cold Winds control the rise temperature at day time.
Punjab state experiences minimum temperature during December to February months. The lowest temperature was recorded at Amritsar (0.2o C) and Ludhiana stood second with 0.5oC. The minimum temperature of the region remains below 5oC for almost two months during the winter season. The highest minimum temperature of these regions in the June month is more than the day temperatures experienced in the Jan and Feb month. Ludhiana experiences minimum temperature above 27o C for more than two months. The annual average temperature in the entire state is approximately 21oC. Further, the mean monthly temperature range varies between 9oC in July to approximately 18oC in Nov month.
Rainfall:-
The total rainfall received by the state ranges between 250 mm and 1000 mm. The regions near the Shivalik Hills experience the maximum and deserts in the west receive the minimum rainfall. The south west Monsoon Winds bring bulk of rainfall in the state which lasts for three months between July to September. The remaining occasional rainfall is received during winter months. Rainfall experienced by various parts of the state indicates a varying trend. The hilly regions receive rainfall more than 1000 mm. Ropar, Hoshiarpur, Gurdaspur and parts of the eastern Patiala region receives rainfall above 750 mm. Almost all the remaining areas receive rainfall in the range of 500 mm. The extreme west region of the state receives rainfall below 250 mm.
Monsoon Rainfall:-
Monsoon season provides most of the rainfall for the region. Punjab region receives rainfall through the monsoon current of the Bay of Bengal. This monsoon current enters Punjab state through the south-east direction in the first week of Jul.
Winter Rainfall:-
The winter season remains very cool with temperature going down below zero degree at some places. Winter season also brings in some western disturbances. The rainfall in winter season provides relief to the farmers as some of the winter crops in the region of Shivalik Hills are entirely dependent on this rainfall. As per the meteorological statistics, the sub-Shivalik area receives more than hundred mm rainfall in the winter months.
Current scenario:-
Punjab has begun experiencing impacts of Climate Change and urgent steps are needed to help farming communities adapt to this. To begin with, a project is underway to utilize paddy straw for making briquettes which can be used to replace coal in brick kilns. Another adaptation projects relate to management of indigenous Livestock facing heat Stress.
,
The climate of Punjab is a temperate climate with hot summers and cold winters. The average temperature in Punjab ranges from 10 degrees Celsius in winter to 40 degrees Celsius in summer. The annual rainfall in Punjab is about 700 mm. The monsoon rains are the main source of rainfall in Punjab. The climate of Punjab is suitable for agriculture. The main crops grown in Punjab are wheat, rice, Cotton, and sugarcane.
Temperature
The temperature in Punjab varies greatly throughout the year. The summers are hot and humid, with temperatures often reaching above 40 degrees Celsius. The winters are cold and dry, with temperatures often dropping below 10 degrees Celsius.
Rainfall
The annual rainfall in Punjab is about 700 mm. The monsoon rains are the main source of rainfall in Punjab. The monsoon rains usually start in June and last until September. The monsoon rains are essential for agriculture in Punjab.
Monsoon
The monsoon is a seasonal wind that blows from the southwest to the northeast across the Indian subcontinent. The monsoon rains are caused by the difference in temperature between the land and the ocean. The land heats up faster than the ocean, causing the air to rise. The rising air creates an area of low pressure, which draws in moist air from the ocean. The moist air rises and cools, causing the water vapor to condense and fall as rain.
Agriculture
The climate of Punjab is suitable for agriculture. The main crops grown in Punjab are wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane. Wheat is the most important crop in Punjab. It is grown in the winter season. Rice is the second most important crop in Punjab. It is grown in the summer season. Cotton is grown in the summer season. Sugarcane is grown in the winter season.
Crops
The main crops grown in Punjab are wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane. Wheat is the most important crop in Punjab. It is a staple food in Punjab. Rice is the second most important crop in Punjab. It is also a staple food in Punjab. Cotton is grown for its fiber. Sugarcane is grown for its sugar.
The climate of Punjab is a major factor in the success of agriculture in the region. The temperate climate with hot summers and cold winters is ideal for growing a variety of crops. The annual rainfall of about 700 mm is also sufficient for agriculture. The monsoon rains are the main source of rainfall in Punjab, and they are essential for the Growth of crops. The climate of Punjab is also suitable for livestock farming. The region is home to a variety of livestock, including cattle, buffalo, sheep, and goats. The livestock Industry is an important part of the economy of Punjab.
Here are some frequently asked questions about climate change:
What is climate change?
Climate change is the long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns in a place. Climate change could refer to a particular location or the planet as a whole. Climate change may cause weather patterns to be less predictable. A region might experience lower or higher than average temperatures. Climate change may cause more frequent and severe weather events, such as storms, floods and droughts.What are the Causes of Climate Change?
The main cause of climate change is human activity. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and gas, releases greenhouse gases into the Atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun, which warms the planet. Other human activities that contribute to climate change include deforestation, agriculture and industrial processes.What are the effects of climate change?
Climate change is already having a significant impact on the planet. The average global temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius since the late 19th century. This warming is causing the ice caps to melt, sea levels to rise and extreme weather events to become more common. Climate change is also having a negative impact on human Health, agriculture and Ecosystems.What can be done to address climate change?
There are a number of things that can be done to address climate change. These include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in RENEWABLE ENERGY sources, improving Energy Efficiency and protecting forests. Individuals can also help to address climate change by making changes to their own lifestyles, such as driving less, using less energy and eating less meat.What is the future of climate change?
The future of climate change depends on the actions that we take to address it. If we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the planet will continue to warm. This could lead to more extreme weather events, sea level rise and a decline in Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity. However, if we take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we can limit the Impact Of Climate Change and build a more sustainable future.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Environment:
What is the environment?
The environment is the natural world that surrounds us. It includes the air we breathe, the water we drink, the food we eat and the land we live on. The environment is essential for our survival. It provides us with the Resources we need to live, such as food, water and shelter. It also regulates the climate and provides us with a place to live, work and play.What are the main environmental problems?
The main environmental problems are climate change, pollution, deforestation, overfishing and biodiversity loss. Climate change is caused by the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, which causes the planet to warm. Pollution is caused by the release of harmful substances into the environment. These substances can cause air, water and land pollution. Deforestation is the clearing of forests. This can lead to Soil erosion, flooding and climate change. Overfishing is the catching of too many fish. This can lead to the collapse of fish populations. Biodiversity loss is the decline in the variety of life on Earth. This can be caused by habitat loss, pollution and climate change.What can be done to solve environmental problems?
There are a number of things that can be done to solve environmental problems. These include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency and protecting forests. Individuals can also help to solve environmental problems by making changes to their own lifestyles, such as driving less, using less energy and eating less meat.What is the future of the environment?
The future of the environment depends on the actions that we take to protect it. If we do not take action to reduce pollution, deforestation and overfishing, the environment will continue to decline. This could lead to climate change, food shortages, water shortages and the extinction of many species. However, if we take action to protect the environment, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and for future generations.
Sure. Here are some MCQs on the topics of climate, weather, and seasons:
Which of the following is not a type of climate?
(A) Tropical
(B) Temperate
(C) Polar
(D) Climate changeWhich of the following is not a type of weather?
(A) Sunny
(B) Rainy
(C) Snowy
(D) Climate changeWhich of the following is not a season?
(A) Spring
(B) Summer
(C) Fall
(D) Climate changeThe climate of a place is determined by its:
(A) Location
(B) Elevation
(C) Distance from the ocean
(D) All of the aboveThe weather of a place is determined by its:
(A) Temperature
(B) Humidity
(C) Wind speed
(D) All of the aboveThe seasons are determined by the Earth’s tilt on its axis and its orbit around the sun.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe Earth’s climate is changing due to human activity.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe main cause of climate change is the burning of fossil fuels.
(A) True
(B) FalseClimate change is causing the Earth’s temperature to rise.
(A) True
(B) FalseClimate change is causing the Earth’s ice caps to melt.
(A) True
(B) FalseClimate change is causing the Earth’s sea levels to rise.
(A) True
(B) FalseClimate change is causing the Earth’s weather patterns to become more extreme.
(A) True
(B) FalseClimate change is a serious threat to the planet.
(A) True
(B) FalseWe need to take action to address climate change.
(A) True
(B) FalseWe can reduce our impact on climate change by reducing our reliance on fossil fuels, using energy more efficiently, and planting trees.
(A) True
(B) False