&<–2/”>a >nbsp;
- Computer Classification: By Size and Power
Computers differ based on their data processing abilities. They are classified according to purpose, data handling and functionality.
According to functionality, computers are classified as:
- Analog Computer: A computer that represents numbers by some continuously variable physical quantity, whose variations mimic the properties of some system being modeled.
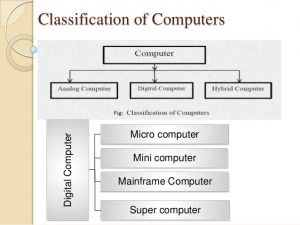
- Personal computer: A personal computeris a computer small and low cost. The term”personal computer” is used to describe desktop computers (desktops).
- Workstation: A terminal or desktop computer in a Network. In this context, workstation is just a generic term for a user’s machine (client machine) in contrast to a “server” or “mainframe.”
- Minicomputer: A minicomputer isn’t very mini. At least, not in the way most of us think of mini. You know how big the personal computer is and its related family.
- Mainframe: It refers to the kind of large computer that runs an entire corporation.
- Supercomputer: Itis the biggest, fastest, and most expensive computers on earth.
- Microcomputer: A personal computer is a
According to purpose or functionality, computers are classified as general purpose and special purpose computers. General purpose computers solve large variety of problems.They are said to be multi purpose for they perform a wide range of tasks. Examples of general purpose computer include desktop and laptops.
On the other hand,special purpose computers solve only specific problems.They are dedicated to perform only particular tasks.Examples of special purpose computers can include calculators and Money counting machine.
Generation of Digital Computers
According to age,computers are grouped in terms of generations. They include;1st generation computers,2nd generation computers,3rd generation computers,4th generation computers, and finally 5th generation.
1st generation computers.This is a generation of computers that were discovered between the years 1946 and 1957.These computers had the following characteristics: They used vacuum tubes for circuiting.They used magnetic drums as memory for data processing.Their operating system was quite low as compared to the later generations.An operating system can be defined as a collection of programs designed to control the computer’s interaction and Communication with the user. A computer must load the operating system like Microsoft into memory before it can load an application program like Ms Word.These computers required large space for installation.They were large in size and could take up the entire room.They consumed a lot of power.They also produced huge amounts of energy and power which saw machines breaking down oftenly. Using the computers,programming capabilities was quite low since the computers relied on machine language.Machine language can only be understood by the computer but not human beings .Their input was based on punched cards and paper tapes.
2nd generation computers. These computers existed between the years 1958 and 1964.They possessed the following features:These computers used transistors for circuitry purposes.They were quite smaller in size compared to the 1st generation computers. Unlike the 1st generation computers, they consumed less power. Their operating system was faster.During this generation, programming languages such as COBOL and FORTRAN were developed.This phase of computers relied on punched cards too for input and printouts.
3rd generation computers.These are computers that existed between 1965 and 1971.The computers used integrated circuits(ICs) for circuitry purposes.The computers were smaller in size due to the introduction of the chip.They had a large memory for processing data. Their processing speed was much higher.The technology used in these computers was small scale integration (SSI) technology.
4th generation computers. The computers under this generation were discovered from 1972 to 1990s. The computers employed large scale integration (LSI) technology.The size of memory was /is high/large,hence faster processing of data.Their processing speed was high.The computers were also smaller in size and less costly in terms of installation.This phase of computers saw introduction of keyboards that could interface well with processing system.During this phase, there was rapid Internet evolution.Other advances that were made included the introduction of GUI(graphical user interface) and mouses.Other than GUI, there exist other user interfaces like natural-language interface,question-and-answer interface,command line interface(CLI).
5th generation computers.These are computers that are still under development and invention. There development might have began in 1990s and continues in to the future. These computers use very large scale integration (VLSI) technology. The memory speed of these computers is extremely high.The computers can perform parallel processing. It is during this generation that Artificial Intelligence (AI) concept was generated e.g voice and speech recognition. These computers will use quantum computation and molecular technology.They will be able to interpret data and respond to it without direct control by human beings.
Applications and Limitations of Digital Computers
In a very general way, it can be said that the advantages of the digital computer compared to the analog computer,I are its greater flexibility and precision, while its disadvantages are its higher cost and complexity.
Information storage can be easier in digital computer systems than in analogue ones. New features can often be added to a digital system more easily too.
Computer-controlled digital systems can be controlled by Software, allowing new functions to be added without changing hardware. Often this can be done outside of the factory by updating the product’s software. So, the product’s design errors can be corrected after the product is in a customer’s hands.
Information storage can be easier in digital systems than in analog ones. The noise-immunity of digital systems permits data to be stored and retrieved without degradation. In an analog system, noise from aging and wear degrade the information stored. In a digital system, as long as the total noise is below a certain level, the information can be recovered perfectly.
Digital computers play an important role in life today as they can be used to control industrial processes, analyse and organize business data, assist in scientific research and designing of automobiles and aircraf, and even help making special effects in movies. Some Main Applications of Digital Computers are as follows –
Recording Information
Official statistics keepers and some scouts use computers to record statistics, take notes and chat online while attending and working at a Sports event.
Analyzing Movements
The best athletes pay close attention to detail. Computers can slow recorded video and allow people to study their specific movements to try to improve their tendencies and repair poor habits.
Writers
Many sportswriters attend several sporting events a week, and they take their computers with them to write during the game or shortly after while their thoughts are fresh in their mind.
The main disadvantages are that digital circuits use more energy than analogue circuits to accomplish the same tasks, thus producing more heat as well. Digital circuits are often fragile, in that if a single piece of digital data is lost or misinterpreted, the meaning of large blocks of related data can completely change.
,
Classifications of Digital Computers
Digital computers are classified into three types: analog computers, digital computers, and hybrid computers.
Analog computers represent data as continuous physical quantities, such as voltage, current, or rotation. They are used to solve problems that involve continuous variables, such as temperature, pressure, or velocity. Analog computers are often used in engineering and scientific applications.
Digital computers represent data as discrete values, such as 0s and 1s. They are used to solve problems that involve discrete variables, such as numbers, letters, or symbols. Digital computers are the most common type of computer and are used in a wide variety of applications, including business, Education, and entertainment.
Hybrid computers combine the features of analog and digital computers. They are used to solve problems that involve both continuous and discrete variables. Hybrid computers are often used in military and aerospace applications.
Generations of Digital Computers
The history of digital computers can be divided into five generations: first generation (1940sâ1950s), second generation (1950sâ1960s), third generation (1960sâ1970s), fourth generation (1970sâ1980s), and fifth generation (1980sâpresent).
First generation computers were large, expensive, and unreliable. They were made with vacuum tubes, which were prone to failure. First generation computers were used for scientific and military applications.
Second generation computers were smaller, faster, and more reliable than first generation computers. They were made with transistors, which replaced vacuum tubes. Second generation computers were used for business and scientific applications.
Third generation computers were even smaller, faster, and more reliable than second generation computers. They were made with integrated circuits, which replaced transistors. Third generation computers were used for business, scientific, and engineering applications.
Fourth generation computers were the first to use microprocessors. Microprocessors are small, powerful computers that are embedded in many devices, such as cars, appliances, and toys. Fourth generation computers are used for a wide variety of applications, including business, education, entertainment, and communication.
Fifth generation computers are still in development. They are expected to be even smaller, faster, and more powerful than fourth generation computers. Fifth generation computers are expected to be used for artificial intelligence, expert systems, and natural language processing.
Applications of Digital Computers
Digital computers are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Business: Digital computers are used for accounting, inventory management, payroll, and other business tasks.
- Education: Digital computers are used for teaching, Learning, and research.
- Engineering: Digital computers are used for design, analysis, and simulation.
- Government: Digital computers are used for administration, planning, and decision-making.
- Healthcare: Digital computers are used for diagnosis, treatment, and research.
- Manufacturing: Digital computers are used for production control, quality control, and inventory management.
- Military: Digital computers are used for command and control, weapons systems, and intelligence gathering.
- Science: Digital computers are used for research, data analysis, and simulation.
- Space exploration: Digital computers are used for navigation, guidance, and control.
Limitations of Digital Computers
Digital computers have several limitations, including:
- Cost: Digital computers can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Size: Digital computers can be large and bulky.
- Speed: Digital computers can be slow to perform some tasks.
- Power consumption: Digital computers can consume a lot of power.
- Reliability: Digital computers can be unreliable and may fail.
- Security: Digital computers can be vulnerable to security threats.
- Storage capacity: Digital computers have limited storage capacity.
Despite these limitations, digital computers are an essential part of modern life. They are used in a wide variety of applications and have revolutionized the way we live and work.
Classifications of digital computers
- Analog computers: These computers represent data using continuous physical quantities, such as voltage or current. Analog computers are often used for real-time applications, such as controlling machines or simulating physical systems.
- Digital computers: These computers represent data using discrete values, such as 0 and 1. Digital computers are more versatile than analog computers and are used for a wide variety of applications, including data processing, scientific computing, and artificial intelligence.
- Hybrid computers: These computers combine the features of analog and digital computers. Hybrid computers are used for applications that require the high speed and accuracy of analog computers, as well as the flexibility and programmability of digital computers.
Generations of digital computers
- First generation (1940s-1950s): These computers were large, expensive, and slow. They used vacuum tubes as their primary components.
- Second generation (1950s-1960s): These computers were smaller, faster, and less expensive than first-generation computers. They used transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
- Third generation (1960s-1970s): These computers were even smaller, faster, and less expensive than second-generation computers. They used integrated circuits instead of transistors.
- Fourth generation (1970s-1980s): These computers were the first to use microprocessors. Microprocessors are small, powerful computers that are embedded in many devices, such as cars, appliances, and toys.
- Fifth generation (1980s-present): These computers are the most advanced computers to date. They use artificial intelligence and other advanced technologies to perform tasks that were once thought to be impossible for computers to do.
Applications of digital computers
- Data processing: Computers are used to process large amounts of data, such as financial records, customer lists, and medical records.
- Scientific computing: Computers are used to solve complex mathematical problems, such as those that arise in physics, chemistry, and engineering.
- Artificial intelligence: Computers are used to create artificial intelligence (AI) systems, which can perform tasks that are normally associated with human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Graphics and animation: Computers are used to create graphics and animations, such as those used in movies, video games, and websites.
- Communication: Computers are used to communicate with other people, either through email, instant messaging, or Social Media.
- Entertainment: Computers are used to play games, watch movies, and listen to music.
- Education: Computers are used to teach students, either in a traditional classroom setting or through online courses.
- Business: Computers are used to manage businesses, such as tracking inventory, processing orders, and managing finances.
- Healthcare: Computers are used to diagnose and treat patients, as well as to manage medical records.
- Government: Computers are used to manage government operations, such as collecting taxes, issuing passports, and providing social Services.
Limitations of digital computers
- Speed: Computers are limited by the speed of their processors. The faster the processor, the faster the computer can perform tasks.
- Memory: Computers are limited by the amount of memory they have. The more memory a computer has, the more data it can store and the more programs it can run at the same time.
- Storage: Computers are limited by the amount of storage they have. The more storage a computer has, the more data it can store.
- Power: Computers are limited by the amount of power they require. The more powerful a computer is, the more power it requires.
- Cost: Computers are limited by their cost. The more powerful and sophisticated a computer is, the more expensive it is.
- Complexity: Computers are complex devices that can be difficult to understand and use. This can be a limitation for people who are not familiar with computers.
- Security: Computers are vulnerable to security threats, such as viruses, malware, and hackers. This can be a limitation for people who store sensitive data on their computers.
- Ethics: Computers can be used for unethical purposes, such as spreading misinformation, cyberbullying, and identity theft. This can be a limitation for people who are concerned about the ethical implications of using computers.
What is the most common type of digital computer?
(A) Analog computer
(B) Digital computer
(C) Hybrid computerWhat is the main difference between analog and digital computers?
(A) Analog computers represent data as continuous quantities, while digital computers represent data as discrete quantities.
(B) Analog computers are faster than digital computers.
(C) Analog computers are more accurate than digital computers.What are the three main components of a digital computer?
(A) Input, output, and processing
(B) Memory, processing, and storage
(C) Input, processing, and outputWhat is the most common type of input device?
(A) Keyboard
(B) Mouse
(C) TouchscreenWhat is the most common type of output device?
(A) Monitor
(B) Printer
(C) SpeakerWhat is the most common type of storage device?
(A) Hard drive
(B) Solid-state drive
(C) Flash driveWhat is the most common programming language?
(A) Java
(B) Python
(C) C++What is the most common operating system?
(A) Windows
(B) macOS
(C) LinuxWhat is the most common application for digital computers?
(A) Word processing
(B) Spreadsheets
(C) Database managementWhat is the most common limitation of digital computers?
(A) They can only process discrete quantities.
(B) They can only store a finite amount of data.
(C) They can only perform a finite number of operations per second.