<–2/”>a >Chhattisgarh: Relief and Structure–Chhattisgarh has area of 135194 square km which is 4.14% of the geographical area of India. It is located in the centre of 17.43′ to 24.5 degree North latitude and 80.15 to 84.20 degree East longitude.
Chhattisgarh was formed on 1 November 2000 by partitioning 16 Chhattisgarhi-speaking southeastern districts of Madhya Pradesh. The capital city of Chhattisgarh is Raipur. Uttar Pradesh in North, Jharkhand in North-East, Orissa in East, Andhra Pradesh in South, Maharashtra in South-West and M.P. & Maharashtra in West form its borders. Currently chhattisgarh comprises 27 districts.. 43% Land is covered by Forests.
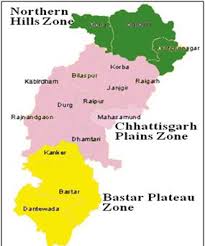
There are 3geographical zones northen hills, central plains and Bastar plateau.
- Northern Hills: The area of this agroclimatic zone accounts for 21% of the total geographical area. Koriya, Sarguja, Surajpur, BalrampurJashpur, Raigarh and Korba are districts situated in this part.
- Central Plain Zone: this agroclimatic zone covers 50% of the geographical area of the state. Raipur, BalodabajarBhathpara, Gariyaband, Bilaspur, MungeliJanjgir-Champa, Kabirdham, Rajnandgaon, Durg, Balod, BemetaraDhamtari and Mahasamund are districts included in this plain region.
River System – There is a Network of 4 rivers. These rivers are Mahanadi, Godawari, Ganga and Narmada. In this network, 31 large, small rivers and tributories, flow from East to West, covering a length of about 3573 Kms. in the State.
- Bastar Plateau Zone: It account for 29% of the geographical area of the state. Kanker (North Bastar), Bastar, Kondagaon, Dantewada (South Bastar), Bijapur, Sukma and Narayanpur are districts included in this region.
Soil, has water retention capacity in the range of Light to medium 55%-65% i.e. the Soil represents low water retention capacity.
| Region Name | Soil Type | Water Retention Capacity |
| Northern Hills Zone | Light to medium (Reddish-Yellow) | 55% |
| Med. Heavy to heavy(Brownish-Black) | 15% | |
| Central Plain Zone | Light to medium (Reddish-Yellow) | 65% |
| Light to medium (Reddish-Yellow) | 35% | |
| Southern Plateau Zone | Light to medium (Reddish-Yellow) | 58% |
| Light to medium (Reddish-Yellow) | 42% |
,
Chhattisgarh is a state in central India. It is the 10th largest state in India by area and the 17th most populous state. The state is bordered by Jharkhand to the north, Odisha to the east, Andhra Pradesh to the south, Telangana to the southwest, Maharashtra to the west, and Madhya Pradesh to the northwest. The capital of Chhattisgarh is Raipur.
The state of Chhattisgarh is divided into three physiographic divisions: the Chhattisgarh Plain, the Bastar Plateau, and the Maikal Hills. The Chhattisgarh Plain is the largest physiographic division in the state. It is a flat, alluvial plain that is drained by the Mahanadi River and its tributaries. The Bastar Plateau is a hilly region that is located in the southeastern part of the state. The Maikal Hills are a mountain range that is located in the eastern part of the state.
The Drainage System of Chhattisgarh is dominated by the Mahanadi River. The Mahanadi River is the longest river in the state. It originates in the Maikal Hills and flows through the Chhattisgarh Plain before emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The other major rivers in the state are the Indravati River, the Hasdeo River, and the Son River.
The Climate-of-chhattisgarh/”>Climate of Chhattisgarh is tropical. The state experiences a hot, humid summer from March to June. The monsoon season is from July to September. The winter season is from October to February. The Average temperature in the state ranges from 20 degrees Celsius in winter to 40 degrees Celsius in summer.
The soils of Chhattisgarh are predominantly alluvial. The alluvial soils are fertile and are suitable for agriculture. The other types of soils found in the state are red soil, black soil, and laterite soil.
The vegetation of Chhattisgarh is diverse. The state is home to a variety of forests, including tropical evergreen forests, tropical deciduous forests, and dry deciduous forests. The forests of Chhattisgarh are home to a variety of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, elephants, and deer.
The mineral Resources of Chhattisgarh are abundant. The state is a major producer of coal, iron Ore, bauxite, and manganese. The other mineral resources found in the state are limestone, dolomite, and gypsum.
The industries of Chhattisgarh are diverse. The state is home to a variety of industries, including steel, cement, power, and fertilizer industries. The other industries found in the state are textiles, Food Processing, and engineering industries.
The agriculture of Chhattisgarh is based on rice, wheat, and pulses. The other crops grown in the state are sugarcane, Cotton, and oilseeds. The state is also home to a Dairy Industry.
The tourism of Chhattisgarh is based on its natural beauty, historical sites, and tribal culture. The state is home to a number of national parks and sanctuaries, including Kanha National Park, Bandhavgarh National Park, and Pench National Park. The state is also home to a number of historical sites, including the temples of Khajuraho and the ruins of the old capital of Raipur. The tribal culture of Chhattisgarh is also a major tourist attraction.
Chhattisgarh is a state with a rich history and culture. The state is home to a diverse Population and a variety of Natural Resources. The state is also home to a number of industries and tourist attractions.
What is the relief and structure of Chhattisgarh?
Chhattisgarh is a state in central India. It is bordered by the states of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Maharashtra to the west, Andhra Pradesh to the south, and Odisha to the east. The capital of Chhattisgarh is Raipur.
The relief of Chhattisgarh is characterized by a plateau in the north and a plain in the south. The plateau is part of the Deccan Plateau, which is a large plateau that covers much of central and southern India. The plain is part of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, which is a large plain that covers much of northern India.
The structure of Chhattisgarh is characterized by a number of mountain ranges. The main mountain ranges are the Vindhya Range, the Satpura Range, and the Eastern Ghats. The Vindhya Range is a mountain range that runs from Gujarat in the west to Madhya Pradesh in the east. The Satpura Range is a mountain range that runs from Madhya Pradesh in the north to Maharashtra in the south. The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that runs from West Bengal in the north to Andhra Pradesh in the south.
What are the major rivers in Chhattisgarh?
The major rivers in Chhattisgarh are the Mahanadi, the Godavari, and the Indravati. The Mahanadi is the longest river in Chhattisgarh. It is a tributary of the Ganges River. The Godavari is the second longest river in Chhattisgarh. It is a tributary of the Krishna River. The Indravati is the third longest river in Chhattisgarh. It is a tributary of the Mahanadi River.
What are the major cities in Chhattisgarh?
The major cities in Chhattisgarh are Raipur, Bilaspur, Durg, and Rajnandgaon. Raipur is the capital of Chhattisgarh. It is the largest city in the state. Bilaspur is the second largest city in Chhattisgarh. It is located in the northern part of the state. Durg is the third largest city in Chhattisgarh. It is located in the central part of the state. Rajnandgaon is the fourth largest city in Chhattisgarh. It is located in the southern part of the state.
What are the major industries in Chhattisgarh?
The major industries in Chhattisgarh are mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. Mining is the largest industry in Chhattisgarh. The state is home to a number of coal mines. Agriculture is also a major industry in Chhattisgarh. The state is home to a number of rice and wheat farms. Manufacturing is a growing industry in Chhattisgarh. The state is home to a number of factories that produce steel, cement, and textiles.
What are the major tourist attractions in Chhattisgarh?
The major tourist attractions in Chhattisgarh are the Kanger Valley National Park, the Indravati National Park, and the Bastar Wildlife Sanctuary. The Kanger Valley National Park is a national park located in the northern part of the state. It is home to a number of animals, including tigers, leopards, and elephants. The Indravati National Park is a national park located in the central part of the state. It is home to a number of animals, including tigers, leopards, and wild boars. The Bastar Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary located in the southern part of the state. It is home to a number of animals, including tigers, leopards, and sloth bears.
Which of the following is not a part of Chhattisgarh?
(A) Bilaspur
(B) Raipur
(C) Durg
(D) PuducherryThe capital of Chhattisgarh is:
(A) Raipur
(B) Bilaspur
(C) Durg
(D) PuducherryThe total area of Chhattisgarh is:
(A) 135,000 sq km
(B) 138,000 sq km
(C) 141,000 sq km
(D) 144,000 sq kmThe population of Chhattisgarh is:
(A) 25 million
(B) 30 million
(C) 35 million
(D) 40 millionThe Official Language of Chhattisgarh is:
(A) Hindi
(B) Chhattisgarhi
(C) English
(D) MarathiThe main religion of Chhattisgarh is:
(A) Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism
(B) Islam
(C) Christianity
(D) SikhismThe main crops of Chhattisgarh are:
(A) Rice
(B) Wheat
(C) Sugarcane
(D) CottonThe main industries of Chhattisgarh are:
(A) Coal mining
(B) Iron and steel
(C) Cement
(D) All of the aboveThe main tourist attractions of Chhattisgarh are:
(A) The Kanger Valley National Park
(B) The Indravati National Park
(C) The Achanakmar Wildlife Sanctuary
(D) All of the aboveThe famous freedom fighter from Chhattisgarh is:
(A) Veer Narayan Singh
(B) Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose
(C) Mahatma Gandhi
(D) Jawaharlal Nehru