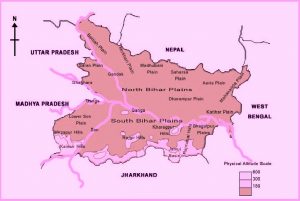
Introduction: Situated in the eastern piece of India, Bihar is a state with rich social legacy and is one of the most established occupied places on the planet. Atmosphere is one of the real reasons that made Bihar a noteworthy farming center, which may had influenced individuals to occupy this district in old circumstances.
Bihar atmosphere is as per the atmosphere winning in different parts of the Indian sub landmass. The place appreciates outrageous frosty with downpours and serious summer season too.
In Light of its topographical area, its atmosphere is highly impacted by the Himalayas and Ganga level. Bihar’s climatic conditions can be partitioned into four sections: summer, winter, storm and post rainstorm. Winter season is set apart with low temperatures which might be as low as 5-10°C degrees while summer is set apart with high temperature and a trademark sweltering breeze ‘loo’. Bihar gets a sensible decent Precipitation that contributes much to the Horticulture-2/”>Horticulture and Fisheries-2/”>Fisheries segments. Individuals in Bihar and their way of life are quite adjusted to the climatic conditions.
Winter:
The frosty climate starts right on time in November and proceeds until the center of the March. It is amid this time, the temperatures floats around 8 degree Celsius to 10 degrees.
January is the coldest month, be that as it mayWinters begin toward the beginning of November and stretches out up to mid-March. Days are frosty yet charming with warm sun and splendid light at the same time, temperature falls when the sun sets. Evenings are by and large colder than days.
The mean temperature in November is around 21°C, while in December it might drop down to a normal of 17°C. Temperature falls still down in January, which denotes the coldest month in the entire year. Normal temperature in the long stretch of January is around 16°C, however it might drop down to 4°C-10 °C. Days in March are by and large wonderful. Bihar gets little rain amid winter, with a normal of around 3-4mm.
Summer
Beginning of sweltering climate is from mid March onwards. It proceeds until mid June. Amid this time, it is to a great degree hot in Bihar. This is the time when as a rule people stay inside. Notwithstanding, on the off chance that one wishes to go for investigating the regions of Bihar, one needs to get ready, which incorporates taking plentiful of drinking water to stay away from lack of hydration and related issues.
Summer begins from April and keeps going up to the center of June. Temperature ascends from the lovely March climate (mean temperature around 24°C) because of westerly breezes. Days in April are significantly hot with a normal temperature of 30°C. Temperature achieves the statures amid May with a normal temperature of around 35 °C (it might reach as high as at least 42°c), which makes it the most sweltering month in the entire year. Summer in Bihar, much the same as the majority of the North Indian States, is set apart with tidy tempests and thunder-storms.
Tidy tempests for the most part happen in May and a large portion of them have a speed of around 48-64 km/hr. They are most incessant in May while April and Junes Shares the lower positions. Hot breezes called ‘Loo” blows through the Bihar fields amid April and May with a normal speed of 8-16 km/hour. ‘Loo’ is more similar to warm waves and causes extensive distress for the general Population there. Precipitation amid summer is sparse, with a normal of 45mm.
Monsoon
Monsoon can be further divided as pre-monsoon, monsoon and post monsoon.
Not long after the burning sun hits the state, stormy season proceeds until mid September. The start of this climate is the point at which a tempest emerges from the Bay of Bengal. It is additionally a decent time to visit Bihar as yields hypnotizes your spirit with their lavish green appearance. The temperature stays direct more often than not in this season. For the individuals who love to stroll in rain, this is the best time to visit Bihar, as there is sufficient of chance for them.
Monsoon begins by mid-June and endures till end of September. Temperature drops with the appearance of Monsoon be that as it may, the moistness increments. Rainstorm initiates when the ‘storm twist’ from Bay of Bengal disregards Bihar. In spite of the fact that the season starts at June, contingent on the landing of Monsoon wind it might come as ahead of schedule as a week ago of May or as late as first or second seven day stretch of July.
July and August for the most part get greatest precipitation. Storm precipitation is talented by the south west rainstorm. The harsh warmth of the blustery season may persevere till August. Normal precipitation amid June is around 185.5mm, which ascends to a normal of around 340mm in July. It drops down again in August to a normal of around 259mm.
There are three particular territories in Bihar which gets high precipitation, more than 1800mm/annum. Two of these areas lie on northern and north-western wings of Bihar and the third locale lies on the Netarhat congratulate in the Chota Nagpur Plateau. Rainstorm is responsible for over 90% of the aggregate precipitation in Bihar. The normal temperature is around 31°C. The south-west rainstorm that causes precipitation in Bihar for the most part pulls back in the main seven day stretch of October.
The withdraw of Monsoon clear way to the attack of tropical violent winds to race into the state. These violent winds begin in the Bay of Bengal at around 12°N Latitude. Bihar is impacted by the tropical storms, which begin in the South China Sea. The periods of September and October are set apart with the recurrence of the tropical twisters in Bihar.
These typhoons have extraordinary impact in Bihar’s horticultural part. These violent winds are viewed as basic for the developing of paddy. Additionally, they help in dampening of the dirt making it reasonable for the development of Rabi Crops. The normal temperature amid these months is around 27°C. Bihar keeps accepting precipitation amid this period too. It might get a normal precipitation of 240 mm in September, while in October it drops down to around 39mm.,
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the third-most populous state in India, with over 100 million inhabitants. The state has a tropical climate, with hot and humid summers and mild winters. The Average temperature in Bihar ranges from 20°C to 40°C. The state receives an average annual rainfall of 1,000-1,500 mm. The monsoon season is from June to September, and the state receives most of its rainfall during this time.
Bihar is prone to a number of natural disasters, including floods, droughts, and Cyclones-2/”>Cyclones. The state has also been affected by Climate Change in recent years. The average temperature in Bihar has increased by 1°C in the past 50 years, and the state has experienced more frequent and severe droughts. Climate change is also expected to lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of floods in Bihar.
The government of Bihar has taken a number of steps to address climate change. The state has developed a climate change action plan, and is working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The government is also working to improve the resilience of the state’s Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE to climate change.
The people of Bihar are also taking steps to adapt to climate change. Farmers are adopting new agricultural practices that are more resilient to droughts and floods. Communities are also working to protect their water Resources and build flood-resistant infrastructure.
Climate change is a serious threat to Bihar. The state is already experiencing the effects of climate change, and these effects are expected to worsen in the future. The government of Bihar and the people of Bihar are taking steps to address climate change, but more needs to be done to protect the state from the impacts of climate change.
Here are some of the effects of climate change in Bihar:
- Increased frequency and intensity of floods: Climate change is expected to lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of floods in Bihar. This is because climate change is causing the Himalayas to melt, which is leading to an increase in the flow of water in rivers.
- Increased frequency and intensity of droughts: Climate change is also expected to lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of droughts in Bihar. This is because climate change is causing the monsoon rains to become less predictable.
- Sea level rise: Climate change is also causing the sea level to rise. This is a threat to the coastal areas of Bihar, which are home to millions of people.
- Increased heat waves: Climate change is also causing the heat waves to become more frequent and more intense. This is a threat to the Health of people in Bihar, especially the elderly and the young.
Here are some of the adaptation measures that are being taken in Bihar to address climate change:
- Improved water management: The government of Bihar is working to improve the management of Water Resources in the state. This includes building Dams and reservoirs, and improving Irrigation systems.
- Improved Disaster Management: The government of Bihar is also working to improve the disaster management system in the state. This includes building early warning systems, and improving the preparedness of the state to respond to disasters.
- Sustainable agriculture: The government of Bihar is also promoting Sustainable Agriculture in the state. This includes encouraging farmers to adopt practices that are more resilient to climate change, such as using drought-tolerant crops.
- Reforestation: The government of Bihar is also planting trees in the state. This helps to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, and also helps to protect the Environment.
Here are some of the mitigation measures that are being taken in Bihar to address climate change:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: The government of Bihar is working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the state. This includes promoting RENEWABLE ENERGY, and improving Energy Efficiency.
- Raising awareness: The government of Bihar is also working to raise awareness about climate change among the people of the state. This includes organizing workshops and seminars, and producing educational materials.
- Capacity building: The government of Bihar is also working to build the capacity of the state to address climate change. This includes training government officials and other stakeholders on climate change issues.
What is the climate of Bihar?
The climate of Bihar is tropical, with hot, humid summers and mild winters. The average temperature ranges from 20°C (68°F) in winter to 40°C (104°F) in summer. The monsoon rains, which are essential for agriculture, occur from June to September.
What are the main geographical features of Bihar?
Bihar is located in the eastern part of India, and is bordered by Nepal to the north, Uttar Pradesh to the west, Jharkhand to the south, and West Bengal to the east. The Ganges River flows through the state, and the Son River is another important river. The state is mostly flat, with some hills in the north.
What are the main industries in Bihar?
The main industries in Bihar are agriculture, textiles, and mining. Agriculture is the most important Industry, and the state is a major producer of rice, wheat, and sugarcane. Textiles are another important industry, and the state is a major producer of Cotton and silk. Mining is also an important industry, and the state is a major producer of coal and iron Ore.
What are the main tourist attractions in Bihar?
The main tourist attractions in Bihar are the Mahabodhi Temple, the Nalanda University, and the Rajgir hills. The Mahabodhi Temple is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and is one of the most important Buddhist temples in the world. The Nalanda University was a major center of Learning in ancient India, and is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Rajgir hills are a popular tourist destination, and are home to several Buddhist temples and monasteries.
What are the main languages spoken in Bihar?
The main languages spoken in Bihar are Hindi, Urdu, and Maithili. Hindi is the Official Language of the state, and is spoken by the majority of the population. Urdu is a minority language, but is spoken by a significant number of people in the state. Maithili is a regional language, and is spoken by a large number of people in the northern part of the state.
What are the main religions practiced in Bihar?
The main religions practiced in Bihar are Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism, Islam, and Buddhism-2/”>Buddhism. Hinduism is the majority religion, and is practiced by the majority of the population. Islam is a minority religion, but is practiced by a significant number of people in the state. Buddhism is a minority religion, but is practiced by a large number of people in the northern part of the state.
What are the main festivals celebrated in Bihar?
The main festivals celebrated in Bihar are Holi, Diwali, and Chhath Puja. Holi is a Hindu festival of colors, and is celebrated with great pomp and show. Diwali is a Hindu festival of lights, and is celebrated with great joy and happiness. Chhath Puja is a Hindu festival dedicated to the sun god, and is celebrated with great devotion and faith.
What are the main food items eaten in Bihar?
The main food items eaten in Bihar are rice, wheat, lentils, vegetables, and fish. Rice is the staple food, and is eaten with almost every meal. Wheat is also a popular food item, and is used to make roti, chapati, and paratha. Lentils are a common ingredient in many dishes, and are used to make dal, sambar, and rasam. Vegetables are also a popular food item, and are used to make a variety of dishes. Fish is a popular food item in the coastal areas, and is used to make a variety of dishes.
What are the main customs and traditions of Bihar?
The main customs and traditions of Bihar are marriage, birth, and death. Marriage is a very important event in the life of a Bihari, and is celebrated with great pomp and show. Birth is also a very important event, and is celebrated with great joy and happiness. Death is a very sad event, and is mourned with great grief and sorrow.
What are the main challenges facing Bihar?
The main challenges facing Bihar are POVERTY, illiteracy, and Unemployment. Poverty is a major problem, and a large number of people in the state live below the Poverty Line. Illiteracy is also a major problem, and a large number of people in the state are illiterate. Unemployment is also a major problem, and a large number of people in the state are unemployed.
What are the main hopes and aspirations of the people of Bihar?
The main hopes and aspirations of the people of Bihar are to improve their standard of living, to get a good Education, and to get a good job. They also hope for a better future for their children.
Here are some MCQs about Bihar:
Which of the following is the capital of Bihar?
(A) Patna
(B) Ranchi
(C) Jamshedpur
(D) GayaWhich of the following is the largest river in Bihar?
(A) Ganges
(B) Yamuna
(C) Brahmaputra
(D) NarmadaWhich of the following is the main language spoken in Bihar?
(A) Hindi
(B) Urdu
(C) Bengali
(D) MaithiliWhich of the following is the main religion in Bihar?
(A) Hinduism
(B) Islam
(C) Christianity
(D) SikhismWhich of the following is the main crop grown in Bihar?
(A) Rice
(B) Wheat
(C) Sugarcane
(D) MaizeWhich of the following is the main mineral found in Bihar?
(A) Coal
(B) Iron ore
(C) Copper
(D) BauxiteWhich of the following is the main industry in Bihar?
(A) Agriculture
(B) Mining
(C) Manufacturing
(D) ServicesWhich of the following is the main tourist attraction in Bihar?
(A) Patna Museum
(B) Mahabodhi Temple
(C) Nalanda University
(D) RajgirWhich of the following is the famous dish of Bihar?
(A) Litti Chokha
(B) Pabda jhaal
(C) Tilkut
(D) RasagullaWhich of the following is the famous person from Bihar?
(A) Jayaprakash Narayan
(B) Rajendra Prasad
(C) Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam
(D) Lalu Prasad Yadav