Archeological sites of Andhra Pradesh
Bavikonda
Bavikonda Buddhist Complex lies about 16 km from Visakhapatnam, in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, on a hill about 130 metres above mean sea level. The term Bavikonda in Telugu means a hill of wells. As per its name, Bavikonda is a hill which has wells for the collection of rainwater. Bavikonda Monastery dates back to the 3rd century BCE. A large Buddhist complex was excavated at this site.
Erravaram Caves
Erravaram Caves are located on the left bank of Yeleru river, at a distance of 45 km from Rajahmundry on Vishakhapatnam route. The caves are located on Dhanla–dibba hillock. The excavations revealed historic remains dated back to 100 A.D.. This site flourished from 1st century B.C. to 2nd century A.D.
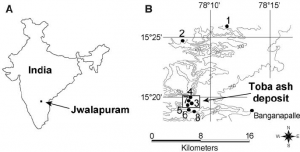
Jwalapuram
Jwalapuram (meaning “City of fire” in Sanskrit) is an archaeological site in the Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh, southern India, which shows hominid habitation before and after the Toba event according to the Toba catastrophe theory. It is unclear what species of humans settled Jwalapuram as no fossil remains have yet been found.
Jwalapuram is of particular importance in understanding the emergence of microlithic technology in South Asia and the role of environmental change on lithic technological change. At Jwalapuram Locality 9, five stratigraphic units provide a record of technological change throughout time. Microblade technology dominates lithic assemblages from Stratum E to the top deposit. There are many different definitions for “microblade” and Clarkson et al. define microblade with a 40mm maximum length in the direction of striking and a length:width ratio greater than 2:1; they also include that the dorsal surface has nearly no cortex (less than 20 percent) and at least on dorsal ridge in the direction of striking as well as nearly parallel lateral margins. Using this definition of microblade, Clarkson et al. track the changing density of microblade technology throughout the strata. The changes in microlithic technology is speculated to have been caused by Climate change, which made the area more arid and therefore groups of people had to become more mobile, causing changes in their technological tool kits.
Bojjannakonda
Bojjannakonda and Lingalakonda are two Buddhist rock-cut caves on adjacent hillocks, situated near a village called Sankaram, which is a few kilometres away from Anakapalle, Vishakhapatnam in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. The sites are believed to date between 4th and 9th Century A.D, when the 3 phases of Buddhism-2/”>Buddhism (Hinayana, Mahayana, and Vajrayana) flourished at Sankaram (Sangharam as it was called then) .
Pavurallakonda
Pavurallakonda or Pavurallabodu is the local name of a hill, popularly known as Narasimhaswamy Konda, near Bheemunipatnam about 25 km towards north of Visakhapatnam, in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located at a height of about 150 meters above mean sea level. Pavurallakonda consists of a ruined hill-top Buddhist monastic complex probably witnessed human habitation from 3rd Century BCE to 2nd century CE. It is one of the Largest Buddhist Monasteries of North Coastal Andhra Region. Hinayana Buddhism may have flourished at this hill-top site.
Initial Excavation of this site yielded many relics. Two Brahmi label inscriptions, foundations of Viharas, circular chaityas, votive stupas, halls etc. are located among the ruins. Coins, polished ware, beads etc. were recovered from the site by the state archaeology Department of Andhra Pradesh. Nearly Sixteen rock-cut cisterns are carved on the hill for the storage of rain water. Excavations and Restoration Program are under progress at Pavurallakonda.
Dharanikota
In 500 BCE, Dharanikota was known as Dhanyakatakam.This is the capital of a great kingdom ruled by Satavahanas. Archaeological excavations at Dharanikota revealed viharas in Dharanikota and nearby areas. It is the site of ancient Dhanyakataka, which was the capital of the Satavahana dynasty that ruled in the Deccan around the 1st to 3rd centuries CE. It was also the capital of the Kota Vamsa, which ruled during the medieval period until the mid 12th century. The Krishna River Valley is an important rice producing area. It was also an important centre of trade with other parts of India and foreign countries. The place is also famous for the great stupa; a very large Kalachakra ceremony was conducted there in January, 2006. Xuanzang visited Amaravathi village, Guntur district and wrote a glorious account of the place and the viharas that existed then.
Salihundam
Salihundam, a historically important Buddhist monument and a major tourist attraction is a village lying on top of the hill on the south bank of the Vamsadhara River. It is about 9 miles from Srikakulam. There are numerous Buddhist stupas, discovered in 1919 by Gidugu Venkata Rama Murthy. Four stupas, relic caskets, and architectural shrines were discovered during digging performed by state authorities, as well as sculptures of Buddhist dieties Mareechi and Tara. All of the remnants were built between the 2nd century and 12th century, reflecting the different times of Buddhism: Mahayana, Theravada and Vajrayana. Salihundam is one of the main Buddhist excavation sites, due to its status as showing evidence that Buddhism thrived in the local area during the 2nd and 3rd centuries.
Thotlakonda
Thotlakonda Buddhist Complex is situated on a hill near Bheemunipatnam about 15 kilometres from Visakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh, India. The hill is about 128 metres above sea level and overlooks the sea. The Telugu name Toṭlakoṇḍa derived from the presence of a number of rock-cut cisterns hewn into the bedrock of the hillock. Thotlakonda was well within the influence of ancient Kalinga, which was an important source of dissemination of Buddhism to Sri Lanka and various parts of Southeast Asia. It provides an insight into the process of transoceanic diffusion of Indic culture, especially Buddhism.,
Andhra Pradesh is a state in south-central India. It is bordered by Telangana to the north, Chhattisgarh to the northeast, Odisha to the east, Tamil Nadu to the south, and Karnataka to the west. The state has a coastline of about 972 kilometers (603 mi) along the Bay of Bengal.
Andhra Pradesh is a land of Ancient History and culture. The state is home to many important archaeological sites, including Amaravati, Belum Caves, Bhongir Fort, Golconda Fort, Hampi, Kondapalli Fort, Nagarjunakonda, Ramalingeswara Temple, Srisailam, Udayagiri and Khandagiri Caves, Vijayawada, and Warangal Fort.
Amaravati is a city in Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh. It was the capital of the Satavahana dynasty from the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century CE. The city is home to many important Buddhist monuments, including the Mahachaitya, a large stupa that is one of the largest in India.
Belum Caves are a series of limestone caves located in Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh. The caves are home to a variety of rock formations, including stalactites and stalagmites. The caves are also home to a number of prehistoric paintings.
Bhongir Fort is a hill fort located in Bhongir district of Andhra Pradesh. The fort was built in the 12th century by the Kakatiya dynasty. The fort is surrounded by a moat and has a number of towers and bastions.
Golconda Fort is a ruined fort located in Hyderabad, the capital of Telangana. The fort was built in the 16th century by the Qutb Shahi dynasty. The fort is known for its intricate architecture and its massive walls.
Hampi is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Bellary district of Karnataka. Hampi was the capital of the Vijayanagara Empire from the 14th century to the 16th century. The city is home to a number of important Hindu and Jain temples, as well as palaces and other monuments.
Kondapalli Fort is a hill fort located in Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh. The fort was built in the 16th century by the Qutb Shahi dynasty. The fort is surrounded by a moat and has a number of towers and bastions.
Nagarjunakonda is an archaeological site located in Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh. The site was once a Buddhist university and monastery. The site is home to a number of important Buddhist monuments, including the Nagarjunakonda stupa.
Ramalingeswara Temple is a Hindu temple located in Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh. The temple was built in the 12th century by the Chola dynasty. The temple is dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva.
Srisailam is a Hindu pilgrimage site located in Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh. The site is home to the Srisailam temple, which is dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva.
Udayagiri and Khandagiri Caves are a series of rock-cut caves located in Bhubaneswar, the capital of Odisha. The caves were built in the 2nd century BCE by the Kalinga kings. The caves are home to a number of Hindu and Jain sculptures.
Vijayawada is a city in Krishna district of Andhra Pradesh. The city was the capital of the Satavahana dynasty from the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century CE. The city is home to a number of important Hindu temples, including the Kanaka Durga Temple.
Warangal Fort is a ruined fort located in Warangal district of Telangana. The fort was built in the 13th century by the Kakatiya dynasty. The fort is surrounded by a moat and has a number of towers and bastions.
These are just a few of the many archaeological sites that can be found in Andhra Pradesh. The state is a treasure trove of history and culture, and visitors can explore a variety of different sites to learn more about the region’s rich past.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about Andhra Pradesh:
What is the capital of Andhra Pradesh?
The capital of Andhra Pradesh is Amaravati.What is the Population of Andhra Pradesh?
The population of Andhra Pradesh is 84,654,445.What is the language spoken in Andhra Pradesh?
The language spoken in Andhra Pradesh is Telugu.What is the religion of the majority of people in Andhra Pradesh?
The religion of the majority of people in Andhra Pradesh is Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism.What is the Literacy rate in Andhra Pradesh?
The literacy rate in Andhra Pradesh is 67.02%.What is the GDP of Andhra Pradesh?
The GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100.2 billion.What is the main Source Of Income in Andhra Pradesh?
The main source of income in Andhra Pradesh is agriculture.What are some of the major industries in Andhra Pradesh?
Some of the major industries in Andhra Pradesh are textiles, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.What are some of the major tourist attractions in Andhra Pradesh?
Some of the major tourist attractions in Andhra Pradesh are the temples of Tirupati, the beaches of Vizag, and the hills of Araku Valley.What are some of the famous people from Andhra Pradesh?
Some of the famous people from Andhra Pradesh are the freedom fighter Alluri Sitarama Raju, the actor Nagarjuna Akkineni, and the cricketer VVS Laxman.What are some of the challenges facing Andhra Pradesh?
Some of the challenges facing Andhra Pradesh are POVERTY, Unemployment, and Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE-development/”>Infrastructure Development.What are some of the opportunities for Andhra Pradesh?
Some of the opportunities for Andhra Pradesh are its rich natural Resources, its skilled workforce, and its strategic location.What is the future of Andhra Pradesh?
The future of Andhra Pradesh is bright. The state has a young population, a growing economy, and a strong commitment to development.
Question 1
Which of the following is not a state in India?
(A) Andhra Pradesh
(B) Telangana
(C) Karnataka
(D) Kerala
Answer
(D) Kerala
Question 2
Which of the following is the capital of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) Hyderabad
(B) Vijayawada
(C) Amaravati
(D) Visakhapatnam
Answer
(C) Amaravati
Question 3
Which of the following is the largest city in Andhra Pradesh?
(A) Hyderabad
(B) Vijayawada
(C) Amaravati
(D) Visakhapatnam
Answer
(A) Hyderabad
Question 4
Which of the following is the Official Language of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) Telugu
(B) Hindi
(C) English
(D) Urdu
Answer
(A) Telugu
Question 5
Which of the following is the currency of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) Indian rupee
(B) US dollar
(C) Euro
(D) Pound sterling
Answer
(A) Indian rupee
Question 6
Which of the following is the population of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) 84.6 million
(B) 94.3 million
(C) 104.0 million
(D) 113.7 million
Answer
(C) 104.0 million
Question 7
Which of the following is the literacy rate of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) 67.0%
(B) 72.0%
(C) 77.0%
(D) 82.0%
Answer
(B) 72.0%
Question 8
Which of the following is the GDP of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) $100 billion
(B) $120 billion
(C) $140 billion
(D) $160 billion
Answer
(C) $140 billion
Question 9
Which of the following is the main religion of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) Hinduism
(B) Islam
(C) Christianity
(D) Sikhism
Answer
(A) Hinduism
Question 10
Which of the following is the main agricultural product of Andhra Pradesh?
(A) Rice
(B) Wheat
(C) Sugarcane
(D) Cotton
Answer
(A) Rice