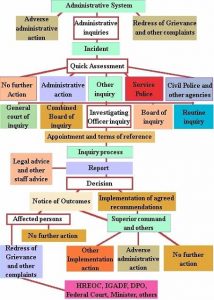
Administrative system of Himachal Pradesh:-
The Government of Himachal Pradesh also known as the State Government of Himachal Pradesh, or locally as State Government, is the supreme governing authority of the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh and its 12 districts. It consists of an executive branch, led by the Governor of Himachal Pradesh, a judiciary and a legislative branch. Like other states in India, the head of state of Himachal Pradesh is the Governor, appointed by the President of India on the advice of the Central government. His or her post is largely ceremonial. The Chief Minister is the head of government and is vested with most of the executive powers. Shimla is the capital of Himachal Pradesh, and houses the Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) and the secretariat (Writers’ Building). The Himachal Pradesh High Court is located in Shimla, which has jurisdiction over the whole of Himachal Pradesh. The present Legislative Assembly of Himachal Pradesh is unicameral.
Administrative Structure of Himachal Pradesh:-
- Since 1st September, 1972, there have been no changes in the administrative structure of Himachal Pradesh except carving out of new sub-divisions, sub- tehsils, raising of sub-tehsils to the level of tehsils within the district boundaries. Presently, there are 12 districts, 52 sub-divisions, 109 tehsils and sub-tehsils in Himachal Pradesh. 2. From development point of view, the Pradesh is divided into 75 development blocks. The smallest unit for development- cum-administration is Panchayat and their number is 3243. The State has a three tier Panchayati Raj structure comprising of 12 Zila Parishads, 75 Panchayat Samitis and 3243 Gram Panchayats on the rural side; and 1 Municipal Corporation, 20 Municipal Councils and 28 Nagar Panchayats on the Urban side besides 7 Cantonment Boards.
State Capital: Shimla
No. of Districts: 12 (Bilaspur, Chamba, Hamirpur, Kangra, Kinnaur, Kullu, Lahaul & Spiti, Mandi, Shimla, Sirmaur, Solan, Una.)
No. of Tehsils: 158 (Amb, Arki, Baijnath, Banjar, Baroh, Bharmour, Barsar, Bharmour, Bhattiyat, Bhoranj, Bilaspur, Chamba, Amb, Arki, Baijnath, Banjar, Baroh, Bharmour, Barsar, Bharmour, Bhattiyat, Bhoranj, Bilaspur, Chamba, Chaurah, Chachyot, Chaupal, Chirgaon, Dalhousie, Dehra Gopipur, Dehra Gopipur, Dharmsala, Dodra Kwar, Fatehpur, Ghumarwin, Hamirpur, Jawali, Jai Singpur, Jaswan, Jhanduta, Joginder Nagar, Jubbal, Kalpa, Kandaghat, Kangra, Karsog, Kasauli, Khundiyan, Kotkhai, Kumhasain, ladbharol, Lahaul, Manali, Mandi, Morang, Nadaun, Nahan, Nalagarh, Nichar, Nirmand, Nurpur, Padhar, Paonta Sahib, Pachhad, Palampur, Pangi, Pooh, Rakkar, Rampur, Rajgarh, Renuka, Rohru, Saluni, Sangla, Sarkaghat, Seoni, Spiti, Shalai, Shimla, Sunder Nagar, Theog, Thunag, Tira Sujanpur, Una)
No of Divisions: 3
No. of Sub Divisions: 69
No. of Police Stations: 125
No. of Blocks : 78
No. of Urban Local Bodies: 54
No. of Gram Panchyats: 3226
No. of Villages: 20690
No. of Towns: 59
No. of Parliament Constituencies:
Lok Sabha: 4
Rajya Sabha: 3
No. of Assembly Constituencies: 68
,
The administrative system of Himachal Pradesh is divided into three levels: state level, district level, and block level.
The state government is headed by the Chief Minister, who is assisted by a Council of Ministers. The State Legislature is unicameral, with a Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) of 68 members.
The district level administration is headed by a Deputy Commissioner, who is assisted by a number of officers, including the Superintendent of Police, the District Magistrate, and the Chief Engineer. The District Administration is responsible for implementing the policies of the state government at the district level.
The block level administration is headed by a Block Development Officer, who is assisted by a number of officers, including the Block Panchayat Officer, the Block Education Officer, and the Block Health Officer. The block administration is responsible for implementing the policies of the state government at the block level.
The panchayats are the third tier of government in Himachal Pradesh. They are responsible for local self-governance and are headed by a Sarpanch. The panchayats are responsible for a variety of functions, including the maintenance of local Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE, the provision of basic Services, and the promotion of social welfare.
The administrative system of Himachal Pradesh is designed to provide effective and efficient governance to the people of the state. The three-tier System of Government ensures that there is a clear division of responsibilities and that each level of government is accountable to the people. The system is also designed to be responsive to the needs of the people and to promote local development.
The administrative system of Himachal Pradesh has been praised for its efficiency and effectiveness. The state has a low crime rate and a high standard of living. The education system is well-developed and the health system is accessible to all. The state has also made significant progress in the areas of agriculture, tourism, and Infrastructure Development.
The administrative system of Himachal Pradesh is constantly being reviewed and updated to ensure that it meets the needs of the people. The state government is committed to providing Good Governance and to improving the lives of the people of Himachal Pradesh.
The following are some of the key challenges facing the administrative system of Himachal Pradesh:
- Corruption: Corruption is a major problem in Himachal Pradesh, as in many other parts of India. It is estimated that corruption costs the state government billions of rupees each year. Corruption can be found in all levels of government, from the state level to the panchayat level. It can take many forms, including bribery, extortion, and Nepotism. Corruption can have a negative impact on the economy, the Environment, and the Quality Of Life of the people.
- POVERTY: Poverty is another major challenge facing Himachal Pradesh. According to the 2011 census, 11.9% of the Population of Himachal Pradesh lives below the Poverty Line. Poverty can be found in all parts of the state, but it is particularly acute in the rural areas. Poverty can have a negative impact on the health, education, and EMPLOYMENT opportunities of the people.
- Lack of infrastructure: Himachal Pradesh is a mountainous state and has a relatively small population. This has made it difficult to develop infrastructure in the state. The state has a poor road Network, inadequate electricity supply, and limited access to healthcare and education. The lack of infrastructure can have a negative impact on the economy and the quality of life of the people.
- Environmental Degradation: Himachal Pradesh is a beautiful state with a rich natural heritage. However, the state is facing a number of environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and Climate change. These challenges can have a negative impact on the economy, the environment, and the quality of life of the people.
Despite these challenges, the administrative system of Himachal Pradesh has made significant progress in recent years. The state has a low crime rate, a high standard of living, and a well-developed education and healthcare system. The state has also made significant progress in the areas of agriculture, tourism, and infrastructure development. The state government is committed to providing good governance and to improving the lives of the people of Himachal Pradesh.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about Himachal Pradesh:
What is the capital of Himachal Pradesh?
The capital of Himachal Pradesh is Shimla.What is the population of Himachal Pradesh?
The population of Himachal Pradesh is 8,749,621 (2011 census).What is the language spoken in Himachal Pradesh?
The Official Language of Himachal Pradesh is Hindi. However, there are many other languages spoken in the state, including Punjabi, Pahari, and Gaddi.What is the religion of Himachal Pradesh?
The majority religion in Himachal Pradesh is Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism. However, there are also significant minorities of Muslims, Christians, and Sikhs.What is the economy of Himachal Pradesh?
The economy of Himachal Pradesh is based on agriculture, tourism, and hydroelectricity.What are some of the tourist attractions in Himachal Pradesh?
Some of the tourist attractions in Himachal Pradesh include the Shimla Hills, the Kullu Valley, the Manali Valley, and the Spiti Valley.What are some of the famous people from Himachal Pradesh?
Some of the famous people from Himachal Pradesh include the former Prime Minister of India, Indira Gandhi, and the former Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh, Virbhadra Singh.What are some of the challenges facing Himachal Pradesh?
Some of the challenges facing Himachal Pradesh include poverty, illiteracy, and environmental degradation.What are some of the opportunities for Himachal Pradesh?
Some of the opportunities for Himachal Pradesh include tourism, agriculture, and hydroelectricity.What is the future of Himachal Pradesh?
The future of Himachal Pradesh is bright. The state has a strong economy, a beautiful landscape, and a rich culture. With continued development, Himachal Pradesh is poised to become one of the most prosperous states in India.
Here are some MCQs about Himachal Pradesh:
Which of the following is not a district of Himachal Pradesh?
(A) Chamba
(B) Kangra
(C) Kullu
(D) Lahaul and SpitiThe capital of Himachal Pradesh is:
(A) Shimla
(B) Dharamshala
(C) Manali
(D) KulluThe official language of Himachal Pradesh is:
(A) Hindi
(B) English
(C) Punjabi
(D) PahariThe population of Himachal Pradesh is about:
(A) 6.8 million
(B) 7.8 million
(C) 8.8 million
(D) 9.8 millionThe Literacy rate of Himachal Pradesh is about:
(A) 80%
(B) 85%
(C) 90%
(D) 95%The main religion of Himachal Pradesh is:
(A) Hinduism
(B) Islam
(C) Christianity
(D) SikhismThe main crops of Himachal Pradesh are:
(A) Rice
(B) Wheat
(C) Maize
(D) ApplesThe main industries of Himachal Pradesh are:
(A) Tourism
(B) Hydroelectricity
(C) Agriculture
(D) MiningThe highest mountain in Himachal Pradesh is:
(A) Nanda Devi
(B) Kamet
(C) Manaslu
(D) DhaulagiriThe longest river in Himachal Pradesh is:
(A) Sutlej
(B) Beas
(C) Ravi
(D) ChenabThe first Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh was:
(A) Yashwant Singh Parmar
(B) Virbhadra Singh
(C) Prem Kumar Dhumal
(D) Jai Ram ThakurThe current Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh is:
(A) Yashwant Singh Parmar
(B) Virbhadra Singh
(C) Prem Kumar Dhumal
(D) Jai Ram ThakurThe Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly has:
(A) 60 members
(B) 75 members
(C) 87 members
(D) 90 membersThe Himachal Pradesh Legislative Council has:
(A) 30 members
(B) 40 members
(C) 50 members
(D) 60 membersThe Himachal Pradesh High Court is located in:
(A) Shimla
(B) Dharamshala
(C) Manali
(D) KulluThe Himachal Pradesh State Animal is:
(A) Snow Leopard
(B) Musk Deer
(C) Red Panda
(D) Himalayan TahrThe Himachal Pradesh State Bird is:
(A) Western Tragopan
(B) Monal
(C) Impeyan Pheasant
(D) Blood PheasantThe Himachal Pradesh State Tree is:
(A) Deodar
(B) Pine
(C) Fir
(D) SpruceThe Himachal Pradesh State Flower is:
(A) Rhododendron
(B) Blue Poppy
(C) Wild Lily
(D) OrchidThe Himachal Pradesh State Emblem is:
(A) A snow-capped mountain
(B) A river
(C) A tree
(D) A bird