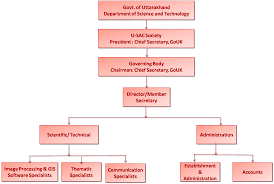
Administration system in Uttarakhand
Being one of the youngest Legislative Assembly in India, it has a Unicameral structure. The total strength of the assembly is 71. The assembly is held at the Vidhan Sabha Bhawan in Dehradun, which is the provisional capital of the state.
Like any other state of India, the Governor remains the Head of the State, who is appointed by the President of India.The Chief Minister, the elected head of the members of the state legislative assembly is the political head and Chief Executive of the State Government. The Chief Minister’s tenure is limited by the extent of majority enjoyed by the political party in the State Assembly and the pleasure of the President. The normal tenure of the assembly and the government is five years after which fresh general Elections are held.
State Government Uttarakhand
Council of Members in Uttarakhand Government
Trivendra Singh Rawat was sworn in as the new Chief Minister on 18th March 2017. He belongs to the Bharatiya Janata Party, his constituency is Doiwala. He is the head of the Government. He holds additional charge for the following departments viz. Suraaj, General Administration (GAD), Home, Vigilance, State Assets Personnel and Establishment of Services-2/”>All India Services Thematic Working, State Government Judicial/ Legal Field Nominations/Appointments, Public Grievances, Public Works, RENEWABLE ENERGY, Medical Services, Information, Industrial Development and Disaster Management and Rehabilitation.
Shri. Satpal Maharaj, belongs to the Bharatiya Janata Party. He is from the constituency of Chaubattakal. As a Cabinet Minster he holds important portfolios like Irrigation, Flood Control, Minor Irrigation, Rain Water Harvesting and Water Management
Mr Prakash Pant, is a minister from the Pithoragarh Constituency. He belongs to the Bharatiya Janata Party. The portfolios he hold include Parliamantary Affairs, Legislative Affairs, Languages, Finance and Commercial Tax.
His constituency being Haridwar, Madan Kaushik, belongs to the Bharatiya Janata Party. He is the minister for Urban Development, Housing and Rajiv Gandhi Urban Housing Scheme.
Yashpal Arya, Minister for Transportation, Social Welfare, Minority Welfare, Students Welfare, is from the Bajpur Constituency and belongs to the Bharatiya Janata Party.
Mr. Arvind Pandey, from Gadarpur holds charge of School Education, Adult Education and Sanskrit Education.
Mr. Subodh Uniyal from Narendranagar is the Minister for agriculture, Agricultural Marketing and Agricultural Processing.
Dhan Singh Rawat, Minister of State (Independent Charge), is the Minister of Co-operatives and Higher Education . He is from the Srinagar constituency and belongs to the Bharatiya Janata Party.
Administrative Setup of Uttarakhand
For the purpose of administration, Uttarakhand is divided into two regions namely Kumaon and Garhwal. These two are further divided into fourteen districts. Chamoli, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal, UttarKashi, Pauri, Dehradun and Haridwarfall under the Garhwal region, while Champawat, Bhageshwar, Udham Singh Nagar, Almora, Pithoragarh and Nainital falls under the Garhwal region. Each district is an administrative geographical unit.
Various Administrative Departments Of Uttarakhand
Department of Planning (20 point programme and implementation): The fundamental objective of this department is to improve the living standards, assuring EMPLOYMENT, reducing income disparities, organising social, welfare and sanitation programmes for the economically weaker sections. ‘Eradication of POVERTY’ and ‘Development with Social Justice’ being the main goal of this department.
Agriculture: Sustainable Agriculture, improvement of economic status of the farmers, reduction in cost of cultivation and drudgery in agriculture, improving and maintaining self sufficiency in Cereals production are some of the main objectives of the department. The Vision of the department being, long term food, nutrient and security of the farmers.
Accounts and Entitlement: The main function of the department is to serve the State Government Employees the benefit of pension by issuing the Pension Pradhikar Patra (PPO).
Animal Husbandry: Livestock farming forms an integral part of the people of Uttarakhand. It remains as a main Source Of Income in the rural areas. The Vision of the department is to intensify and create new opportunities in the field of animal husbandry for increasing employment generation and enterprise development in the State.
Budget: Budget contains the entire framework laid by the Finance Department for the guidance of officers and departments of the Secretariat. It contains all the rules and regulations with regard to the budget procedure. It prepares and examines the annual budget estimates and the subsequent control over expenditure to ensure that it is kept within the limits.
Chief Development Officer: The primary responsibility of this department is to ensure and co-ordinate smooth functioning of different departments of State and Central Government of planning and development. These departments are responsible for the execution and monitoring of poverty eradication as well as development of infrastructures.
Commercial Tax: It functions under the Finance Department of Government of Uttarakhand. This department is responsible for administering various Taxation Acts and corresponding rules.
Commissioner Tax is the head of this department.
Dairy Development: The main purpose of this department is to set up dairy cooperatives in rural areas to strengthen the economic situation of the milk producers and to ensure clean milk and milk-based products to the consumers at reasonable rates.
Disaster Mitigation and Management Center: It lays out all the disaster policies, prevention mechanisms, mitigation measures, preparedness, and response plans. This department also imparts training programs to the local communities, provides advance information about likely disaster through latest technologies available for the purpose, maintains a Network of experienced experts working in the field.
Election: The Chief Electoral Office in Uttarakhand works under the guidance of the Election Commission of India. The elections to State Assembly and both houses of Parliament are conducted by the office of Chief Electoral Officer.
The Chief Electoral officer is responsible for conducting free and fair elections across the State of Uttarakhand.
Employment: The Vision of this Department is to provide assistance to all categories of job seekers to get employment in Uttarakhand. At present there are 25 employment exchanges under this department. The main function of it is to register the applicants, placement of the applicants and providing vocational guidance.
The whole process and service rendered is free of cost.
Entertainment and Trade tax: This Department lays down the rules, acts and regulations pertaining to the entertainment and trade domain. It prevents illegal broadcast of movies, and ensures entertainment to the public at reasonable rates.
Excise: The prime job of Excise Department is to regulate, monitor and control manufacture, import, transport, possession, export, consumption and sale of liquor and other such substances.
Firms, Societies and Chit Funds: This Department registers and administers the firms, societies and chit funds under the respective acts such as the, PARTNERSHIP Act 1932, Societies Registration Act 1860 and chits Act 1892. It lays out the rules and regulations of the same.
Fisheries-2/”>Fisheries: This Department plans and programs the policies of the fishery sector, and ensures if it is carried out in line within the guidelines of the Directorate of Fisheries.
It promotes scientific aquaculture and works towards the upliftment and welfare of the fishermen.
Food and Civil Supplies: The mission of the Department of Food & Civil Supplies is to ensure supply of food grains and other commodities to the consumer in a transparent manner under the Public Distribution System and other Government schemes at fair price.
Forest: The Forest Department in Uttarakhand has the responsibility of managing some of the richest forests and Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity in India. Biodiversity conservation in Protected Areas of Uttarakhand is primarily the responsibility of the Department. Promotion of eco-tourism, research and providing training for forest guards are also few of the functions this Department executes.
Geology and Geo Mining Unit: The main activities of this department include geo technical inspection in various districts, mineral exploration, mining administration and the Environmental Impact Assessment Program which ensures that the activities are executed as per existing environmental Act.
ITDA: It is an autonomous body that guides and monitors various projects and provides inputs, monitors, evaluates and executes State’s IT initiatives and projects under the National e-Governance Plan.
Labour: This Department enforces various labour laws that are charted out both by the central and state Government.
It also ensures compliance with The Supreme Court‘s directions regarding Child Labour.
Medical, Health and Family Welfare: The main objective of the Department is to improve the health status and Quality Of Life of its people. It also focuses on ensuring proper water and sanitation facilities. It also has a lot of programs and schemes for the people, which sensitise them on many health-related issues.
Police: This Department plays a pivotal role by maintaining order, preventing crime, detecting crime and providing peace. This department directly comes under the Department of Home Affairs.
Mr. B.S. Sidhu is the present DGP of Uttarakhand.
Public Works: Public Works Department is responsible for construction, maintenance and planning of roads, bridges and government buildings. The department also adopts and practices use of modern techniques and machinery for construction purposes. This department has a multi-tier system for the assurance of quality.
Revenue: The aim of the Board of Revenue is to control, regulate and upgrade all the judicial and administrative work of the revenue department. The main role and responsibility of this department is Land Acquisition, Revenue Collection, Chakbandi, hearing of revenue cases, transfer of land to departments and budget.
Rural Development: The main and sole focus of this Department is development and welfare of the people belonging to the rural areas. It provides livelihood opportunities to those in need, including Women and other vulnerable sections with focus on Below Poverty Line (BPL) households. It also has various schemes and programs for the enhancement of livelihood security of households in rural areas by providing at least 100 days of guaranteed wage employment in every financial year to every household demanding it. This department works towards offering urban amenities in rural areas for improvement of quality of rural life.
Rural Engineering Services: It executes the construction works of various government departments like Medical and Health, Social Welfare, Revenue, Rural Development, Police, Forest, Primary and Secondary Education, Border Area Development Programme, Tourism, Fisheries, Empowerment/”>Women Empowerment, Food and Supply, Agriculture, Ayurvedic, RMSA, SSA department including Vidyak Nidi and Sansad Nidi.
Sericulture: Uttarakhand is the only state in India which produces all four types of Silk. This department focuses on generating employment opportunities for unemployed people as well as the upliftment of the socio-economic condition of rural people in the state. It works under the Ministry of Horticulture-2/”>Horticulture.
Social Welfare: This Social Welfare Department provides welfare programs for handicapped individuals, social security for old people and destitute. It has many financial and welfare schemes in place.
Sports: The main focus of this department is to provide the right facilities for sportsmen to excel in their respective fields, both on a National andIinternational platform. Ensuring the code and conduct as per the guidelines prescribed.
Stamps and registration: The main function of this Department includes, registration of documents, registration of marriages, issuing of encumbrance certificates, preservation and maintenance of original documents, registration of partnership firms etc.
State Horticulture Mission: This Department focuses on increasing the area for production and productivity of fruits, vegetable, medicinal and floriculture crops. It also provides training to farmers on latest technology. It also encourages more farmers to take up cultivation so that additional income is generated. This department also implements different programs and ensures that it is run as per the terms and conditions prescribed.
State Planning Department: This Department is primarily responsible for making a development plan for the State. It initiates and takes necessary exercises for this purpose. It oversees and takes an over-all view of the implementation of the plan.
Sugarcane and Sugar: This Department focuses on increasing the produce of sugarcane. Sensitizing the farmers about proper usage of land and manure. It has welfare programs and schemes for the farmers.
Tourism: The vision of this department is to place Uttarakhand on the tourism map of the world as one of the leading tourist destinations. It strives towards developing tourism as a major source of employment and revenue generation thereby, increasing the economic and social development in the State.
Town and Country Planning: It prepares master plans for urban centres, zonal plans and Uttarakhand Jalsansthan: industrial zones. The Department also renders advisory services to all the Development Authorities, Regulated Areas, Urban Local Bodies of the State. It is also involved in framing out the State Housing policies, Zoning Regulations etc.
Transport: This Department provides services on nationalized routes as well as on interstate routes. It also ensures smooth-functioning by adhering to the guidelines, rules and acts, which has been laid out.
To plan, promote and execute schemes and operate an efficient system of water supply. It also operates the sewerage, sewage, treatment and disposal and treatment of trade effluents.
Uttarakhand Renewable Development Agency: This department is responsible for implementation of renewable energy programmes, operation and execution of various schemes based on non – conventional Resources/”>Energy Resources. It conducts conferences and workshop towards awareness and technological modifications. It also promotes various measures for the renewable energy development.
Vigilance: This department is dedicated towards the eradication of Corruption by civil servants. It ensures that the Public servants do not misuse their power, accept any bribes or any kind of malpractice. It checks for any kind of corruption in various government departments too.
Women Empowerment and Child Development: It ensures overall development of women & children, by providing essential momentum in an integrated manner through various schemes. It strives for the upliftment both economically and socially.,
The administration system in Uttarakhand is divided into the following sub-topics:
- Executive
- Chief Minister
- Council of Ministers
- Secretariat
- District Administration
- Legislature
- Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly
- Uttarakhand Legislative Council
- Judiciary
- High Court of Uttarakhand
- District Courts
- Local Self-Government
- Panchayati Raj Institutions
- Municipalities
- Other
- State Election Commission
- State Information Commission
- State Human Rights Commission
- State Vigilance Commission
- State Legal Services Authority
- State Commission for Women
- State Commission for Protection of Child Rights
Executive
The executive branch of the government of Uttarakhand is headed by the Chief Minister. The Chief Minister is the head of the state government and is responsible for the day-to-day running of the state. The Chief Minister is appointed by the Governor of Uttarakhand and is usually the leader of the party or coalition that has the most seats in the Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly.
The Chief Minister is assisted by a Council of Ministers. The Council of Ministers is a group of ministers who are responsible for different departments of the state government. The ministers are appointed by the Chief Minister and are usually members of the party or coalition that the Chief Minister belongs to.
The Secretariat is the administrative body of the state government. The Secretariat is headed by the Chief Secretary, who is the highest-ranking civil servant in the state. The Secretariat is responsible for implementing the policies of the government and for providing administrative support to the Chief Minister and the Council of Ministers.
The District Administration is the administrative body of the district. The District Administration is headed by the District Magistrate, who is the highest-ranking civil servant in the district. The District Administration is responsible for implementing the policies of the government and for providing administrative support to the people of the district.
Legislature
The legislative branch of the government of Uttarakhand is the Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly. The Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly is a unicameral legislature, which means that it has only one house. The Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly has 70 members, who are elected from single-member constituencies.
The Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly is responsible for making laws for the state. The Assembly also has the power to approve the budget of the state and to oversee the functioning of the government.
Judiciary
The judicial branch of the government of Uttarakhand is the High Court of Uttarakhand. The High Court of Uttarakhand is the highest court in the state. The High Court has jurisdiction over all civil and criminal cases in the state.
The High Court is headed by the Chief Justice of Uttarakhand. The Chief Justice is appointed by the President of India. The other judges of the High Court are also appointed by the President of India.
The High Court has the power to hear appeals against the decisions of the lower courts. The High Court also has the power to issue writs, which are orders that can be used to protect the Fundamental Rights of the people.
Local Self-Government
The local self-government in Uttarakhand is divided into two levels: the panchayat level and the municipal level.
The panchayat level is the lowest level of local self-government. The panchayats are responsible for providing basic services to the people, such as water, sanitation, and education.
The municipal level is the highest level of local self-government. The municipalities are responsible for providing urban services, such as roads, drainage, and electricity.
Other
The other important institutions in the administration of Uttarakhand are the State Election Commission, the State Information Commission, the State Human Rights Commission, the State Vigilance Commission, the State Legal Services Authority, the State Commission for Women, and the State Commission for Protection of Child Rights.
The State Election Commission is responsible for conducting elections to the Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly and the local self-government bodies.
The State Information Commission is responsible for ensuring that the people have access to information about the government.
The State Human Rights Commission is responsible for protecting the human rights of the people.
The State Vigilance Commission is responsible for investigating cases of corruption in the government.
The State Legal Services Authority is responsible for providing free legal aid to the poor and the needy.
The State Commission for Women is responsible for protecting the rights of women.
The State Commission for Protection of Child Rights is responsible for protecting the rights of children.
1. What is the capital of Uttarakhand?
The capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun.
2. What is the Population of Uttarakhand?
The population of Uttarakhand is 10,116,752 (2011 census).
3. What is the area of Uttarakhand?
The area of Uttarakhand is 53,483 sq km.
4. When was Uttarakhand formed?
Uttarakhand was formed on 9 November 2000.
5. What are the languages spoken in Uttarakhand?
The languages spoken in Uttarakhand are Hindi, Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, Bhoti, and Tharu.
6. What are the major rivers of Uttarakhand?
The major rivers of Uttarakhand are the Ganga, Yamuna, Alaknanda, Bhagirathi, Mandakini, and Kali.
7. What are the major tourist attractions in Uttarakhand?
The major tourist attractions in Uttarakhand are the Kedarnath Temple, Badrinath Temple, Gangotri Temple, Yamunotri Temple, Haridwar, Rishikesh, Mussoorie, Nainital, Almora, and Ranikhet.
8. What are the major crops grown in Uttarakhand?
The major crops grown in Uttarakhand are rice, wheat, maize, barley, sugarcane, and potatoes.
9. What are the major industries in Uttarakhand?
The major industries in Uttarakhand are tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing.
10. What are the major challenges faced by Uttarakhand?
The major challenges faced by Uttarakhand are poverty, Unemployment, illiteracy, and Environmental Degradation.
The capital of Uttarakhand is:
(A) Dehradun
(B) Haridwar
(C) Mussoorie
(D) NainitalThe highest peak in Uttarakhand is:
(A) Nanda Devi
(B) Kedarnath
(C) Badrinath
(D) GangotriThe main language spoken in Uttarakhand is:
(A) Hindi
(B) Garhwali
(C) Kumaoni
(D) PahariThe main religion in Uttarakhand is:
(A) Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism
(B) Islam
(C) Christianity
(D) SikhismThe main crops grown in Uttarakhand are:
(A) Rice
(B) Wheat
(C) Maize
(D) SugarcaneThe main industries in Uttarakhand are:
(A) Tourism
(B) Agriculture
(C) Mining
(D) ManufacturingThe main exports of Uttarakhand are:
(A) Tea
(B) Timber
(C) Handicrafts
(D) Gems and jewelryThe main imports of Uttarakhand are:
(A) Petroleum products
(B) Machinery
(C) Food grains
(D) FertilizersThe main tourist attractions in Uttarakhand are:
(A) The Himalayas
(B) The temples of Haridwar and Rishikesh
(C) The hill stations of Mussoorie and Nainital
(D) All of the aboveThe main festivals celebrated in Uttarakhand are:
(A) Holi
(B) Diwali
(C) Dussehra
(D) All of the above