Census of Haryana
According to Census 2011, Haryana has Population of approx 2.54 Crores, an increase from figure of 2.11 Crore in 2001 census. Total population of Haryana as per 2011 census is 25,351,462 of which male and female are 13,494,734 and 11,856,728 respectively. In 2001, total population was 21,144,564 in which males were 11,363,953 while females were 9,780,611.
The total population Growth in the decade from 2001 to 2011 was 19.90 percent while in previous decade it was 28.06 percent. The population of Haryana forms 2.09 percent of India in 2011.
The economy is dominated by agricultural and its related industries. The entire state is divided into four divisions of Ambala, Rohtak, Gurgaon and Hisar for administrative purposes. Haryana consists of total 21 districts, 58 sub-divisions, 80 tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils and 125 blocks. According to Census Of India, there are 154 cities and towns and 6,955 villages in Haryana. Haryana has witnessed a huge influx of immigrants from all over the nation, primarily from Bihar, Bengal, Uttrakhand, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Nepal.
Total Area of the state 44,212 square kilometres
Density of the state 573 persons per square kilometres
Total Population
Total population of the state in 2011 is 25,351,462,
of which males and females are given below
Male 13,494,734
Female 11,856,728
Population Growth of Haryana is 19.90%. It is thus increasing at a slow rate as compared to last decade from 1990-91 to 2000-01.
Percantage of total Population 2.09%
Total Population of Haryana constitutes 2.09 % of the Indian population.
Sex ratio in Haryana
Sex Ratio 879
Child Sex Ratio 834
Sex ratio has increased for both rural and urban areas. Overall sex ratio has improved from 861 in 2001 to 879 in 2011.
District wise Sex Ratio
Out of the total districts, 12 have recorded to have gender ratio of above 900. Sirsa district recorded the highest sex ratio with 999 girls available for every 1,000 boys. The district of Panchkula recorded a sex ratio of 961, Karnal (959), Fatehabad (952), Gurgaon (946), Sonipat (942), Jind (940), Rewari (931), Mewat (923), Bhiwani (912), Mahendragarh (912), Hisar (906). All these figures reveal positive signs of a healthy sex ratio started to increase in the Haryana state.
Improvement in Sex Ratio
However, with Government schemes and initiatives, the sex ratio in Haryana has started to show an upward movement. The state recorded a child sex ratio (0-6 age group) of over 900 for the first time in December, 2015. This is the first time since 2011 that Haryana sex ratio crossed the 900 mark. Haryana’s gender ratio is 903 (2016) according to state’s Health department. The state has witnessed a huge success under ‘Beti Bachao Beti Padhao’ campaign. Prime Minister Narendra Modi has launched the much applauded ‘Beti Bachao Beti Padhao’ campaign in Panipat on January 22, 2015. The State Government took strict measures to counter female feticide in the entire districts.
Census of child from (0-6) years of age
Total Child Population (0-6 Age) 3,380,721
Male Population (0-6 Age) 1,843,109
Female Population (0-6 Age) 1,537,612
Literacy rate of Haryana census 2011
Total Literacy 76.64 %
Male Literacy 85.38 %
Female Literacy 66.67 %
Total Population of Literates i.e. in absolute figures
Total Literate 16,598,988
Male Literate 9,794,067
Female Literate 6,804,921
Haryana’s economy is centered towards agriculture and industries related to it. In terms of Education, Haryana has seen a tremendous increase in its literacy rate. As of 2011, the state recorded a literacy rate of 76.64 %. This further consist of male literacy 85.38 % while female literacy is at 66.67 %. Literacy rate in Haryana has improved from 67.91 % in 2001 to 76.64 % in 2011. The city of Gurgaon with 86.30% has the highest literacy rate. Panchkula at 81.9 % and Ambala at 81.7 % are other cities with high literacy rate. Overall literacy rate in the state is descent with 76.64 % of population being able to read and write in Haryana.
Urban and Rural Population of Haryana
Urban Population of Haryana census 2011
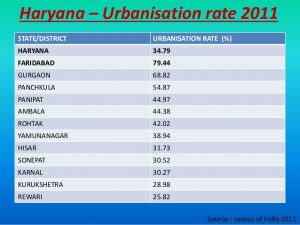
Out of total population of Haryana, 34.88% people live in urban regions. The total figure of population living in urban areas is 8,842,103 of which 4,720,728 are males and while remaining 4,121,375 are females. The urban population in the last 10 years has increased by 34.88 percent.
Sex Ratio in urban regions of Haryana was 873 females per 1000 males.
Average Literacy rate in Haryana for Urban regions was 83.14 percent in which males were 88.63% literate while female literacy stood at 65.98%. Total literates in urban region of Haryana were 6,440,546.
Rural population census of Haryana 2011
Of the total population of Haryana state, around 65.12 percent live in the villages of rural areas. In actual numbers, males and females were 8,774,006 and 7,735,353 respectively. Total population of rural areas of Haryana state was 16,509,359. The population growth rate recorded for this decade (2001-2011) was 65.12%.
In rural regions of Haryana state, female sex ratio per 1000 males was 882 while same for the child (0-6 age) was 835 girls per 1000 boys.
In rural areas of Haryana, literacy rate for males and female stood at 81.55 % and 51.96 %. Average literacy rate in Haryana for rural areas was 71.42 percent. Total literates in rural areas were 10,158,442.
Population by Religion
A vast majority (84.45%) of population in Haryana are Hindu followers. Further, Sikhs with (4.91%), Muslims (7.03%) are the largest minorities in the state. After Punjab, Haryana has the second largest Sikh Population in India. Islam followers are mainly found in Mewat and Yamuna Nagar districts.,
The Census of Haryana is a decennial census of the population of the Indian state of Haryana. The first census was conducted in 1961, and the most recent census was conducted in 2011. The census provides a detailed snapshot of the state’s population, including its size, distribution, and characteristics.
The 2011 census found that the population of Haryana was 28,803,979, an increase of 21.6% from the 2001 census. The sex ratio was 879 females per 1,000 males, and the literacy rate was 76.6%. The majority of the population (87.5%) lived in rural areas, and the average household size was 5.2 persons.
The census also provides data on the state’s economy, education, health, and social and cultural characteristics. The data from the census is used to plan and implement development programs, and to monitor the progress of the state.
The Census of Haryana is conducted by the Haryana State Census Organization (HSCO). The HSCO is a department of the Government of Haryana, and is responsible for planning, conducting, and disseminating the results of the census. The HSCO is headed by a Director General, who is assisted by a team of officers and staff.
The census is conducted using a house-listing and house-holding schedule. The house-listing schedule is used to collect information on the physical characteristics of the house, such as its size, type, and construction material. The house-holding schedule is used to collect information on the members of the household, such as their age, sex, education, occupation, and religion.
The census data is collected by a team of enumerators, who are recruited and trained by the HSCO. The enumerators visit each household in the state and collect the data from the house-listing and house-holding schedules. The data is then entered into a computer system and processed by the HSCO.
The results of the census are disseminated through a variety of media, including reports, publications, and websites. The data is also used to prepare development plans, to monitor the progress of the state, and to make policy decisions.
The Census of Haryana is an important tool for planning and development. The data from the census is used to make informed decisions about the allocation of Resources and the implementation of programs. The census also provides a valuable snapshot of the state’s population, and its characteristics.
Here are some of the key findings of the 2011 census:
- The population of Haryana was 28,803,979, an increase of 21.6% from the 2001 census.
- The sex ratio was 879 females per 1,000 males.
- The literacy rate was 76.6%.
- The majority of the population (87.5%) lived in rural areas.
- The average household size was 5.2 persons.
- The population of Haryana is growing at a rate of 2.1% per year.
- The sex ratio is declining, due to a higher mortality rate among females.
- The literacy rate is increasing, but is still lower than the national average.
- The majority of the population lives in rural areas, but the urban population is growing rapidly.
- The average household size is declining, due to factors such as Urbanization and nuclear families.
The Census of Haryana is a valuable tool for planning and development. The data from the census is used to make informed decisions about the allocation of resources and the implementation of programs. The census also provides a valuable snapshot of the state’s population, and its characteristics.
What is a census?
A census is a count of the population of a country or region. It is used to collect information about the population, such as age, sex, race, ethnicity, and housing.
What is the purpose of a census?
The purpose of a census is to provide information about the population that can be used to make decisions about government Services, such as education, healthcare, and transportation.
How is a census conducted?
A census is conducted by the government. The government sends out forms to every household in the country or region. The residents of each household fill out the forms and return them to the government.
What information is collected in a census?
The information collected in a census varies from country to country. However, most censuses collect information about the following:
- Age
- Sex
- Race
- Ethnicity
- Housing
- Marital status
- Education
- EMPLOYMENT
How often is a census conducted?
The frequency of censuses varies from country to country. In the United States, a census is conducted every 10 years.
What are the benefits of a census?
The benefits of a census include:
- It provides information about the population that can be used to make decisions about government services.
- It helps to ensure that all people are counted in the population.
- It can be used to track changes in the population over time.
What are the challenges of conducting a census?
The challenges of conducting a census include:
- Ensuring that everyone is counted.
- Collecting accurate information.
- Protecting the privacy of the data.
What is the future of censuses?
The future of censuses is uncertain. Some experts believe that censuses will become less important as technology advances and more data becomes available. Others believe that censuses will remain important because they provide essential information about the population.
The population of Haryana as per the 2011 census is:
(a) 28,803,984
(b) 28,460,776
(c) 28,164,685
(d) 27,915,703The sex ratio of Haryana as per the 2011 census is:
(a) 879
(b) 884
(c) 893
(d) 900The literacy rate of Haryana as per the 2011 census is:
(a) 76.64%
(b) 75.64%
(c) 74.64%
(d) 73.64%The decadal growth rate of Haryana as per the 2011 census is:
(a) 18.09%
(b) 17.09%
(c) 16.09%
(d) 15.09%The density of population of Haryana as per the 2011 census is:
(a) 556 per sq km
(b) 566 per sq km
(c) 576 per sq km
(d) 586 per sq kmThe urban population of Haryana as per the 2011 census is:
(a) 11,081,323
(b) 10,881,323
(c) 10,681,323
(d) 10,481,323The rural population of Haryana as per the 2011 census is:
(a) 17,722,661
(b) 17,522,661
(c) 17,322,661
(d) 17,122,661The number of districts in Haryana is:
(a) 21
(b) 20
(c) 19
(d) 18The capital of Haryana is:
(a) Chandigarh
(b) Panchkula
(c) Faridabad
(d) GurgaonThe chief minister of Haryana is:
(a) Manohar Lal Khattar
(b) Bhupinder Singh Hooda
(c) Om Prakash Chautala
(d) Devi Lal