<<–2/”>a >h3>Endothermic Reactions
Endothermic reactions are those chemical reactions where energy is absorbed by the system from the surroundings mostly in the form of heat. The concept is applied in the physical sciences like chemical reactions where hear is converted to chemical bond energy by way of experiments. Common examples of endothermic reactions are cooking an egg, Photosynthesis, and Evaporation. This reactions process accounts for the enthalpy change of a reaction only. The overall energy analysis of any reaction is the Gibbs free energy that includes temperature and entropy in addition to the enthalpy. The point to mention here is that endothermic reactions release energy always in the form of heat only. Moreover, the products have more energy as compared to the reactants. The end result of any endothermic reaction is in an increase in chemical potential energy. The endothermic reaction always needs a greater amount of energy to break the existing Bonds in the reactants in order to need the new bonds form in the products. In a nutshell in the endothermic reactions process, less energy is added to the Environment as compared to the amount of energy absorbed to initiate and maintain the reaction.
Exothermic Reactions
An exothermic reaction is a Chemical Reaction that releases energy in the form of heat, Light, Sound or even electricity. It can be expressed as the reaction where reactants results in products and energy. Overall it adds energy to the surroundings. Moreover, it is the energy that is needed to start the reaction process and is always less than the energy released. It ‘s hard to measure the amount of energy released during the chemical process. However, the enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is easier to work, and it always equals the change in internal energy of the system and the amount of work required to change the volume of the system against constant ambient pressure. The concept of exothermic reactions process is applied in the physical sciences to chemical reactions where the energy of chemical bond is converted into thermal energy. It explains two kinds of chemical systems or reactions found in nature. In a nutshell in the overall process, more energy is added to the environment as compared to the amount of energy that was absorbed to initiate and maintain the reaction.
Key Differences
- Endothermic reactions absorbed the heat while exothermic reactions give out the heat.
- In the case of endothermic reactions, the content of energy of the reactants is always less than the products while it happens reverse in the case of the exothermic reactions.
- The change of enthalpy for endothermic reactions is always positive while it tends to negative in case of AH in a change of enthalpy in the exothermic reactions.
- In endothermic reactions, small positive free energy while in exothermic reactions large negative free energy.
- All endergonic reactions are exothermic while all exergonic reactions are exothermic.
- The common examples of endothermic reactions are cooking an egg, photosynthesis, and evaporation. The common examples of exothermic reactions are a fireplace, Respiration, and combustion.
- Endothermic results in an increase in chemical potential energy while exothermic reactions result in a decrease in chemical potential energy.
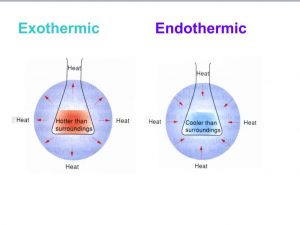
- Exothermic reactions are hotter than surroundings while endothermic reactions are cooler than surroundings.
- In endothermic reactions, energy is always present in the form of heat while in the case of exothermic reactions; energy is always present in the form of heat, electricity, sound or light.
- In the endothermic reactions process, less energy is added to the environment as compared to the amount of energy absorbed to initiate and maintain the reaction. In exothermic reactions process, more energy is added to the environment as compared to the amount of energy that was absorbed to initiate and maintain the reaction.
,
Exothermic Reactions
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat. The word “exothermic” comes from the Greek words “exo,” meaning “out,” and “therme,” meaning “heat.” In an exothermic reaction, the reactants have more energy than the products. This extra energy is released as heat, which can be used to do work.
One example of an exothermic reaction is the combustion of gasoline. When gasoline is burned, it reacts with Oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide and water vapor. This reaction releases a large amount of heat, which is what powers your car.
Another example of an exothermic reaction is the decomposition of baking soda. When baking soda is heated, it decomposes into sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide gas. This reaction also releases a large amount of heat, which is why baking soda is often used in baking.
Endothermic Reactions
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that absorbs energy in the form of heat. The word “endothermic” comes from the Greek words “endo,” meaning “in,” and “therme,” meaning “heat.” In an endothermic reaction, the products have more energy than the reactants. This extra energy is absorbed from the surroundings, which can cause the temperature of the surroundings to decrease.
One example of an endothermic reaction is the melting of ice. When ice melts, it absorbs heat from the surroundings. This is why ice cubes melt in your drink on a hot day.
Another example of an endothermic reaction is the dissolving of salt in water. When salt dissolves in water, it absorbs heat from the surroundings. This is why you feel a cold sensation when you put salt on your tongue.
Heat of Reaction
The heat of reaction is the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction. The heat of reaction is usually measured in joules (J) or calories (cal).
The heat of reaction can be positive or negative. A positive heat of reaction indicates that the reaction is endothermic, while a negative heat of reaction indicates that the reaction is exothermic.
The heat of reaction can be calculated using the following equation:
$q = \Delta H$
where $q$ is the heat of reaction, $\Delta H$ is the enthalpy change, and $n$ is the number of moles of reactants.
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic quantity that is used to measure the heat content of a system. The symbol for enthalpy is $H$.
Enthalpy is a state function, which means that it depends only on the state of the system, not on the path taken to reach that state.
The enthalpy of a system can be calculated using the following equation:
$H = U + PV$
where $U$ is the internal energy of the system, $P$ is the pressure of the system, and $V$ is the volume of the system.
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic quantity that is used to measure the disorder of a system. The symbol for entropy is $S$.
Entropy is a state function, which means that it depends only on the state of the system, not on the path taken to reach that state.
The entropy of a system can be calculated using the following equation:
$S = k\ln W$
where $k$ is Boltzmann’s constant and $W$ is the number of possible microstates of the system.
Gibbs Free Energy
Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic quantity that is used to measure the spontaneity of a reaction. The symbol for Gibbs free energy is $G$.
Gibbs free energy is a state function, which means that it depends only on the state of the system, not on the path taken to reach that state.
The Gibbs free energy of a system can be calculated using the following equation:
$G = H – TS$
where $H$ is the enthalpy of the system, $T$ is the temperature of the system, and $S$ is the entropy of the system.
Spontaneity
A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that occurs without the need for an external input of energy. A spontaneous reaction is always accompanied by an increase in entropy.
The spontaneity of a reaction can be determined using the Gibbs free energy. A reaction is spontaneous if the Gibbs free energy is negative.
Le Châtelier’s Principle
Le Châtelier’s principle states that if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, the system will shift in a way to counteract the disturbance.
Le Châtelier’s principle can be used to predict the effect of changes in temperature
What is a chemical reaction?
A chemical reaction is a process that changes one or more substances into new substances.
What are the different types of chemical reactions?
There are many different types of chemical reactions, but some of the most common include:
- Combination reactions: Two or more substances combine to form a new substance.
- Decomposition reactions: A single substance breaks down into two or more substances.
- Single replacement reactions: One element replaces another element in a compound.
- Double replacement reactions: Two compounds exchange ions to form new compounds.
- Combustion reactions: A substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
What are the reactants and products in a chemical reaction?
The reactants are the substances that are present at the beginning of a chemical reaction. The products are the substances that are formed at the end of a chemical reaction.
What is a chemical equation?
A chemical equation is a way of representing a chemical reaction using symbols and formulas.
What are the different types of chemical equations?
There are two main types of chemical equations: word equations and balanced equations.
- Word equations: Word equations use words to describe the reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- Balanced equations: Balanced equations use symbols and formulas to describe the reactants and products in a chemical reaction, and they also show that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
What is a Catalyst?
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up The Rate of a Chemical Reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
What is an inhibitor?
An inhibitor is a substance that slows down the rate of a chemical reaction.
What is a rate of reaction?
The rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction occurs.
What are the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction?
The rate of a chemical reaction can be affected by several factors, including:
- The concentration of the reactants: The higher the concentration of the reactants, the faster the rate of reaction.
- The temperature: The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of reaction.
- The presence of a catalyst: A catalyst can speed up the rate of a chemical reaction.
- The surface area of the reactants: The larger the surface area of the reactants, the faster the rate of reaction.
What is a chemical equilibrium?
A chemical equilibrium is a state of balance in which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
What are the different types of chemical equilibrium?
There are two main types of chemical equilibrium: homogeneous equilibrium and heterogeneous equilibrium.
- Homogeneous equilibrium: A homogeneous equilibrium is an equilibrium in which all of the reactants and products are in the same phase.
- Heterogeneous equilibrium: A heterogeneous equilibrium is an equilibrium in which the reactants and products are in different phases.
What is the law of mass action?
The law of mass action states that the rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the concentrations of the reactants raised to their respective powers.
What is Le Châtelier’s principle?
Le Châtelier’s principle states that if a Stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift in a way that relieves the stress.
What is a buffer solution?
A buffer solution is a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acids or bases are added.
What is a redox reaction?
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons.
What are the different types of redox reactions?
There are two main types of redox reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and disproportionation reactions.
- Oxidation-reduction reactions: Oxidation-reduction reactions are reactions in which one substance is oxidized and another substance is reduced.
- Disproportionation reactions: Disproportionation reactions are reactions in which one substance is both oxidized and reduced.
What is oxidation?
Oxidation is the loss of electrons.
What is reduction?
Reduction is the gain of electrons.
What is an oxidizing agent?
An oxidizing agent is a substance that causes another substance to be oxidized.
What is a reducing agent?
A reducing agent is a substance that causes another substance to be reduced.
What is the electrochemical series?
The electrochemical series is a list of Elements arranged in order of their standard reduction potentials.
What is a standard reduction potential?
A standard reduction potential is the potential of an electrode in
Question 1
Which of the following is an example of an exothermic reaction?
(A) Burning wood
(B) Melting ice
(C) Dissolving salt in water
(D) Rusting iron
Answer
(A) is the correct answer. Burning wood is an example of an exothermic reaction because it releases heat.
Question 2
Which of the following is an example of an endothermic reaction?
(A) Cooking food
(B) Freezing water
(C) Dissolving salt in water
(D) Photosynthesis
Answer
(B) is the correct answer. Freezing water is an example of an endothermic reaction because it absorbs heat.
Question 3
In an exothermic reaction, the products have ____ energy than the reactants.
(A) More
(B) Less
(C) The same
Answer
(A) is the correct answer. In an exothermic reaction, the products have more energy than the reactants. This energy is released as heat.
Question 4
In an endothermic reaction, the products have ____ energy than the reactants.
(A) More
(B) Less
(C) The same
Answer
(B) is the correct answer. In an endothermic reaction, the products have less energy than the reactants. This energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Question 5
Which of the following is a sign of an exothermic reaction?
(A) A decrease in temperature
(B) A release of heat
(C) A rise in temperature
(D) A formation of a precipitate
Answer
(B) is the correct answer. A release of heat is a sign of an exothermic reaction.
Question 6
Which of the following is a sign of an endothermic reaction?
(A) A decrease in temperature
(B) A release of heat
(C) A rise in temperature
(D) A formation of a precipitate
Answer
(C) is the correct answer. A rise in temperature is a sign of an endothermic reaction.