Natural & Power Resources of Madhya Pradesh
Mineral resources
Minerals in Madhya Pradesh occur in abundance in its several districts. The state of Madhya is said to have a favourable geotectonic setting that accommodates every episode of mineralisation the earth has experienced. It includes the occurrences of almost all varieties of minerals required as industrial input in the growing economy. 16 Major Minerals are considered of specific importance as they contribute significantly in development of economy of the state. These include the Limestone, Bauxite, Coal, Manganese Ore, Diamond, Base metals, Dolomite, Rock Phosphate and Granite. Others include Marble, Flagstone, Slate, Calcite, Quartz and Silica sand, Molybdenum and Fire clay.
Madhya Pradesh is the only diamond producing State in the country and is the leading producer of copper conc., pyrophyllite, manganese ore, diaspore and clay (others). The State hosts the country’s 90% diamond, 63% diaspore, 61% laterite, 56% pyrophyllite, 41% molybdenum, 29% dolomite, 17% each of rock phosphate & fireclay resources.
Important mineral occurrences in the State are: bauxite in Balaghat, Guna, Jabalpur, Katni, Mandla, Rewa, Satna, Shahdol Shivpuri, Sidhi & Vidisa districts; calcite in Barwani, Jhabua, Khandwa & Khargone districts; china clay in Betul, Chhatarpur, Chhindwara, Gwalior, Hoshangabad, Jabalpur, Khargone, Narsinghpur, Raisen, Satna, Shahdol & Sidhi districts; copper in Balaghat, Betul & Jabalpur districts; coal in Betul, Shahdol & Sidhi districts; diamond in Panna district; diaspore & pyrophyllite is found in Chhatarpur, Shivpuri & Tikamgarh districts.
Dolomite is found in Balaghat, Chhindwara, Damoh, Dewas, Harda, Hoshangabad, Jabalpur, Jhabua, Katni, Mandla, Narsinghpur, Sagar and Seoni districts; fireclay in Betul, Chhindwara, Jabalpur, Katni, Narsinghpur, Panna, Sagar, Shahdol & Sidhi districts; iron ore (hematite) in Betul, Gwalior, Jabalpur & Katni districts; limestone in Balaghat, Chhindwara, Damoh, Dhar, Hoshangabad, Jabalpur, Jhabua, Khargone, Katni, Mandsaur, Morena, Narsinghpur, Neemach, Rewa, Sagar, Satna, Sehore, Shahdol & Sidhi districts and manganese ore is found in Balaghat and Jhabua districts.
Ochre(a family of earth pigments) is found in in Dhar, Gwalior, Jabalpur, Katni, Mandla, Rewa, Satna, Shahdol & Umaria districts; pyrophyllite in Chhatarpur, Sagar, Shivpuri & Tikamgarh districts; quartz/silica sand in Balaghat, Dewas, Dhar, Jabalpur, Khandwa, Khargone, Morena, Rewa & Shahdol districts; talc/steatite/soapstone in Dhar, Jabalpur, Jhabua, Katni, Narsinghpur & Sagar district and vermiculite is found in Jhabua district.
Other minerals that occur in the State are: barytes in Dewas, Dhar, Shivpuri, Sidhi & Tikamgarh districts; calcareous shales (used in slate pencil) in Mandsaur district; felspar in Jabalpur & Shahdol districts; fuller’s earth in Mandla district; gold in Jabalpur and Sidhi districts; granite in Betul, Chhatarpur, Chhindwara, Datia, Jhabua, Panna, Seoni & Shivpuri districts; graphite in Betul & Sidhi districts; gypsum in Shahdol district; lead-zinc in Betul district; molybdenum in Balaghat district; potash in Panna district; quartzite in Sehore district; rock phosphate in Chhatarpur, Jhabua & Sagar districts; and sillimanite in Sidhi district.
Power resources in Madhya Pradesh
Conventional Energy Resources
Energy resources in Madhya Pradesh have two major types, first conventional resources and second non-conventional resources. Conventional energy resources in Madhya Pradesh include Indian coal, petroleum, natural gas, atomic mineral, and hydropower. Except hydropower, all the other conventional resources are non-renewable. In Madhya Pradesh, coal is one of the main sources of energy. Non-conventional sources of energy include Solar Energy, Wind Energy, biogas, Biomass/”>Biomass energy, Tidal energy, geo-thermal energy, etc. All these are RENEWABLE ENERGY resources. Energy production in Madhya Pradesh has started from the year 1905. The main energy sources in the state are thermal power, hydropower, wind and solar energy.
Thermal power is the main Source Of Energy in the state. The main thermal power Plants are located in the main coal producing areas. The main thermal power plants of Madhya Pradesh are Amarkantak Thermal Power Plant, Satpura Thermal Power Plant, Chandani Thermal Power Centre, Jabalpur Thermal Power Plant, Sanjay GandhiThermal Power Plant and Pench River Thermal Power plant. Satpura Thermal Power Plant is located in Pather kheda coal area near Itarsi in Betul district, which is in the north slope of Satpura ranges. The construction in the plant was started in 1962 and completed in 1967. With the establishment of the plant, the production was started in the same year. It is joint venture of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh government.
Hydropower is one of the most important renewable energy resources used in Madhya Pradesh. Along with declining Natural Resources due to excessive utilisation the importance of hydropower is remarkable. In Madhya Pradesh, there are ideal situations for constructing dam projects, particularly in the western part where many perennial rivers originate and flow.
The hydropower capacity of the state is 665 MW presently. Some of the main hydropower projects are Gandhi Sagar Hydropower Centre, Rana Pratap Sagar Hydropower Centre, Kota or Jawahar Sagar Hydropower Centre, Bergee Project and Ban Sagar Hydropower Centre. The degenerating trends of traditional energy resources due to excessive utilisation and limited availability pose severe threat for the future development of the area or region. The non-traditional resources are eco-friendly resources and they have much more capacity then to the traditional one. The non-conventional sources of energy are solar energy, wind energy, biogas, biomass, etc. Madhya Pradesh also has the ideal conditions for the development solar energy generation. Wind energy is another popular energy resource and the first wind energy plant is located at Dewas District.
Non-conventional energy in Madhya Pradesh
Renewable energy is high on India’s development agenda. The National Solar Mission is one of the eight Elements of the National Action Plan on Climate Change, and has set an ambitious target of providing 20 GW of grid-connected solar power by 2022.
Madhya Pradesh has a rich natural resource base with enormous possibilities for renewable energy generation. In particular, the topographic and climatic conditions of the State favour the development of wind and solar energy, but small hydroelectric and biomass initiatives are also likely to be important. At present, renewable energy sources make up only 2.95% of the total installed capacity of the State.
The Madhya Pradesh State Government is already actively promoting the development of renewable energy. It provides favourable Investment conditions through concessional rates for land and commercial tax, capital subsidies, and exemptions from entry tax and electricity duty. Realising the potential of renewable energy in Madhya Pradesh, the State Government has implemented policies for solar, biomass and wind energy and has taken steps to promote renewable energy and to attract investment.
The International Panel on Climate Change’s Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources, published in 2011, notes that “government policies play a crucial role in accelerating the deployment of renewable technologies. Under most conditions, increasing the share of renewable energy in the energy mix will require policies to stimulate changes in the energy system”. Under the SAPCC, the Government of Madhya Pradesh will reinforce its existing policy initiatives by:
- Ensuring that draft policies for promoting investment in solar, wind and biomass energy are implemented and that RPO targets are met.
- Building stakeholder capacity on generating, handling and maintaining renewable energy, and on the CDM.
- Promoting research into new technologies for renewable energy, particularly when they show declining cost trends.
- Promoting the inclusion of biogas and solar energy applications in panchayat annual plans.
- Promoting renewable alternatives to fuelwood in forest villages.
,
Mineral Resources
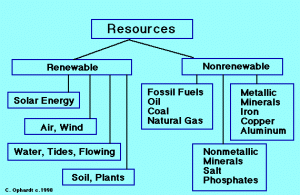
Mineral resources are non-renewable resources that are formed naturally in the earth’s crust. They are essential for the production of many goods and Services, including construction materials, electronics, and energy.
The most common mineral resources are metals, such as iron, copper, and aluminum. Metals are used to make a wide variety of products, including cars, appliances, and buildings. Other important mineral resources include coal, oil, and natural gas. These resources are used to generate electricity and power transportation.
Mineral resources are a finite resource, meaning that they will eventually run out. As the world’s Population grows, the demand for mineral resources is increasing. This is putting a strain on the world’s supply of minerals, and it is leading to increased prices.
The mining of mineral resources can have a negative impact on the Environment. Mining can cause deforestation, Soil erosion, and Water Pollution. It can also lead to the displacement of people who live near mining sites.
It is important to manage mineral resources sustainably. This means using them efficiently and minimizing the environmental impact of mining. It also means investing in research and development to find new ways to use mineral resources.
Forest Resources
Forests are a vital part of the Earth’s ecosystem. They provide habitat for many plants and animals, and they help to regulate the climate. Forests also play an important role in the water cycle, and they help to prevent soil erosion.
Forests are a renewable resource, but they are being destroyed at an alarming rate. Deforestation is caused by a number of factors, including logging, agriculture, and development. Deforestation has a number of negative consequences, including climate change, loss of Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity, and soil erosion.
It is important to protect forests and to manage them sustainably. This means planting new trees to replace those that are cut down, and it means using forests for products that can be recycled or reused. It also means reducing the demand for products that are made from wood, such as paper and furniture.
Water is a vital resource for life on Earth. It is used for drinking, bathing, cooking, and cleaning. Water is also used for agriculture, Industry, and energy production.
The Earth’s water supply is limited. Only about 3% of the Earth’s water is fresh water, and most of that is frozen in Glaciers and ice caps. The remaining fresh water is found in lakes, rivers, and groundwater.
Water is a renewable resource, but it is being used at a rate that is unsustainable. Human activities, such as agriculture, industry, and Urbanization, are putting a strain on the Earth’s water supply. This is leading to water shortages, water pollution, and conflicts over water resources.
It is important to conserve water and to use it wisely. This means reducing our water consumption, and it means using water-efficient technologies. It also means protecting our water resources from pollution and overuse.
Power Resources
Power resources are the sources of energy that we use to generate electricity. The most common power resources are fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These resources are non-renewable, meaning that they will eventually run out.
Other important power resources include nuclear power, hydropower, and renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. Nuclear power is a non-renewable resource, but it is a clean source of energy. Hydropower is a renewable resource, but it can have a negative impact on the environment. Renewable energy sources are clean and sustainable, but they are not yet able to meet all of the world’s energy needs.
The choice of power resources is a complex issue. There are many factors to consider, including the environmental impact, the cost, and the availability of each resource. It is important to choose power resources that are sustainable and that will meet the needs of the future.
Renewable Energy Resources
Renewable energy resources are those that can be replenished naturally over time. They include solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy. Renewable energy resources are becoming increasingly important as the world looks for ways to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
Solar energy is the most abundant renewable energy resource on Earth. It can be used to generate electricity, heat water, and power vehicles. Wind energy is another clean and abundant renewable energy resource. Wind turbines can be used to generate electricity, and they are becoming increasingly popular in many parts of the world.
Hydropower is a renewable energy resource that has been used for centuries. Hydroelectric Dams can be used to generate electricity, and they can also be used to control flooding and improve water quality. Geothermal Energy is a renewable energy resource that can be used to generate electricity and heat buildings. Biomass energy is a renewable energy resource that can be used to generate electricity, heat buildings, and produce transportation fuels.
Here are some frequently asked questions about Madhya Pradesh:
What is the capital of Madhya Pradesh?
The capital of Madhya Pradesh is Bhopal.What is the Population of Madhya Pradesh?
The population of Madhya Pradesh is 72,698,448 (2011 census).What is the area of Madhya Pradesh?
The area of Madhya Pradesh is 308,244 sq km.What is the language spoken in Madhya Pradesh?
The Official Language of Madhya Pradesh is Hindi. However, there are many other languages spoken in the state, including Marathi, Bundeli, Bhojpuri, and Malvi.What is the religion of the people of Madhya Pradesh?
The majority of the people of Madhya Pradesh are Hindu. However, there are also significant Muslim, Christian, and Sikh minorities.What is the economy of Madhya Pradesh like?
The economy of Madhya Pradesh is based on agriculture, industry, and services. The main agricultural products are rice, wheat, Cotton, and soybeans. The main industries are textiles, steel, and automobiles. The main services are tourism, Education, and healthcare.What are some of the tourist attractions in Madhya Pradesh?
Some of the tourist attractions in Madhya Pradesh include the Taj Mahal, the Agra Fort, the Red Fort, and the Jama Masjid.What are some of the famous people from Madhya Pradesh?
Some of the famous people from Madhya Pradesh include Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, Indira Gandhi, and Rajiv Gandhi.What are some of the challenges facing Madhya Pradesh?
Some of the challenges facing Madhya Pradesh include POVERTY, illiteracy, and Unemployment.What are some of the opportunities for Madhya Pradesh?
Some of the opportunities for Madhya Pradesh include tourism, agriculture, and industry.
Here are some frequently asked questions about natural resources:
What are natural resources?
Natural resources are the materials and substances that occur naturally in the environment and can be used for economic or environmental purposes.What are the different types of natural resources?
Natural resources can be classified into renewable and non-renewable resources. Renewable resources are those that can be replenished naturally, such as water, forests, and wildlife. Non-renewable resources are those that cannot be replenished naturally, such as fossil fuels and minerals.What are the benefits of natural resources?
Natural resources provide us with food, water, shelter, and other essential goods and services. They also play an important role in the economy, providing jobs and income for millions of people.What are the challenges of natural resources?
Natural resources are often overused and depleted, leading to environmental problems such as pollution, deforestation, and climate change. They are also often unevenly distributed, leading to conflict and poverty.What are some ways to conserve natural resources?
There are many ways to conserve natural resources, such as using energy-efficient appliances, recycling, and planting trees. We can also support policies that promote Sustainable Development and protect the environment.
Here are some frequently asked questions about power resources:
What are power resources?
Power resources are the sources of energy that we use to generate electricity.What are the different types of power resources?
Power resources can be classified into renewable and non-renewable resources. Renewable resources are those that can be replenished naturally, such as solar and wind power. Non-renewable resources are those that cannot be replenished naturally, such as coal and oil.What are the benefits of power resources?
Power resources provide us with the energy we need to power our homes, businesses, and industries. They also play an important role in the economy, providing jobs and income for millions of people.What are the challenges of power resources?
Power resources can have a negative impact on the environment. For example, burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. Power resources can also be expensive to develop and maintain.What are some ways to conserve power resources?
There are many ways to conserve power resources, such as using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when you leave a room, and unplugging electronics when you’re not using them. We can also support policies that promote Energy Efficiency and renewable energy.
Sure, here are some MCQs without mentioning the topic Natural & Power Resources of Madhya Pradesh:
Which of the following is not a natural resource?
(A) Water
(B) Coal
(C) Oil
(D) GoldWhich of the following is not a power resource?
(A) Coal
(B) Petroleum
(C) Natural gas
(D) WindWhich of the following states has the largest coal reserves in India?
(A) Jharkhand
(B) Odisha
(C) Chhattisgarh
(D) Madhya PradeshWhich of the following states has the largest hydroelectric power potential in India?
(A) Uttarakhand
(B) Himachal Pradesh
(C) Jammu and Kashmir
(D) Arunachal PradeshWhich of the following states has the largest wind power potential in India?
(A) Gujarat
(B) Tamil Nadu
(C) Karnataka
(D) Andhra PradeshWhich of the following states has the largest solar power potential in India?
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Gujarat
(C) Tamil Nadu
(D) KarnatakaWhich of the following states has the largest nuclear power potential in India?
(A) Maharashtra
(B) Tamil Nadu
(C) Karnataka
(D) Andhra PradeshWhich of the following states has the largest installed capacity of renewable energy in India?
(A) Gujarat
(B) Tamil Nadu
(C) Karnataka
(D) Andhra PradeshWhich of the following states has the largest installed capacity of thermal power in India?
(A) Maharashtra
(B) Tamil Nadu
(C) Karnataka
(D) Andhra PradeshWhich of the following states has the largest installed capacity of hydropower in India?
(A) Uttarakhand
(B) Himachal Pradesh
(C) Jammu and Kashmir
(D) Arunachal Pradesh