<<–2/”>a >a href=”https://exam.pscnotes.com/state-legislature-organization-powers-and-functions/”>State Legislature : Organization, Powers and functions
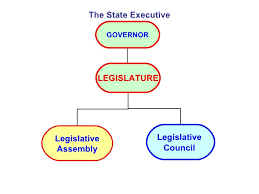
Articles 168 to 212 in Part VI of the Constitution deal with the organisation, composition, duration, officers, procedures, privileges, powers and so on of the state legislature.In most of the States, the Legislature consists of the Governor and the Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha). This means that these State have unicameral Legislature. In a Six States( Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh.), there are two Houses of the Legislature namely, Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha) and Legislative council (Vidhan Parishad) besides the Governor.Where there are two Houses, the Legislature, is known as bicameral.Five States have the bicameral, legislature. The Legislative Assembly is known as lower House or popular House. The Legislative Council is known as upper House.
There is a Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha) in every State. It represents the people of State. The members of Vidhan Sabha are directly elected by people on the basis of universal Adult Franchise. They are directly elected by all adult citizens registered as voters in the State. All men and Women who are 18 years of age and above are eligible to be included in the voters’ List.
There are certain qualifications prescribed by the Constitution for being elected as an M. L. A. The candidate must:
- be a citizen of India;
- have attained the age of 25 years;
- have his/her name in the voters’ list;
- not hold any Office of Profit; and
- not be a government servant.
Subject to the provisions of ARTICLE 333, the Legislative Assembly of each State shall consist of not more than five hundred, and not less than sixty, members chosen
by direct election from territorial constituencies in the State.
The Legislative council or Vidhan Parishad is partly
elected and partly nominated. Most of the members are indirectly elected in accordance with the principle of Proportional Representation by means of single transferable vote system. Different categories of members represent different interests. The composition of the Legislative Council is as follows:
i. One-third members of the Council are elected by the members of the Vidhan Sabha.
ii. One-third of the members of the Vidhan Parishad are elected by the electorates consisting of members of Municipalities, District Boards and other local bodies in the State;
iii. One-twelfth members are elected by the electorate consisting of graduates in the State with a standing of three years;
iv. One-twelfth members are elected by the electorate consisting of teachers of educatioal institutions within the State not lower in standard than a secondary school who have teaching experience of at least three years;
v. The remaining, i.e. about one-sixth members are nominated by the Governor from amongst the persons having special knowledge in the sphere of literature, science, arts, co-operative movement and social service.
The State Legislature is empowered to make laws on State List and Concurrent List. The Parliament and the Legislative Assemblies have the right to make the laws on the subjects mentioned in the Concurrent List. But in case of contradiction between the Union and State law on the subject the law made by the Parliament shall prevail.
State legislature has exclusive powers over subjects enumerated in List II of the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution and concurrent powers over those enumerated in List III. Financial powers of legislature include authorisation of all expenditure, Taxation and borrowing by the State Government. Legislative assembly alone has power to originate Money bills. Legislative council can make only recommendations in respect of changes it considers necessary within a period of fourteen days of the receipt of money bills from Assembly. Assembly can accept or reject these recommendations.
State legislatures, apart from exercising the usual power of financial control, use all normal parliamentary devices like questions, discussions, debates, adjournments and no-confidence motions and resolutions to keep a watch over day-to-day work of the executive. They also have their committees on estimates and public accounts to ensure that grants sanctioned by legislature are properly utilised.,
A state legislature is the law-making body of a state. In the United States, each state has its own legislature, which is responsible for making laws that govern the state. The legislature is typically made up of two houses, a lower house and an upper house. The lower house is usually called the House of Representatives, while the upper house is usually called the Senate.
The legislative process begins with the introduction of a bill. A bill is a proposed law that is introduced by a member of the legislature. Once a bill is introduced, it is referred to a committee for study. The committee may hold hearings and debate the bill. If the committee approves the bill, it is sent back to the full legislature for debate. If the full legislature passes the bill, it is sent to the governor for signature. The governor can either sign the bill into law, veto the bill, or allow it to become law without his or her signature.
The legislative term is the length of time that a member of the legislature is elected to serve. The length of the legislative term varies from state to state. In some states, members of the legislature are elected to two-year terms. In other states, members of the legislature are elected to four-year terms.
The legislative veto is a power that allows the legislature to overturn a decision made by the executive branch. The legislative veto is not used in all states. In some states, the legislature must pass a law to overturn a decision made by the executive branch. In other states, the legislature can simply vote to overturn a decision made by the executive branch.
The list of state legislatures includes the name of each state and the number of members in each house of the state legislature. The number of members in each house of the state legislature varies from state to state. In some states, the lower house has more members than the upper house. In other states, the upper house has more members than the lower house.
The members of the state legislature are elected by the people of the state. The qualifications for state legislators vary from state to state. In some states, there is no minimum age requirement for state legislators. In other states, there is a minimum age requirement of 21 years old. In some states, there is no residency requirement for state legislators. In other states, there is a residency requirement of one year or two years.
A Quorum is the minimum number of members of the legislature that must be present in order for the legislature to conduct business. The quorum requirement varies from state to state. In some states, the quorum requirement is a Simple Majority of the members of the legislature. In other states, the quorum requirement is a two-thirds majority of the members of the legislature.
Redistricting is the process of redrawing the boundaries of legislative districts. Redistricting is done every ten years after the census. The purpose of redistricting is to ensure that each legislative district has approximately the same number of people.
A session is a period of time during which the legislature meets. The length of a legislative session varies from state to state. In some states, the legislature meets every year. In other states, the legislature meets every other year.
The speaker of the house is the leader of the lower house of the state legislature. The speaker of the house is elected by the members of the lower house. The speaker of the house is responsible for presiding over the meetings of the lower house.
The state constitution is the supreme law of the state. The state constitution establishes the structure of the state government and the powers of the state government. The state constitution can be amended by a majority vote of the legislature or by a constitutional convention.
The state government is the government of a state. The state government is responsible for providing Services to the people of the state, such as Education, healthcare, and transportation. The state government is also responsible for enforcing the laws of the state.
The state senate is the upper house of the state legislature. The state senate is usually smaller than the lower house. The state senate is responsible for confirming the appointments made by the governor. The state senate is also responsible for trying impeachment cases.
Term limits are restrictions on the number of terms that a person can serve in a particular office. Term limits are used in some states to limit the number of terms that a person can serve in the state legislature.
A veto is the power of the governor to reject a bill passed by the legislature. The governor can either sign the bill into law, veto the bill, or allow it to become law without his or her signature. If the governor vetoes a bill, the legislature can override the veto with a two-thirds majority vote.
What is a state legislature?
A state legislature is the legislative body of a state government, responsible for making laws for the state.
What are the different types of state legislatures?
There are two main types of state legislatures: bicameral and unicameral. Bicameral legislatures have two chambers, while unicameral legislatures have only one.
What are the powers of a state legislature?
The powers of a state legislature vary from state to state, but they generally include the power to make laws, the power to raise taxes, and the power to approve the state budget.
How are members of a state legislature elected?
Members of a state legislature are elected by the people of the state. In most states, members of the lower house are elected from single-member districts, while members of the upper house are elected from multi-member districts.
What is the term of office for a member of a state legislature?
The term of office for a member of a state legislature varies from state to state. In most states, members of the lower house serve two-year terms, while members of the upper house serve four-year terms.
What is the salary for a member of a state legislature?
The salary for a member of a state legislature varies from state to state. In most states, members of the lower house are paid less than members of the upper house.
What are the qualifications for being a member of a state legislature?
The qualifications for being a member of a state legislature vary from state to state. In most states, members of the lower house must be at least 21 years old and citizens of the state for at least two years. Members of the upper house must be at least 25 years old and citizens of the state for at least four years.
What are the duties of a member of a state legislature?
The duties of a member of a state legislature vary from state to state, but they generally include the following:
- Attending legislative sessions
- Voting on legislation
- Serving on committees
- Representing the interests of their constituents
What are the challenges of being a member of a state legislature?
The challenges of being a member of a state legislature vary from state to state, but they generally include the following:
- The long hours and the demanding schedule
- The need to balance the needs of their constituents with the needs of the state
- The need to deal with difficult and controversial issues
What are the rewards of being a member of a state legislature?
The rewards of being a member of a state legislature vary from state to state, but they generally include the following:
- The opportunity to make a difference in the lives of their constituents
- The opportunity to serve their state
- The opportunity to work with other elected officials
The legislative branch of the United States government is called the:
(A) Congress
(B) Senate
(C) House of Representatives
(D) Supreme CourtThe House of Representatives has how many members?
(A) 435
(B) 100
(C) 535
(D) 1,000The Senate has how many members?
(A) 435
(B) 100
(C) 535
(D) 1,000The Vice President of the United States is the President of the Senate.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe Speaker of the House is the Leader of the House of Representatives.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe Senate is made up of two senators from each state.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe House of Representatives is made up of representatives from each state, with the number of representatives based on the Population of the state.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe President can veto a bill passed by Congress.
(A) True
(B) FalseCongress can override a veto by a two-thirds vote of both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
(A) True
(B) FalseThe legislative branch of the United States government is responsible for making laws.
(A) True
(B) False