Introduction
- If you exercise on a hot day, you are likely to lose a lot of water in sweat. Then, for the next several hours, you may notice that you do not pass urine as often as normal and that your urine is darker than usual.
- Do you know why this happens? Your body is low on water and trying to reduce the amount of water lost in urine. The amount of water lost in urine is controlled by the kidneys, the main organs of the excretory system.
- Excretion is the process of removing wastes and excess water from the body. It is one of the major ways the body maintains homeostasis.
- Although the kidneys are the main organs of excretion, several other organs also excrete wastes.
- They include the large intestine, liver, skin, and lungs. All of these organs of excretion, along with the kidneys, make up the excretory system.
- The roles of the other excretory organs are summarized below:
- The large intestine eliminates solid wastes that remain after the digestion of food.
- The liver breaks down excess amino acids and toxins in the blood.
- The skin eliminates excess water and salts in sweat.
- The lungs exhale water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Urinary System
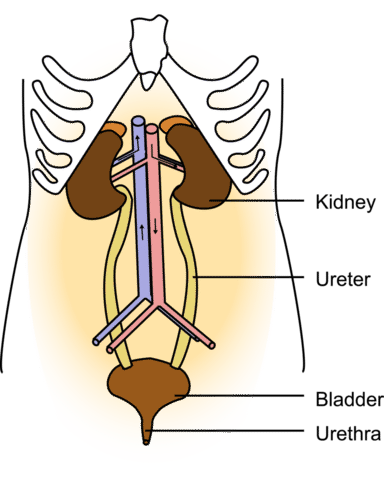
- The kidneys are part of the urinary system, which is shown in Figure below.
- The main function of the urinary system is to filter waste products and excess water from the blood and excrete them from the body.
Kidneys and Nephrons
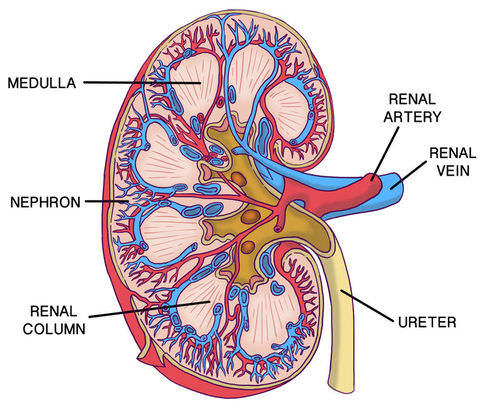
- The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs just above the waist. A cross-section of a kidney is shown in Figure below.
- The function of the kidney is to filter blood and form urine.
- Urine is the liquid waste product of the body that is excreted by the urinary system. Nephrons are the structural and functional units of the kidneys.
- A single kidney may have more than a million nephrons!
Filtering Blood and Forming Urine
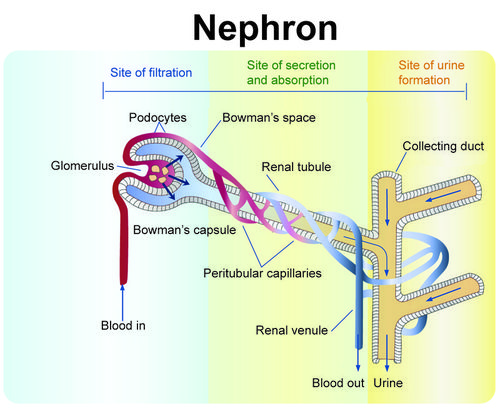
- As shown in Figure below, each nephron is like a tiny filtering plant. It filters blood and forms urine in the following steps:
- Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery, which branches into capillaries. When blood passes through capillaries of the glomerulus of a nephron, blood pressure forces some of the water and dissolved substances in the blood to cross the capillary walls into Bowman’s capsule.
- The filtered substances pass to the renal tubule of the nephron. In the renal tubule, some of the filtered substances are reabsorbed and returned to the bloodstream. Other substances are secreted into the fluid.
- The fluid passes to a collecting duct, which reabsorbs some of the water and returns it to the bloodstream. The fluid that remains in the collecting duct is urine.
Excretion of Urine
- From the collecting ducts of the kidneys, urine enters the ureters, two muscular tubes that move the urine by peristalsis to the bladder (see Figure above). The bladder is a hollow, sac-like organ that stores urine.
- When the bladder is about half full, it sends a nerve impulse to a sphincter to relax and let urine flow out of the bladder and into the urethra.
- The urethra is a muscular tube that carries urine out of the body. Urine leaves the body through another sphincter in the process of urination.
- This sphincter and the process of urination are normally under conscious control.
Kidneys and Homeostasis
- The kidneys play many vital roles in homeostasis. They filter all the blood in the body many times each day and produce a total of about 1.5 liters of urine.
- The kidneys control the amount of water, ions, and other substances in the blood by excreting more or less of them in urine.
- The kidneys also secrete HORMONES that help maintain homeostasis. Erythropoietin, for example, is a kidney hormone that stimulates bone marrow to produce red blood cells when more are needed.
- The kidneys themselves are also regulated by hormones. For example, antidiuretic hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates the kidneys to produce more concentrated urine when the body is low on water.
Kidney Disease and Dialysis
- A person can live a normal, healthy life with just one kidney. However, at least one kidney must function properly to maintain life.
- Diseases that threaten the Health and functioning of the kidneys include kidney stones, infections, and diabetes.
- Kidney stones are mineral crystals that form in urine inside the kidney. They may be extremely painful. If they block a ureter, they must be removed so urine can leave the kidney and be excreted.
- Bacterial infections of the urinary tract, especially the bladder, are very common. Bladder infections can be treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. If untreated, they may lead to kidney damage.
- Uncontrolled diabetes may damage capillaries of nephrons. As a result, the kidneys lose much of their ability to filter blood. This is called kidney failure.
- The only cure for kidney failure is a kidney transplant, but it can be treated with dialysis. Dialysis is a medical procedure in which blood is filtered through a machine.
,
The excretion system is responsible for removing waste products from the blood and body. The main organs of the excretion system are the kidneys, which filter the blood and produce urine. The urine is then transported to the bladder, where it is stored until it is excreted from the body through the urethra.
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located in the lower back, just above the waist. They are about the size of a fist and weigh about 5 ounces each. The kidneys are responsible for filtering the blood and removing waste products, such as urea, creatinine, and uric acid. They also produce hormones that help to regulate blood pressure and red blood cell production.
The kidneys are made up of millions of tiny units called nephrons. Each nephron has a glomerulus, which is a Network of capillaries that filters the blood. The glomerulus is surrounded by Bowman’s capsule, which collects the filtered blood. The filtered blood then flows into the proximal convoluted tubule, where nutrients are reabsorbed into the bloodstream. The remaining fluid then flows into the loop of Henle, which is a U-shaped structure that helps to concentrate the urine. The urine then flows into the distal convoluted tubule, where more nutrients are reabsorbed. The final step in the formation of urine is secretion, which is the process of adding substances to the urine. The urine then flows into the collecting duct, which transports the urine to the ureters.
The ureters are two muscular tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine until it is time to urinate. The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The excretion process is a complex process that involves filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion. Filtration is the process of removing waste products from the blood. Reabsorption is the process of returning nutrients to the bloodstream. Secretion is the process of adding substances to the urine. Excretion is the process of removing urine from the body.
The excretion system is an important part of the body’s overall health. It helps to remove waste products from the blood and body, and it helps to regulate blood pressure and red blood cell production. If the excretion system is not working properly, it can lead to a variety of health problems, such as kidney failure, high blood pressure, and anemia.
Here are some tips to keep your excretion system healthy:
- Drink plenty of fluids. Water is the best choice, but you can also drink other fluids, such as juice, milk, and tea.
- Eat a healthy diet. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise helps to keep your kidneys healthy and functioning properly.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can damage your kidneys.
- See your doctor regularly. If you have any concerns about your kidneys, see your doctor for a checkup.
What is the excretory system?
The excretory system is responsible for removing waste products from the body. These waste products are produced as a result of the body’s metabolic processes. The excretory system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
What are the functions of the excretory system?
The functions of the excretory system are to:
- Remove waste products from the blood
- Regulate blood volume and blood pressure
- Maintain acid-base balance
- Produce hormones that regulate red blood cell production
What are the waste products that are removed by the excretory system?
The waste products that are removed by the excretory system are:
- Urea
- Creatinine
- Uric acid
- Ammonia
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chloride
How does the excretory system work?
The excretory system works by filtering the blood and removing waste products. The kidneys are the main organs of the excretory system. They filter the blood and produce urine. The urine is then transported to the bladder, where it is stored until it is excreted from the body through the urethra.
What are some common problems with the excretory system?
Some common problems with the excretory system include:
- Kidney stones
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Bladder infections
- Kidney failure
- Polycystic kidney disease
What are some ways to keep the excretory system healthy?
Some ways to keep the excretory system healthy include:
- Drinking plenty of fluids
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Getting regular check-ups with your doctor
The main function of the excretory system is to:
(a) remove waste products from the body
(b) produce urine
(c) regulate blood pressure
(d) produce hormonesThe kidneys are located in the:
(a) abdomen
(b) chest
(c) head
(d) backThe ureters are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the:
(a) bladder
(b) urethra
(c) kidneys
(d) ureterThe bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine until it is time to urinate.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
(a) True
(b) FalseUrine is a waste product that is made up of water, urea, and other waste products.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe kidneys filter the blood to remove waste products and produce urine.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe bladder contracts to empty urine out of the body.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe urethra is a muscular tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
(a) True
(b) FalseThe excretory system is responsible for removing waste products from the body.
(a) True
(b) False