<–2/”>a >A.H. Dani (1960) has devided the Neolithic Cultures of Assam into six distinct zones: namely Cachar Hills Zone, Sadiya Frontiers, Naga Hills Zone, Khasi Hills Zone, Garo Hills Zone, and Brahmaputra Valley Zone. Regarding the discovery of Neolithic tools and implements in the Brahmaputra valley, it has been written that the materials
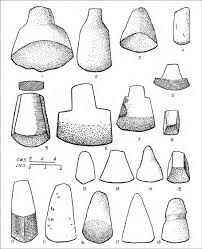
available for study are few and far between. , whereas he made the Classification of tool types under seven categories such as facetted tools, shouldered tools, splayed axe, rounded but axe with broad cutting edge, wedges and grooved hammer stones.
On the basis of his analytical study of tool types, he was also of the opinion that Southeast Asian Elements came in different waves at different times through Myanmar (former Burma) and a definite chronology could be ascribed on the basis of a black polished ware associated with the specialised tools of the later complexes of Burma.
Various Prehistoric sites located in Assam are:-
Daojali Hading is an important Neolithic site in Dima Hasao District of Assam.Extensive digging at this site has yielded polished stone tools, ceramics and kitchen items such as grinders, pestles and mortars.
Sarutaru is an important Neolithic site in Kamrup district, Assam.It is a hamlet situated at 25 km southeast of Guwahati, and the Neolithic site lies on the top of a small hillock about 125 m high from the foothill.
Marakdola is a low mound situated at distance of 1 km from the Neolithic site of Sarutaru.
 ,
,
The Neolithic Culture of Assam is a period of human history that lasted from about 8000 to 2000 BC. It is characterized by the development of agriculture, the use of stone tools, and the construction of permanent settlements.
The Neolithic Culture of Assam can be divided into three phases:
- Early Neolithic (8000-6000 BC): This phase is characterized by the development of agriculture and the use of stone tools.
- Middle Neolithic (6000-4000 BC): This phase is characterized by the construction of permanent settlements and the development of Pottery.
- Late Neolithic (4000-2000 BC): This phase is characterized by the decline of agriculture and the rise of metalworking.
Neolithic settlements in Assam were typically located near rivers or other sources of water. They were often surrounded by walls or ditches for protection.
The economy of the Neolithic people of Assam was based on agriculture. They grew rice, millet, and other crops. They also raised Livestock, such as cattle, pigs, and chickens.
The Neolithic people of Assam used stone tools for a variety of purposes, including hunting, farming, and construction. They also made pottery and baskets.
The Neolithic people of Assam produced a variety of art, including pottery, stone sculptures, and paintings. They also had a complex religion, which included a belief in a variety of gods and spirits.
The Neolithic Culture of Assam declined around 2000 BC. This decline was likely due to a number of factors, including Climate change, warfare, and the spread of new technologies.
The Neolithic Culture of Assam left a lasting legacy on the region. Its people developed a number of important technologies, such as agriculture and pottery. They also produced a rich body of art and religion.
The Neolithic Culture of Assam is a fascinating period of human history. It is a time when people began to develop new technologies and ways of life. The people of Assam were pioneers in the development of agriculture, and their culture had a lasting impact on the region.
The Neolithic Culture of Assam is a reminder of the importance of innovation and adaptation. The people of Assam were able to thrive in a challenging Environment, and their culture continues to inspire people today.
What is Neolithic Culture?
Neolithic culture is a period in human history when people began to live in settled communities and practice agriculture. This period began around 10,000 years ago and lasted until the beginning of the Bronze Age.
What are the characteristics of Neolithic Culture?
Neolithic culture is characterized by the following:
- Settled agriculture: People began to live in settled communities and grow their own food. This led to a more stable and predictable way of life.
- Domesticated animals: People began to domesticate animals, such as cows, pigs, and sheep. This provided them with a source of food and labor.
- Pottery: People began to make pottery, which was used for cooking, storing food, and carrying water.
- Stone tools: People began to make stone tools, which were used for hunting, farming, and building.
- Art: People began to create art, such as paintings, sculptures, and jewelry.
What are the benefits of Neolithic Culture?
Neolithic culture had a number of benefits, including:
- Increased food production: Settled agriculture allowed people to produce more food than they could by hunting and gathering. This led to a more stable and predictable way of life.
- Improved Health: Domesticated animals provided people with a source of food and labor. This improved their diet and allowed them to produce more goods.
- Increased social complexity: Settled communities led to the development of more complex social structures. This included the development of governments, religions, and trade networks.
- Increased technological innovation: The development of pottery, stone tools, and art led to the development of new technologies. This improved people’s lives and made their communities more efficient.
What are the drawbacks of Neolithic Culture?
Neolithic culture also had a number of drawbacks, including:
- Environmental Degradation: Settled agriculture can lead to environmental degradation, such as deforestation and Soil erosion.
- Social inequality: The development of more complex social structures can lead to social inequality. This includes the development of classes, castes, and slavery.
- Warfare: The development of more complex social structures can also lead to warfare. This is because people are more likely to fight over Resources and power when they live in close proximity to each other.
What is the legacy of Neolithic Culture?
Neolithic culture had a profound impact on the development of human Society. It led to the development of agriculture, which allowed people to produce more food and live in settled communities. This in turn led to the development of more complex social structures, technologies, and art. Neolithic culture is still evident in the world today, as many people still live in agricultural societies and use stone tools and pottery.
Here are some MCQs on the topics of Neolithic Culture, without mentioning the topic of Neolithic Culture of Assam:
-
Which of the following is not a characteristic of Neolithic culture?
(A) The use of polished stone tools
(B) The development of agriculture
(C) The construction of permanent settlements
(D) The domestication of animals -
Neolithic culture first developed in which of the following regions?
(A) The Middle East
(B) South Asia
(C) East Asia
(D) Europe -
Which of the following is not a type of Neolithic pottery?
(A) Red ware
(B) Black and red ware
(C) Painted gray ware
(D) Black ware -
Which of the following is not a Neolithic site in India?
(A) Mehrgarh
(B) Harappa
(C) Mohenjo-daro
(D) Lothal -
Which of the following is not a Neolithic site in China?
(A) Yangshao
(B) Longshan
(C) Dawenkou
(D) Sanxingdui -
Which of the following is not a Neolithic site in Europe?
(A) Sesklo
(B) Dimini
(C) Lerna
(D) Knossos -
Which of the following is not a characteristic of Neolithic religion?
(A) The worship of nature spirits
(B) The belief in an afterlife
(C) The construction of temples
(D) The practice of human sacrifice -
Neolithic culture began to decline in which of the following periods?
(A) The Bronze Age
(B) The Iron Age
(C) The Classical Age
(D) The Middle Ages -
Which of the following is not a reason for the decline of Neolithic culture?
(A) The development of new technologies
(B) The spread of new diseases
(C) The rise of new Social Classes
(D) The onset of Climate Change -
Which of the following is not a legacy of Neolithic culture?
(A) The development of agriculture
(B) The construction of permanent settlements
(C) The domestication of animals
(D) The invention of writing