Minerals of Madhya Pradesh:-
Minerals in Madhya Pradesh occur in abundance in its several districts. In terms of the mineral production the state ranks third next only to Jharkhand and Chhatisgarh. The state of Madhya is said to have a favourable geotectonic setting that accommodates every episode of mineralisation the earth has experienced. It includes the occurrences of almost all varieties of minerals required as industrial input in the growing economy. The oldest group of rocks comprising of Archaeans and Proterozoic formation constitute nearly 45% area of the State. The next younger formation of Carboniferous to lower Cretaceous comprising Gondwana Super Group covers 10% area while the formation of Cretaceous to Paleocene comprising mostly of Deccan Trap basalt constitutes 38% area of the State. 16 Major Minerals are considered of specific importance as they contribute significantly in development of economy of the state. These include the Limestone, Bauxite, Coal, Manganese Ore, Diamond, Base metals, Dolomite, Rock Phosphate and Granite. Others include Marble, Flagstone, Slate, Calcite, Quartz and Silica sand, Molybdenum and Fire clay.
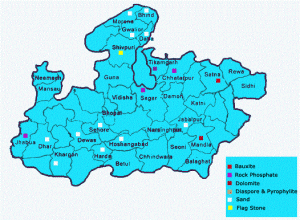
SALIENT FEATURES OF MINERAL WEALTH IN MP:-
- The only working mines of diamond in India are in Panna district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Thickest coal seam of Asia lies in the Singrouli Coal Field, dist. Sidhi and other coal blocks near Chhindwara of the state.
- Country’s largest Open Cast Copper Mine is at Malajkhand in Balaghat district of the state.
- Occurrences of Paradiso granite is in a large tract of M.P.
- Highest cement producing state in India with 8 major and 3 mini cement Plants, producing 15 percent cement of the country.
- Largest producer of copper, limestone, slate, diaspore and pyrophyllite.
- Leading producer of manganese , dolomite, rock phosphate and fire clay.
Limestone:-
Limestone forms an important segment of mineral Resources of Madhya Pradesh. As per the available statistics of Indian Bureau of Mines, the total reserve of limestone in the state is around 4.79 percent of the total national reserve of several million tonnes. Vast terrain of the state is prevalent with suitable grade of limestone for manufacturing of cement.
Bauxite:-
Another significant mineral resource of the state is Bauxite. The state has vast deposits of Bauxite, mainly in Balaghat district, Mandla district, Shahdol district, Rewa district, and Sidhi district. The highest degree of bauxite deposits of Jabalpur district are mainly used for calcinations to be used in refractory units.
Coal:-
Coal constitutes the vital raw material required for consumption in the Energy sector. The state of Madhya Pradesh contributes about 14.09 percent of the total national reserve of coal. Madhya Pradesh has a large tract of favourable rock formation where coal is found which is distributed in Shahdol district, Chhindwara district, Betul district, Narsinghpur district and Sidhi district. The deposit of Sidhi district is considered as one of the largest deposits in the country. This mineral resource is mostly utilised in the thermal power plants, railways and industries. Based on the deposits of coal, three Thermal Power Plants are in operation in this state. Madhya Pradesh has large reserves of medium coking coal deposits in Shahdol district.
Manganese Ore:-
High strategic importance is given to Manganese Ore. Madhya Pradesh is India’s foremost source of manganese ore with a reserve of around 23.64 million tonnes accounting for near about 14.13 percent of the national reserve. The deposits are mostly located in Balaghat and Chhindwara districts constituting the bulk of deposit available in the state. Manganese is seldom used directly as Metal and it also finds its application in various value added products like Ferro manganese, steel making, dry batteries, glass and chemical industries. The bulk of reserve of manganese ore found in Balaghat belt is of blast furnace grade and the reserve of Ferro manganese ore is very limited.
Copper:-
Base metals of Madhya Pradesh include copper, lead and zinc. In Madhya Pradesh as many as 117 base metals are on record. The copper ore occurrences are in Balaghat, Bastar region, Jabalpur, Betul, Hoshangabad district , Chhindwara, Sagar, Datia, Sidhi, Dewas, Shivpuri districtand Tikamgarh districts. The Malanjkhand copper mine is the largest hard rock opencast pit of the country.
Dolomite:-
Dolomite is another significant mineral found in the state. High grade dolomite has become the major industrial mineral because of its use in iron and steel and refractory industries. Occurrences of dolomite have been recorded in Mandla district, Seoni district, Chhatarpur district, Sagar district and Jabalpur district. The dolomite deposits of Mandla district are mainly used in iron and steel industries in and outside the state. The dolomite deposit of Jabalpur is mainly consumed in the refractory industries. The dolomite deposits of Mandla, Sagar and Chhatarpur districts have attained significance because of their high content of magnesia.
Rock Phosphate:-
Rock Phosphate is another mineral resource found in the state of Madhya Pradesh. In this state, reserve of rock phosphate has been estimated around 35.99 million tonnes constituting almost 24.76 percent of the national reserve. The deposits are located in Jhabua, Sagar and Chhatarpur districts.
Granites:-
Granites are in much demand in the modern construction work as decorative and ornamental stones. Granite deposits are widespread throughout the state.
Marble:-
Moreover, Madhya Pradesh is fast emerging as marble producing state in the country. Exotic varieties of marble are available in Katni, Narsinghpur, Jabalpur, Mandla, Hoshangabad, Sidhi and Jhabua districts. The polished marble of Katni district is considered as good as Italian marble.
Pyrophyllite:-
Other major mineral of Madhya Pradesh is Pyrophyllite. The deposits of Pyrophyllite occur in Chhatarpur, Shivpuri and Tikamgarh districts of the state. Its occurrences have also been found in Gwalior district.
Molybdenum :-
Molybdenum is an important strategic mineral. It is mainly found in Malanjkhand area of Balaghat district. Over 94 million tonnes of fireclays of various grades have been estimated in Madhya Pradesh. The deposits distributed in Shahdol district, Gwalior, Katni, Jabalpur, Sidhi, Betul and Chhindwara districts has led to the establishment of a number of refractory and some ceramic industries in the state.
Other Minerals:-
Madhya Pradesh is the sole producer of slate in the country. White and red coloured slate found in Mandsaur district is used mainly in producing slate pencil. Significant deposits of calcite occur in the western part of Madhya Pradesh mainly in Barwani district. The total reserve of quartz and silica sand in the state of Madhya Pradesh accounts for around 4387 thousand tonnes which is nearly 0.18 percent of the total reserve of the country. The deposits are distributed in the districts of Chhatarpur, Chhindwara, Datia, Gwalior, Jhabua, Mandla, Rewa, etc. Further, the state of Madhya Pradesh has a distinction of having the lone diamond mine in the country located at Majhgawan area in Panna District. Also, wide deposits of white, cream, pink and red coloured sandstone occurs in Shivpuri district, Guna district, Gwalior district, Panna district, Vidisha district, Raisen district and Sagar district.
There are many Mineral Based Industries in Madhya Pradesh including cement plants, thermal power plants, and caustic soda plants.
,
Madhya Pradesh is a state in central India. It is the second-largest state in India by area, after Rajasthan. The state has a Population of over 75 million people, making it the fifth-most populous state in India. The capital of Madhya Pradesh is Bhopal.
Madhya Pradesh is a mineral-rich state. The major minerals found in Madhya Pradesh are bauxite, coal, diamond, fluorite, iron ore, lead, lignite, magnetite, manganese, nickel, potassium feldspar, quartz, sapphire, shale, silicosis, talc, titanium, uranium, and zinc.
Bauxite is a mineral that is used to produce aluminum. The major bauxite deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat, Chhindwara, and Seoni.
Coal is a fossil fuel that is used to generate electricity. The major coal deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Singrauli, Sohagpur, and Umaria.
Diamond is a precious stone that is used in jewelry. The major diamond deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Panna and Chhatarpur.
Fluorite is a mineral that is used to produce hydrofluoric acid. The major fluorite deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Jhabua and Dhar.
Iron ore is a mineral that is used to produce iron and steel. The major iron ore deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Jhabua, Dhar, and Ratlam.
Lead is a metal that is used to produce batteries and other products. The major lead deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
Lignite is a type of coal that is used to generate electricity. The major lignite deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Singrauli and Sohagpur.
Magnetite is a mineral that is used to produce iron and steel. The major magnetite deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Jhabua, Dhar, and Ratlam.
Manganese is a metal that is used to produce steel and other products. The major manganese deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat, Chhindwara, and Seoni.
Nickel is a metal that is used to produce stainless steel and other products. The major nickel deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
Potassium feldspar is a mineral that is used to produce glass and other products. The major potassium feldspar deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
Quartz is a mineral that is used to produce glass and other products. The major quartz deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
Sapphire is a precious stone that is used in jewelry. The major sapphire deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Panna and Chhatarpur.
Shale is a sedimentary rock that is used to produce oil and gas. The major shale deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Singrauli and Sohagpur.
Silicosis is a lung disease that is caused by inhaling silica dust. Silica dust is found in many minerals, including quartz.
Talc is a mineral that is used to produce talcum powder and other products. The major talc deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
Titanium is a metal that is used to produce aircraft and other products. The major titanium deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
Uranium is a radioactive metal that is used to produce nuclear power. The major uranium deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
Zinc is a metal that is used to produce batteries and other products. The major zinc deposits in Madhya Pradesh are located in the districts of Balaghat and Chhindwara.
The mining Industry is an important part of the economy of Madhya Pradesh. The State Government has taken steps to promote the mining industry, including providing subsidies and tax breaks to mining companies. The mining industry has created jobs and helped to improve the economy of Madhya Pradesh.
However, the mining industry has also had some negative impacts on the Environment. Mining can lead to deforestation, Soil erosion, and Water Pollution. The state government is working to address these environmental problems.
Overall, the mining industry is an important part of the economy of Madhya Pradesh. The state government is working to promote the mining industry while also addressing the environmental problems that it can cause.
What are the different types of minerals?
Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, crystalline substances with a definite chemical composition and a characteristic crystal structure.
What are the most common minerals?
The most common minerals are quartz, feldspar, and mica.
What are the uses of minerals?
Minerals are used in a variety of products, including construction materials, electronics, and jewelry.
What are the benefits of minerals?
Minerals provide a variety of benefits, including structural strength, electrical conductivity, and beauty.
What are the risks of minerals?
Minerals can be hazardous if they are not handled properly. Some minerals can be toxic, and others can cause respiratory problems.
How are minerals formed?
Minerals are formed by the cooling and crystallization of magma or lava. They can also be formed by the weathering and erosion of rocks.
Where are minerals found?
Minerals can be found in a variety of places, including the Earth’s crust, the ocean floor, and even outer space.
How are minerals mined?
Minerals are mined using a variety of methods, including open-pit mining, underground mining, and in-situ leaching.
What is the future of minerals?
The future of minerals is uncertain. The demand for minerals is expected to increase as the world’s population grows and economies develop. However, the supply of minerals is limited, and some minerals are becoming increasingly scarce.
What are the different types of mining?
There are three main types of mining: open-pit mining, underground mining, and in-situ leaching.
Open-pit mining is the most common type of mining. It involves removing the overburden (soil and rock) to expose the mineral deposit. The mineral is then extracted using a variety of methods, such as blasting, shoveling, and loading.
Underground mining is used to extract minerals that are located deep below the surface. It is a more expensive and dangerous type of mining than open-pit mining.
In-situ leaching is a method of extracting minerals that are dissolved in water. The water is pumped into the ground and the minerals are extracted using a variety of methods, such as pumping, filtration, and Precipitation.
What are the environmental impacts of mining?
Mining can have a number of negative environmental impacts, including deforestation, water pollution, and Air Pollution.
Deforestation occurs when trees are cut down to make way for mines. This can lead to soil erosion and the loss of habitat for wildlife.
Water pollution can occur when mining operations contaminate surface water and groundwater. This can make water unsafe for drinking, bathing, and Irrigation.
Air pollution can occur when mining operations release dust and other pollutants into the air. This can cause respiratory problems for people living near mines.
What are the social impacts of mining?
Mining can have a number of negative social impacts, including displacement, Health problems, and conflict.
Displacement occurs when people are forced to leave their homes because of mining operations. This can lead to loss of land, livelihood, and culture.
Health problems can occur when people are exposed to mining dust and other pollutants. This can lead to respiratory problems, cancer, and other health issues.
Conflict can occur between mining companies and local communities. This can be due to disputes over land rights, environmental impacts, and compensation.
What are the economic impacts of mining?
Mining can have a number of positive economic impacts, including job creation, tax revenue, and economic Growth.
Job creation occurs when mining companies hire workers to extract and process minerals. This can lead to increased EMPLOYMENT and income in local communities.
Tax revenue is generated when mining companies pay taxes on their profits. This can be used to fund government Services, such as Education and healthcare.
Economic growth can occur when mining companies invest in new Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE and technology. This can lead to increased economic activity in local communities.
What are the ethical issues of mining?
Mining can raise a number of ethical issues, such as child labor, forced labor, and environmental destruction.
Child labor occurs when children are forced to work in mining operations. This can expose them to dangerous conditions and hazardous materials.
Forced labor occurs when people are forced to work in mining operations against their will. This can be a form of modern-day slavery.
Environmental destruction occurs when mining operations damage the environment. This can include deforestation, water pollution, and air pollution.
What are the sustainable mining practices?
Sustainable mining practices are those that minimize the environmental and social impacts of mining.
Some sustainable mining practices include:
- Restoring land
Sure, here are some MCQs about minerals:
-
Which of the following is not a mineral?
(A) Gold
(B) Diamond
(C) Water
(D) Salt -
Which of the following is the most abundant mineral in the Earth’s crust?
(A) Quartz
(B) Feldspar
(C) Olivine
(D) Pyroxene -
Which of the following is the hardest mineral on Earth?
(A) Diamond
(B) Corundum
(C) Topaz
(D) Quartz -
Which of the following is the most common gemstone?
(A) Diamond
(B) Ruby
(C) Sapphire
(D) Emerald -
Which of the following is the most valuable mineral?
(A) Gold
(B) Platinum
(C) Silver
(D) Palladium -
Which of the following is the most important mineral for the construction industry?
(A) Sand
(B) Gravel
(C) Clay
(D) Limestone -
Which of the following is the most important mineral for the electronics industry?
(A) Silicon
(B) Germanium
(C) Gallium
(D) Indium -
Which of the following is the most important mineral for the automotive industry?
(A) Iron
(B) Copper
(C) Aluminum
(D) Zinc -
Which of the following is the most important mineral for the energy industry?
(A) Coal
(B) Oil
(C) Natural gas
(D) Uranium -
Which of the following is the most important mineral for the agriculture industry?
(A) Phosphate
(B) Potash
(C) Nitrogen
(D) Sulfur
I hope these questions were helpful!