Metallurgy of iron
Iron is an important constituent of hemoglobin, which is in blood. Iron is the Metal used most widely in industries and hence may be called the king of metals. It is the second most abundant metal after aluminum. Iron does not occur in native state, since it is oxidized easily.
| Ores of Iron | Chemical Name | Chemical formula |
| Brown haematite or limonite | Hydrated ferric oxide | 2Fe2O3.3H2O |
| Red haematite | Anhydrous hematite | Fe2O3 |
| Iron pyrites | Iron disulphide | FeS2 |
| Magnetite | Triferric tetraoxide | Fe3O4 |
| Siderite | Ferrous carbonate | FeCO3 |
It is usually extracted from haematite and limonite.
Extraction of Iron
Extraction of iron from its Ore is the third and the penultimate process in the Metallurgy. The extraction of metals and its isolation occurs over few major steps:
Concentration of Ore
Extraction of metal from the concentrated Ore
Purification of the metal
How is iron extracted from its ore? It’s a long process which begins with Concentration through calcination roasting. Concentration removes the water and other volatile impurities such as sulphur and carbonates. This concentrated ore is mixed with limestone (CaCO3) and Coke and fed into the blast furnace from the top. It is in the blast furnace that extraction of iron occurs.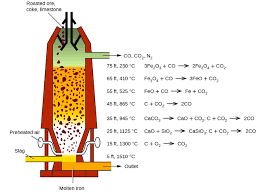
What happens in the Blast Furnace?
The purpose of a Blast Furnace is to reduce the concentrated ore chemically to its liquid metal state. A Blast furnace is a gigantic, steel stack lined with refractory brick where the concentrated iron ore, coke and limestone are dumped from the top, and a blast of hot air is blown into the bottom. All the three ingredients are crushed into small round pieces and mixed and put on a hopper which controls the input.
Hot air is blown from the bottom and coke it burned to yield temperatures up to about 2200K. Burning coke provides the majority of the heat required for this process. At such high temperatures, Coke reacts with the Oxygen in the hot air to form Carbon Monoxide (CO). The CO and heat now move upwards and meet the raw material running down from the top. The temperature in the upper parts of the Blast Furnace is considerably lower than the 2200K at the bottom. In this part, Haematite (Fe2O3) and Magnetite (Fe3O4) are reduced to Ferrous Oxide (FeO).
Reactions in the Blast Furnace
At 500 – 800 K, In the upper parts with lower temperatures,
Process of Extraction of Iron: Inside the Blast Furnace
3Fe2O3+CO→2Fe3O4+CO2 Fe3O4+4CO→3Fe+4CO2 Fe2O3+CO→2FeO+CO2
At 900 – 1500 K, In the lower sections of the furnace,
C+CO2→2CO 3FeO+CO2→Fe+CO2
The limestone also decomposes to CaO which removes the silicate impurity of the ore in the form of Slag. It can be easily separated out of molten iron. The iron manufactured in Blast Furnaces contain about 3 – 4 % of Carbon and smaller quantities of many other impurities such as sulphur, Silicon, etc. This is called Pig Iron. It is a hard but brittle metal and the impurities severely hamper its strength. Carbon seems to play a significant role in influencing the brittleness and hardness balance in iron. To further reduce the carbon content of pig iron, it is melted again with scraps of iron and coke and subjected to the blast of hot air. This kind of iron is called Cast Iron and has a slightly lower carbon content 2 – 3 %. This is even harder than pig iron.
Wrought Iron/ Malleable Iron
Wrought Iron is the purest form of iron available commercially available and is prepared from cast iron by heating cast iron in a furnace lined with Haematite (Fe2O3). The Haematite reacts with Carbon in the cast iron to give pure iron and carbon monoxide gas which escapes.
Fe2O3+3C→2Fe+3CO
Limestone is then added as flux, and it creates the slag. Impurities such as S, Si pass into the slag and the slag later can be easily separated to yield pure iron.
,
Iron ore is a mineral that is the primary raw material used to make iron and steel. It is found in rocks and Minerals all over the world, but the most important iron ore deposits are located in China, Australia, Brazil, and Russia.
Iron ore is mined and then crushed and ground into a fine powder. This powder is then mixed with coke and limestone and heated in a blast furnace to produce molten iron. The molten iron is then poured into molds to form ingots, which are then cooled and shipped to steel mills.
In steel mills, the ingots are melted and then mixed with other Elements, such as carbon, manganese, and silicon, to produce different types of steel. The molten steel is then poured into molds to form slabs, which are then rolled into sheets or bars.
Iron and steel are used to make a wide variety of products, including cars, appliances, buildings, and bridges. The iron and steel Industry is a major economic driver in many countries around the world.
Iron and steel production has increased steadily over the past few decades. In 2018, global iron and steel production was 1.8 billion metric tons. China is the world’s largest producer of iron and steel, followed by India, Japan, and the United States.
Iron and steel recycling is an important part of the iron and steel industry. In 2018, global iron and steel recycling was 680 million metric tons. This represents about 37% of global iron and steel production.
The iron and steel industry is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. In 2018, the iron and steel industry was responsible for about 7% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
The iron and steel industry is also a major source of Air Pollution. Iron and steel mills emit large amounts of particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
The iron and steel industry is facing a number of challenges, including the need to reduce its environmental impact and the need to compete with low-cost producers in China and other countries. The industry is also facing the challenge of technological change, as new technologies are developed that can produce iron and steel more efficiently and with a lower environmental impact.
Despite these challenges, the iron and steel industry is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The global demand for iron and steel is expected to grow by about 2% per year over the next decade. This Growth will be driven by the increasing demand for Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE and construction materials in developing countries.
The iron and steel industry is a vital part of the global economy. It provides jobs for millions of people and produces essential materials that are used in a wide variety of products. The industry is facing a number of challenges, but it is expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
What is metallurgy?
Metallurgy is the science, technology, and art of extracting metals from ores and using them to make useful materials.
What are the different types of metallurgy?
There are two main types of metallurgy: extractive metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Extractive metallurgy is the process of extracting metals from ores, while physical metallurgy is the study of the properties of metals and their alloys.
What are the different stages of metallurgy?
The different stages of metallurgy are:
- Ore mining: The ore is mined from the ground.
- Ore processing: The ore is processed to remove impurities.
- Smelting: The ore is melted to extract the metal.
- Refining: The metal is refined to remove impurities.
- Casting: The metal is cast into a desired shape.
- Forging: The metal is shaped by hammering or rolling.
- Machining: The metal is shaped by cutting.
- Heat treatment: The metal is heat-treated to improve its properties.
- Finishing: The metal is finished to give it a desired appearance.
What are the different types of metals?
There are many different types of metals, including:
- Iron: Iron is a common metal that is used to make steel.
- Steel: Steel is an Alloy of iron and carbon.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is a lightweight metal that is used to make cans and other products.
- Copper: Copper is a red metal that is used to make wires and other electrical products.
- Gold: Gold is a yellow metal that is used to make jewelry and other decorative items.
- Silver: Silver is a white metal that is used to make jewelry and other decorative items.
- Platinum: Platinum is a white metal that is used to make jewelry and other decorative items.
What are the different types of alloys?
An alloy is a mixture of two or more metals. Alloys are often used to improve the properties of metals. For example, steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that is stronger than pure iron.
What are the different types of casting?
Casting is a process of manufacturing metal objects by pouring molten metal into a mold. The mold is then cooled and the metal object is removed.
What are the different types of forging?
Forging is a process of shaping metal by hammering or rolling it. Forging is often used to make objects that require a lot of strength, such as tools and machinery.
What are the different types of machining?
Machining is a process of shaping metal by cutting it. Machining is often used to make objects that require a high degree of precision, such as gears and bearings.
What are the different types of heat treatment?
Heat treatment is a process of heating and cooling metal to improve its properties. Heat treatment is often used to make metal objects stronger, tougher, or more ductile.
What are the different types of finishing?
Finishing is a process of giving metal objects a desired appearance. Finishing can include polishing, painting, or plating.
What are the different applications of metallurgy?
Metallurgy has many different applications, including:
- Construction: Metals are used to make buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Transportation: Metals are used to make cars, airplanes, and other vehicles.
- Electronics: Metals are used to make computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices.
- Machinery: Metals are used to make machines, tools, and other equipment.
- Weapons: Metals are used to make guns, bombs, and other weapons.
- Jewelry: Metals are used to make jewelry, such as rings, necklaces, and earrings.
- Coins: Metals are used to make coins.
- Art: Metals are used to make sculptures, paintings, and other works of art.
What are the future trends in metallurgy?
The future trends in metallurgy include:
- The development of new alloys with improved properties.
- The development of new manufacturing processes that are more efficient and environmentally friendly.
- The use of 3D printing to create metal objects with complex shapes.
- The development of new applications for metals, such as in the field of RENEWABLE ENERGY.
-
Which of the following is not a type of iron ore?
(A) Hematite
(B) Magnetite
(C) Limonite
(D) Bauxite -
The process of extracting iron from iron ore is called:
(A) Smelting
(B) Refining
(C) Casting
(D) Forging -
The main component of pig iron is:
(A) Iron
(B) Carbon
(C) Silicon
(D) Manganese -
Steel is made by:
(A) Removing carbon from pig iron
(B) Adding carbon to pig iron
(C) Melting pig iron and then adding carbon
(D) Melting pig iron and then removing carbon -
The most common type of steel is:
(A) Mild steel
(B) High-carbon steel
(C) Stainless steel
(D) Alloy steel -
Mild steel is used for:
(A) Buildings
(B) Cars
(C) Tools
(D) All of the above -
High-carbon steel is used for:
(A) Knives
(B) Razors
(C) Drill bits
(D) All of the above -
Stainless steel is used for:
(A) Buildings
(B) Cars
(C) Kitchen appliances
(D) All of the above -
Alloy steel is used for:
(A) Tools
(B) Machinery
(C) Airplanes
(D) All of the above -
The process of shaping iron or steel into a desired form is called:
(A) Forging
(B) Casting
(C) Rolling
(D) Extrusion