Main Features of budgets of West Bengal :-
In Feb 2017 West Bengal Finance Minister Amit Mitra presented tax-free Budget even as the redemption of market loans is set to peak at the beginning of the next financial year, further constraining the state’s weak finances.
- Budget provides value-added tax (VAT) relief to small businesses and doling out Rs 50,000 each to about 50,000 skilled workers who have returned to West Bengal from other states after being left jobless due to the note ban.
- The state’s plan outlay will increase by around 12 per cent for 2017-18 at Rs 64,733 crore.
- Financial disarray in West Bengal can be assessed from the fact that in 2017-18 nearly 80 per cent of state’s tax revenues, pegged at around Rs 55,787 crore, will go towards the loan repayment bill, which is around Rs 45,340 crore (against Rs 36,638 crore in 2016-17).
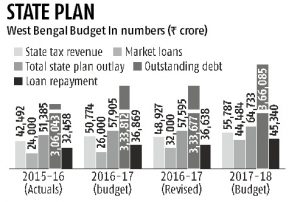
- According to the West Bengal Budget document, repayment obligations on account of institutional loans, including market loans, for West Bengal in 2017-18 were Rs 12,689 crore, against Rs 4,189 crore in 2016-17 (revised), an increase of more than 200 per cent. West Bengal’s outstanding debt in the next fiscal is set to touch Rs 3,66,085 crore.
- The state’s market borrowing in 2017-18 is set at Rs 44,840 crore, against Rs 32,000 crore in the present fiscal year, a rise of about 40 per cent.
Taxation in Budget:-
1.Changes proposed in WBVAT Act, 2003:-
- Threshold for payment of tax:-
In order to give relief to the small businesses, it is proposed to increase the threshold for payment of tax from Rs. 10 lakh to Rs.20 lakh.
- VAT Registration:-
A small section of dealers still have to submit hard copies of the registration documents in the VAT offices. It is proposed in the budget to completely dispense with the requirement of submitting hard copies of registration documents to the VAT offices
- Submission of separate audit report:-
It is proposed to completely abolish the provision of submission of separate VAT audit report. Instead the dealers may submit the income audit report which will be accepted as a VAT audit report as other purposes.
VAT Refund:-
In order to facilitate early refund, It is proposed that all pending refund cases will have to be disposed of and enclosed between 31st December 2017.
- Composition scheme:-
Presently, only traders with annual turnover to less than Rs. 50 lakh are covered under the Composition Scheme in which there is a nominal VAT liability. It is proposed in the budget to bring small manufacturers whose annual turnover is less than Rs. 50 lakh under the Composition scheme
- Tax relief:-
It is proposed in the budget to exempt some Environment‐friendly items like Bio‐ diesel, Biomass/”>Biomass Bricket, Solar water heater, plates and cups made up of Saal leaf, tiles of terracotta, etc and also some items for common use like kerosene stove, hair band and hair clip, etc.
- Cess on tea:-
It is proposed in the budget to extend the exemption on payment of primary Education and rural EMPLOYMENT cess on tea for a further period of one year upto 31st March 2018.
- Stamp Duty and Registration:-
- It is proposed in the budget to reduce the Stamp Duty on Agreement to Sale from the present rate of 5 to 7 percent to 2 percent. In order to get the benefit of the reduced rate, the registration has to be done within a period of 4 years from the date of agreement on payment of the balance stamp duty.
- It is also proposed to reduce the rate of Stamp Duty on a few transactions of Stock Exchanges, like proprietary accounts, currency, interest and debt security and bond.
- It is also proposed to reduce the rate of registration fee on all by 9 percent.
- It is also proposed to incentivise early registration of properties by reducing the registration fee by 20 percent if the registration is done within one year from the date of completion of property.
,
The budget of West Bengal is a financial statement that outlines the government’s revenue and expenditure for the coming year. It is prepared by the finance ministry and presented to the legislature for approval. The budget is a key tool for the government to achieve its economic and social objectives.
The budget of West Bengal is divided into two parts: the Revenue Budget and the Capital Budget. The revenue budget includes the government’s income from taxes, fees, and other sources. The capital budget includes the government’s expenditure on development projects.
The budget of West Bengal is prepared on the basis of the following principles:
- Fiscal responsibility: The government should not spend more than it earns.
- Transparency: The budget should be prepared in a transparent manner and should be made available to the public.
- Accountability: The government should be accountable for its spending.
- Efficiency: The government should spend its Money in an efficient manner.
- Equity: The government should ensure that its spending is equitable and benefits all sections of Society.
The budget of West Bengal has a significant impact on the state’s economy. It provides the government with the Resources to invest in development projects and to provide essential Services to the people. The budget also helps to regulate the state’s economy and to promote economic Growth.
The budget of West Bengal is a complex document that is prepared by a team of experts. It is important to understand the key features of the budget in order to appreciate its impact on the state’s economy and society.
The following are the key features of the budget of West Bengal:
- agriculture: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for agriculture. This money is used to support farmers, to improve agricultural Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE, and to promote agricultural research and development.
- Education: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for education. This money is used to improve the quality of education, to expand access to education, and to provide scholarships and other financial assistance to students.
- Health: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for health. This money is used to improve the quality of healthcare, to expand access to healthcare, and to provide free healthcare to the poor.
- Infrastructure: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for infrastructure. This money is used to build roads, bridges, Airports, and other infrastructure projects.
- Industry: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for industry. This money is used to promote industrial development, to provide subsidies to industries, and to improve the infrastructure for industries.
- Social welfare: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for social welfare. This money is used to provide social security benefits to the poor, to provide housing to the poor, and to provide other social welfare programs.
- Transport: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for transport. This money is used to build roads, bridges, railways, and other transport infrastructure.
- Tourism: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for tourism. This money is used to promote tourism, to improve the infrastructure for tourism, and to provide subsidies to tourism businesses.
- Urban development: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for urban development. This money is used to build roads, bridges, schools, hospitals, and other infrastructure projects in urban areas.
- Water Resources: The budget allocates a significant amount of money for water resources. This money is used to build Dams, canals, and other water infrastructure projects.
- Other: The budget also allocates money for other sectors, such as defense, law and order, and environment.
The budget of West Bengal is a complex document that has a significant impact on the state’s economy and society. It is important to understand the key features of the budget in order to appreciate its impact.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about the main features of budgets of West Bengal:
- What is the budget of West Bengal for the financial year 2022-23?
The budget of West Bengal for the financial year 2022-23 is Rs. 3,45,267 crore.
- What are the major highlights of the budget?
The major highlights of the budget include:
- A focus on agriculture and rural development
- Increased allocation for education and health
- A new scheme to provide employment to the youth
-
A new scheme to provide housing to the poor
-
What are the challenges that the State Government faces in implementing the budget?
The state government faces a number of challenges in implementing the budget, including:
- A slowdown in the economy
- A high Fiscal Deficit
-
A large number of unemployed youth
-
What are the expectations of the people from the budget?
The people of West Bengal expect the budget to address the following issues:
- Unemployment
- POVERTY
- Inflation
-
Lack of basic infrastructure
-
What are the possible outcomes of the budget?
The possible outcomes of the budget include:
- An increase in economic growth
- A decrease in poverty
- A decrease in inflation
-
An improvement in the Quality Of Life of the people
-
What are the risks associated with the budget?
The risks associated with the budget include:
- A slowdown in the economy
- A rise in inflation
- A decrease in Investment
-
A decrease in tax revenue
-
What are the opportunities associated with the budget?
The opportunities associated with the budget include:
- The implementation of new schemes to provide employment, housing, and education to the people
- The increase in investment in infrastructure
-
The increase in tax revenue
-
What are the recommendations for the budget?
The recommendations for the budget include:
- The focus on agriculture and rural development
- The increase in allocation for education and health
- The implementation of new schemes to provide employment, housing, and education to the people
- The increase in investment in infrastructure
- The increase in tax revenue
-
The West Bengal budget is presented in the following format:
(A) Estimates of Receipts and Expenditures
(B) Budget Speech
(C) Demands for Grants
(D) Appropriation Bill -
The West Bengal budget is prepared by the following department:
(A) Finance Department
(B) Planning Department
(C) Economic Affairs Department
(D) Revenue Department -
The West Bengal budget is approved by the following body:
(A) Legislative Assembly
(B) Legislative Council
(C) Finance Commission
(D) Planning Commission -
The West Bengal budget is implemented by the following department:
(A) Finance Department
(B) Planning Department
(C) Economic Affairs Department
(D) Revenue Department -
The West Bengal budget is audited by the following body:
(A) Comptroller and Auditor General of India
(B) Public Accounts Committee
(C) Estimates Committee
(D) Finance Commission -
The West Bengal budget is a statement of the government’s financial plans for the coming year. It includes estimates of receipts and expenditures, as well as proposals for new taxes and spending.
-
The West Bengal budget is prepared by the Finance Department of the state government. It is presented to the Legislative Assembly by the Finance Minister, who also delivers a budget speech outlining the government’s priorities for the coming year.
-
The West Bengal budget is approved by the Legislative Assembly. Once approved, it becomes law and the government is required to implement it.
-
The West Bengal budget is audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG). The CAG’s report is tabled in the Legislative Assembly and is a valuable source of information on the state government’s finances.
-
The West Bengal budget is a key document in the state government’s financial planning process. It provides a clear statement of the government’s priorities and allows for informed public debate on the state’s finances.