<–2/”>a >Electromagnetic Wave
Electromagnetic Wave are waves composed of undulating electrical fields and magnetic fields. The different kinds of Electromagnetic Waves, such as Light and radio waves, form the electromagnetic spectrum. All electromagnetic waves have the same speed in a vacuum, a speed expressed by the letter c (the speed of light) and equal to about 186,000 miles (or 300,000 kilometers) per second. Electromagnetic Wave transport energy, due to oscillating electric and magnetic fields, Electromagnetic Waves are called electromagnetic radiation, light, or photons.
Maxwell‘s equations predicts the existence of electromagnetic waves that travel with speed of light c =1/ μ ? . The reason is due to the fact that a changing electric field produces a Magnetic Field and vice versa, and the coupling between the two fields leads to the generation of electromagnetic waves.
Four Maxwell equations are:-
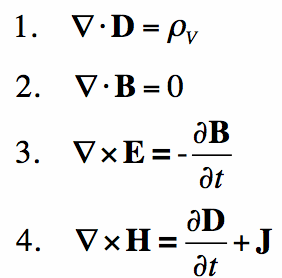
In 1887, Heinrich Hertz generated and detected electromagnetic waves in his lab. The waves radiated from a transmitter circuit and were detected in a receiver circuit. Hertz used the fact that electrical circuits have resonant frequencies just like mechanical systems do.
A stationary charge produces an electric field.
A charge moving at constant speed produces electric and magnetic fields.
A charge that is accelerated will produce variable electric and magnetic fields. These are electromagnetic waves.,
Electromagnetic waves are waves that are generated by the oscillation of an electric field and a magnetic field. They are transverse waves, meaning that the electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation of the wave. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, and they are the fastest form of energy transfer in the universe.
The following are some of the subtopics of electromagnetic waves:
- Wavelength: The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave. It is measured in meters.
- Frequency: The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is the number of waves that pass a given point in a given amount of time. It is measured in hertz (Hz).
- Speed: The speed of an electromagnetic wave is the distance that it travels in a given amount of time. It is equal to the product of its wavelength and frequency.
- Amplitude: The amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is the maximum displacement of the electric or magnetic field from its equilibrium position.
- Polarization: The polarization of an electromagnetic wave is the direction of the electric field at any point on the wave.
- Electromagnetic spectrum: The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic waves. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Applications: Electromagnetic waves have a wide range of applications, including radio, television, radar, microwave ovens, lasers, and medical imaging.
Wavelength
The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave. It is measured in meters. The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is inversely proportional to its frequency. This means that waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and waves with lower frequencies have longer wavelengths.
Frequency
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is the number of waves that pass a given point in a given amount of time. It is measured in hertz (Hz). The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its energy. This means that waves with higher frequencies have more energy, and waves with lower frequencies have less energy.
Speed
The speed of an electromagnetic wave is the distance that it travels in a given amount of time. It is equal to the product of its wavelength and frequency. The speed of an electromagnetic wave is always the same, regardless of its wavelength or frequency. It is equal to the speed of light, which is 299,792,458 meters per second.
Amplitude
The amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is the maximum displacement of the electric or magnetic field from its equilibrium position. It is measured in volts per meter (V/m) for electric fields and amperes per meter (A/m) for magnetic fields. The amplitude of an electromagnetic wave determines its intensity. This means that waves with higher amplitudes are more intense, and waves with lower amplitudes are less intense.
Polarization
The polarization of an electromagnetic wave is the direction of the electric field at any point on the wave. Electromagnetic waves can be polarized in one of two ways: linearly polarized or circularly polarized. Linearly polarized waves have electric fields that oscillate in a single direction. Circularly polarized waves have electric fields that oscillate in a circular motion.
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic waves. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into different regions based on the wavelength of the waves. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths, and gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths.
Applications
Electromagnetic waves have a wide range of applications, including radio, television, radar, microwave ovens, lasers, and medical imaging. Radio waves are used for Communication, television, and radar. Microwaves are used for cooking and communication. Infrared radiation is used for remote sensing and night vision. Visible light is used for vision. Ultraviolet radiation is used for sterilization and tanning. X-rays are used for medical imaging and crystallography. Gamma rays are used for cancer treatment and industrial radiography.
Electromagnetic waves are a vital part of our world. They are used for communication, entertainment, cooking, medicine, and many other things. We are constantly surrounded by electromagnetic waves, and they play a major role in our lives.
What is a wave?
A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium, transporting energy from one point to another.
What are the different types of waves?
There are many different types of waves, including mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves, and matter waves. Mechanical waves are waves that require a medium to travel through, such as Sound waves and water waves. Electromagnetic waves are waves that can travel through the vacuum of space, such as light waves and radio waves. Matter waves are waves that are associated with particles, such as electrons and protons.
What is the frequency of a wave?
The frequency of a wave is the number of waves that pass a given point in a given amount of time. It is measured in hertz (Hz), which is one wave per second.
What is the wavelength of a wave?
The wavelength of a wave is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave. It is measured in meters.
What is the speed of a wave?
The speed of a wave is the distance that the wave travels in a given amount of time. It is measured in meters per second.
What is the amplitude of a wave?
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of the wave from its equilibrium position. It is measured in meters.
What is the energy of a wave?
The energy of a wave is the amount of work that is required to create the wave. It is measured in joules.
What is the intensity of a wave?
The intensity of a wave is the amount of energy that is transported by the wave per unit area. It is measured in watts per square meter.
What is the Doppler effect?
The Doppler effect is the change in the frequency of a wave that is observed by an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The Doppler effect is observed in all types of waves, including sound waves, light waves, and water waves.
What is the principle of superposition?
The principle of superposition states that when two or more waves are traveling through the same medium, the resulting wave is the sum of the individual waves.
What is interference?
Interference is the phenomenon that occurs when two or more waves meet and interact with each other. The resulting wave can be either constructive or destructive, depending on the relative phases of the two waves.
What is diffraction?
Diffraction is the bending of waves as they pass through a narrow opening or around an obstacle. Diffraction is observed in all types of waves, including sound waves, light waves, and water waves.
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of waves as they pass from one medium to another. Refraction is observed in all types of waves, including sound waves, light waves, and water waves.
What is reflection?
Reflection is the bouncing of waves off of a surface. Reflection is observed in all types of waves, including sound waves, light waves, and water waves.
What is scattering?
Scattering is the process by which waves are redirected in many different directions after interacting with a surface or object. Scattering is observed in all types of waves, including sound waves, light waves, and water waves.
What is polarization?
Polarization is the property of waves that have a preferred direction of oscillation. Polarization is observed in electromagnetic waves, such as light waves.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What is light?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the Human Eye. Light is a wave that travels at a speed of 299,792,458 meters per second. Light is made up of photons, which are tiny particles of energy.
What is color?
Color is the property of light that is perceived by the human eye. Color is determined by the wavelength of light. Shorter wavelengths of light are perceived as blue, while longer wavelengths of light are perceived as red.
What is white light?
White light is a mixture of all the colors of the rainbow. White light is produced when sunlight is scattered by the Atmosphere.
What is black light?
Black light is a type of ultraviolet light that is invisible to the human eye. Black light is used to make objects that fluoresce glow.
What is fluorescence?
Fluorescence is the emission of light
Sure, here are some MCQs without mentioning the topic Electromagnetic Wave:
-
Which of the following is not a property of electromagnetic waves?
(A) Wavelength
(B) Frequency
(C) Speed
(D) Mass -
Electromagnetic waves are produced by:
(A) The vibration of electric charges
(B) The movement of electrons
(C) The collision of atoms
(D) The decay of radioactive materials -
Electromagnetic waves can travel through:
(A) Vacuum
(B) Air
(C) Water
(D) All of the above -
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is related to its:
(A) Wavelength
(B) Speed
(C) Energy
(D) All of the above -
The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is related to its:
(A) Frequency
(B) Speed
(C) Energy
(D) All of the above -
The speed of an electromagnetic wave is always the same, regardless of its frequency or wavelength.
(A) True
(B) False -
Radio waves have a longer wavelength than visible light.
(A) True
(B) False -
Microwaves have a shorter wavelength than radio waves.
(A) True
(B) False -
X-rays have a shorter wavelength than ultraviolet light.
(A) True
(B) False -
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength of all electromagnetic waves.
(A) True
(B) False