Effects Of The Policies Of Developed And Developing Countries On India’s interest
Impact of Globalization/”>Globalization-3/”>Globalization on india
Globalization helps developing countries to deal with rest of the world increase their economic Growth, solving the POVERTY problems in their country. In the past, developing countries were not able to tap on the world economy due to trade barriers. They cannot share the same economic growth that developed countries had. However, with globalization the World Bank and International Management encourage developing countries to go through market reforms and radical changes through large loans. Many developing nations began to take steps to open their markets by removing tariffs and free up their economies. The developed countries were able to invest in the developing nations, creating job opportunities for the poor people. For example, rapid growth in India and China has caused world poverty to decrease.
China and india’s development strategies
China and India have become global economic powers. Even at the market exchange rate, China overtook Japan in 2010 as the second largest economy. China’s trade and financial activities, India’s emergence as a technology and innovation hub, and both countries’ commerce and Investment interactions with other developing nations have been covered extensively in all forms of media. They are regarded as economic and political drivers of the international economy, particularly in the trade arena and global governance. Their economic engagement with developing countries and regions entails interactions in the areas of labour, Human Rights, international relations, security, and environmental sustainability. The potential threats are mostly associated with trade and financial flows, and with the social and political implications of China’s financial outflows. Nevertheless, in the midst of the recent global economic crises, China and India’s demand for developing country goods proved to be a cushion to the declining flows of Resources from advanced nations. China and India influence global economic and political dynamics, and can provide alternative sources of development assistance for developing countries. They can also provide a number of potential lessons for other developing countries, three of which are highlighted in this ARTICLE: absorption of surplus labour, raising of domestic and foreign investment, and support for R&D.
India’s neighbourhood and it’s impact on india
The South Asian region is also full of contradictions, disparities and paradoxes. In the post-colonial period, the South Asia has been a theatre of bloody inter-state as well as civil wars; it has witnessed liberation movements, nuclear rivalry, military dictatorships and continues to suffer from insurgencies, religious Fundamentalism And Terrorism, besides serious problems associated with drugs and human trafficking. The region also has the dubious distinction of having over 540mn people who earn less than $ 1.25 a day and account for 44% of developing world’s poor. The region has produced several powerful female leaders and yet in the overall much remains to be done for the Empowerment of Women. On the barometer of religious Tolerance, the constituent countries range anywhere between flexible secular minded and rigidly fundamentalist.
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) has remained in existence for over 27 years; yet South Asia is considered as the least integrated of the global regions; this is despite the stipulation in its Charter that “bilateral and contentious issues shall be excluded” from its deliberations, thus making it possible to put the contentious issues on the back burner and focus on areas of possible cooperation.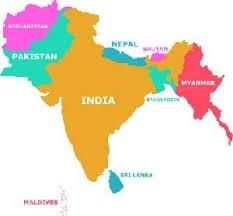
On the positive side, the region has been registering a healthy growth (Average 6% per annum) during the past several years. Also democratic forms of governance (howsoever flawed and feeble) are beginning to gain some ground in most parts of the region.
Where does India stand in this rather volatile region? India’s position is unique in more than one sense. As a matter of an interesting geographic factor, India Shares borders with all other South Asian nations whereas no other South Asian nation (except Afghanistan and Pakistan) shares borders with any other South Asian nation. Notwithstanding some shortcomings, Democracy and Rule of Law as instruments of political governance are well entrenched in India. Transfer of power has been more or less peaceful and transparent. In relative terms India can be arguably considered as the most stable country in the region, moving ahead on the fast tracks of development, even though the growth has of late slowed down.
Further in terms of its Population, territory, GDP, its image as an emerging world economy and a responsible de-facto nuclear State, and as a country which is destined to play a larger role on international arena, and also for several other reasons, India stands apart amongst the bunch of other South Asian countries. In fact India can be said to dwarf others in the South Asian region which in turn has created misperceptions about India and its intention.
There are unjustified and erroneous perceptions about India floating around in the region: “Big Brother bullying the smaller neighbour”; “India treats its neighbours as a neglected backyard” etc. etc. There is no justified explanation for the “trust deficit”. On top of it there are vested interests and lobbies for whom being anti-Indian is synonymous with being patriot and nationalist. And then there are strong institutions within the framework of a more or less failed and rogue State in the neighbourhood (Pakistan) which would like to see relations with India in a state of perpetual suspension. India’s Motives are suspected even in cases of innocent proposals for economic cooperation which would lead to win-win situations.
,
The policies and politics of developed and developing countries can have a significant impact on India’s interests. In this article, we will discuss some of the ways in which these policies and politics can affect India, both positively and negatively.
One of the most important ways in which the policies and politics of developed and developing countries can affect India is through their impact on the Indian economy. Developed countries are India’s largest trading partners, and their economic policies can have a major impact on Indian exports and imports. For example, if a developed country imposes tariffs on Indian goods, this can make it more difficult for Indian companies to sell their products in that country. This can lead to job losses and economic slowdown in India.
The policies and politics of developed and developing countries can also affect India through their impact on foreign investment. Developed countries are the largest source of foreign investment in India, and their policies can make it more or less attractive for foreign companies to invest in India. For example, if a developed country reduces its Corporate tax rate, this can make it more attractive for foreign companies to invest in India. This can lead to job creation and economic growth in India.
The policies and politics of developed and developing countries can also affect India through their impact on immigration. Developed countries are a major destination for Indian immigrants, and their immigration policies can make it more or less difficult for Indians to immigrate to those countries. For example, if a developed country tightens its immigration laws, this can make it more difficult for Indians to obtain visas to live and work in that country. This can lead to brain drain in India, as many of the country’s most talented and educated people are forced to leave.
The policies and politics of developed and developing countries can also affect India through their impact on the Environment. Developed countries are the largest emitters of greenhouse gases, and their Climate change policies can have a major impact on the Indian climate. For example, if a developed country fails to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions, this can lead to more extreme weather events in India, such as floods, droughts, and heat waves. These events can cause widespread damage to Infrastructure-2/”>INFRASTRUCTURE and crops, and can lead to loss of life.
The policies and politics of developed and developing countries can also affect India through their impact on security. Developed countries are India’s major arms suppliers, and their security policies can have a major impact on India’s ability to defend itself. For example, if a developed country decides to stop selling arms to India, this can make it more difficult for India to acquire the weapons it needs to protect itself from its enemies. This can make India more vulnerable to attack, and can increase the risk of war.
In conclusion, the policies and politics of developed and developing countries can have a significant impact on India’s interests. It is important for India to be aware of these impacts and to take steps to mitigate the negative effects and maximize the positive effects.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about the effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests:
- What are the main policies and politics of developed countries that affect India’s interests?
Some of the main policies and politics of developed countries that affect India’s interests include trade, investment, immigration, and Climate Change.
- How do these policies and politics affect India’s interests?
These policies and politics can affect India’s interests in a number of ways. For example, trade policies can affect India’s ability to export its goods and Services, investment policies can affect India’s ability to attract foreign investment, immigration policies can affect India’s ability to attract skilled workers, and climate change policies can affect India’s ability to adapt to the effects of climate change.
- What are the main challenges that India faces in dealing with the policies and politics of developed countries?
Some of the main challenges that India faces in dealing with the policies and politics of developed countries include the need to negotiate favorable trade agreements, the need to attract foreign investment, the need to manage Migration, and the need to adapt to climate change.
- What are some of the ways that India can address these challenges?
Some of the ways that India can address these challenges include strengthening its economy, improving its infrastructure, investing in Education and skills development, and building relationships with developed countries.
- What are the potential benefits of India’s engagement with developed countries?
The potential benefits of India’s engagement with developed countries include increased trade and investment, access to technology and expertise, and cooperation on global issues.
- What are the potential risks of India’s engagement with developed countries?
The potential risks of India’s engagement with developed countries include economic dependence, loss of Sovereignty, and cultural erosion.
- What is the future of India’s relationship with developed countries?
The future of India’s relationship with developed countries is uncertain. However, it is likely that India will continue to engage with developed countries in order to achieve its economic and social goals.
1. Which of the following is not a developed country?
(A) United States
(B) China
(C) Japan
(D) India
2. Which of the following is not a developing country?
(A) Brazil
(B) Mexico
(C) Argentina
(D) United States
3. Which of the following is a major policy issue facing developed countries?
(A) Aging population
(B) Climate change
(C) Income inequality
(D) All of the above
4. Which of the following is a major policy issue facing developing countries?
(A) Poverty
(B) Hunger
(C) Disease
(D) All of the above
5. How does India’s relationship with developed countries affect its interests?
(A) India benefits from trade and investment with developed countries.
(B) India can learn from the experience of developed countries in areas such as Economic Development and technology.
(C) India can cooperate with developed countries on issues such as climate change and terrorism.
(D) All of the above.
6. How does India’s relationship with developing countries affect its interests?
(A) India benefits from trade and investment with developing countries.
(B) India can learn from the experience of developing countries in areas such as poverty reduction and rural development.
(C) India can cooperate with developing countries on issues such as climate change and terrorism.
(D) All of the above.
7. What are some of the challenges facing India in the 21st century?
(A) Economic development
(B) Social development
(C) Environmental protection
(D) All of the above.
8. What are some of the opportunities facing India in the 21st century?
(A) Economic growth
(B) Technological advancement
(C) Demographic dividend
(D) All of the above.
9. What is India’s role in the world?
(A) India is a rising power that is seeking to play a greater role in global affairs.
(B) India is a member of the G20 and is a major player in the global economy.
(C) India is a nuclear power and has a strong military.
(D) All of the above.
10. What are some of the key issues facing India in the 21st century?
(A) Economic development
(B) Social development
(C) Environmental protection
(D) All of the above.