&<–2/”>a >nbsp;
Distinction between Indus Civilization and Vedic Civilization
- These two civilizations have not only played a major role in the development of ancient India, but have also left a lineage that still continues to shape our present Indian culture.
Differences based on Following Major Headings
PERIODICTY BASED DIFFERNENCES:
- Till 20th century, historians thought that the Vedic Society was the earliest civilization of India. However study done by 2 archaeologists – Dayaram Sahani and Raakhaldas Banerjee proved that Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa, though 1400 kms apart, were a part of one civilization older than Vedic.
- Since the region spanned India across the coastal western belt and along the Indus River, the civilization was called Indus Civilization. Indus civilization was at its peak around 2500 B.C.E.
Vedic Civilization:
- After the decline of Indus Civilization, a new civilization grew which was dominated by the Aryans and came to be known as the Vedic Civilization. The period extended from 1500 B.C.E to 500 B.C.E
REGIONAL SPREAD BASED DIFFERNENCES::
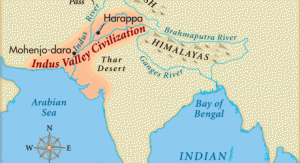
Indus Valley Civilization:
- The Indus civilization was spread across the Indus valley (river Sindhu).
- It spread in the North from Harappa in Punjab province (Pakistan) to Bhogtrar in South Gujarat (1400 kms). In the east, there was Alamgir (Meerut) and to its West was Sutkagen Dor in Baluchistan, next to Iran (1600 kms).
- Thus, the Indus valley spread across 12.15 lac sq.km.
Vedic Civilization
- The Vedic period marked the entry of Aryans on Indian Soil. There has been a huge debate on the Origin of Aryans. Various scholars have postulated theories which are either supported or debated.
- North Pole: Bal Gangadhar Tilak proposed that the Aryans came from North Pole. However there is no concrete evidence for this theory.
- Asia: Scholars like Max Muller suggested Middle Asia could be the place of Aryans, whereas Rhodes thought it should be Bactria and Edward Meyer postulated the plateau of Pamir (Iran).
- Europe: Penka and Hirt thought Germany as the base of Aryans.
- South Russia: Based on archaeological, historical and linguistic study, Meyer, Peek and Gordon Childes postulated that South Russia should be the home of Aryans. Archaeological excavations in Russia unearthed horse skeletons, potteries, earthen wares which were strikingly similar to Aryans.
URBAN DEVLOPMENT BASED DIFFERNENCES:
Indus Valley Civilization:
- The cities of Indus civilization were well planned and built with baked bricks of equal sizes. The streets were at right angle to each other with an elaborate Drainage System.
- There were public buildings, vast granaries and the Great Bath at Mohenjo-Daro.
- Production of several metals like copper, bronze, lead and tin was carried out. The discovery of kilns proves that bricks were extensively used for domestic and public buildings.
Vedic Civilization:
- It was mainly the rural civilization, centered round the village
SOCIETY BASED DIFFERNENCES:
Indus Valley Civilization:
- The social life of Indus Civilization was that of a happy, satisfied society.
- The society by large was “female dominated” and family was a central force.
- Though the society was divided into 4 groups as per the occupation, it does not prove that there could be any discrimination since the housing structure proves that irrespective of the occupation, people lived in each others vicinity.
- The people of Indus Civilization were vegetarian as well as non-vegetarian. Diet usually consisted of wheat, jowar, rice, sesame seed, dal, vegetables, milk and fruits. Meat of sheep, goat, pig, hen, duck as well as fish was consumed.
- Excavations reveal that Women of Indus valley liked to wear ornaments made of gold, precious stones, silver and copper. Men kept long hair, sported moustache and beard whereas women tied their hair in a bun. They also wore bangles made of glass and Metal ware.
Vedic Civilization:
- Compared to the Indus civilization, the early Vedic period civilization was “male dominated”. Though the women were known as “better half’, they were not allowed in politics and did not get share in family property.
- The caste system of 4 varnas became prominent to such an extent that even the burial grounds were segregated.
- The Brahmins and Kshatriyas fought for superior position, Vaishas did business and paid taxes whereas Shudras were considered to be slaves of all the 3 varnas.
- The people of Vedic civilization also followed vegetarian as well as non-vegetarian diet. Milk and milk products were an important part of diet along with vegetables and meat. People drank “som ras” and played dice. Horse race, chariot race, music, dance were the favorite pastime.
- In the Vedic civilization, metals like gold, silver, copper, tin, glass were in use. Iron utensils and equipments were also made during this period.
OCCUPATION BASED DIFFERNENCES:
Indus Valley Civilization:
- The main occupation of Indus Civilization was agriculture. Wheat, jowar, sesame seed, bajra were grown. Animal farming was also carried out. They also grew Cotton and wore clothes.
- There were sites where ornaments and jewelry were made.
- Trade was also another occupation and each merchant family had their own seal. Trading was usually done with neighboring regions of India, Persian Gulf and Iran.
Vedic Civilization:
- The Vedic period people were rural oriented and had agriculture as main occupation. They ploughed sowed and reaped various crops like wheat, jowar, rice, moong dal, udad, sesame. They also reared animals like cows, bulls, horses, goats, donkeys, sheep, pigs and dogs.
- It is during this period that ‘elephant’ was first domesticated.
ART, ARCHITECTURE & CULTURE BASED DIFFERNENCES::
Indus Valley Civilization:
- Indus Civilization had mastered the art of using metals, mud, wood, glass for making ornaments, architecture and various forms.
- They made terracotta vessels with decorative colors and design. They made toys, household utensils, agriculture equipments and ornamental things.
- The people of Indus Civilization were good sculptors carving wood and stone in the form of “relief architecture”, statues and articles. Statues of various birds and animals were also found along with men, women and “mother goddess”.
- The script still remains undecipherable.
Vedic Civilization:
- In the Vedic civilization, metals like gold, copper, silver, tin were used to prepare various artifacts.
- This period contributed to the Vedic literature namely Samhitas (Samved, Yajurved, Atharvaved, Rigved), Brahmanas, Aranyaks and Upanishads
RELIGIOUS ACTIVITY BASED DIFFERNENCES:
Indus Valley Civilization:
- The Indus Civilization people worshipped gods and goddesses. The figures found in excavation reveal some rituals and ceremonies.
- Various terracotta statues of “Mother Goddess” have been discovered from various sites which prove that she was worshipped in nearly every home.
- Many seal depicting rhinoceros, bull, leopard, elephant, ox were found suggesting that the Indus valley people revered them.
Vedic Civilization:
- The religious dogmas increased during the Vedic period and old gods (multiple ‘nature gods’ like wind, water, fire, etc.) were replaced with new formed gods. Prajapati, Vishnu & Rudra Shiva became the new gods.
- It was during this period that ‘animal sacrifice’ became rampant. Some large scale yagnas like Rajsuyagna, Vajpeya and Ashwamedh were performed.
- The belief in soul, magic, tantra increased and people succumbed to blind faith. The only difference was that the Vedic gods were immortal whereas the human beings were not.
Major differences in Both Civilization
The key differences between Harappa and Vedic Civilization are enumerated as follows:
- The sources of information of the Harappan civilization are mainly archaeological, while the Vedic culture is mostly known from the literary sources.
- Harappans are said to have been the original inhabitants of India while the Aryans are believed to have come to India from central Asia.
- The Harappan civilization was urban in nature; Vedic culture was rural and pastoral. At best the Rig Vedic Aryans lived in fortified places protected by mud walls; and these cannot be regarded as towns in the Harappan sense.
- In the Indus civilization trade, internal and external, crafts as well as industries were the main sources of economy, Vedic Economy was initially postoral and later became based upon agriculture and cattle rearing.
- The agricultural operations, including the ploughing of fields, were better known to the later-Vedic people.
- Indus people did not know the use of iron. It was purely a copper-bronze culture, while the Vedic culture in its later phase is replete with references to iron.
- The horse, which played a decisive role in the Aryan system of warfare, was not known to the Indus people. A few bones of horse and terracotta figure of a horse-like animal have been unearthed from Surkotada.
- Indus people were basically peace loving. Their arms (swords, daggers, arrow-heads, and spears) were primitive in nature. Aryans were warlike people and were conversant with all kinds of traditional arms and armour and had devised a full-fledged science of war.
- Aryans worshiped Varuna, Indra, aditi and a large number of other deities which stood for the principal phenomena of nature. They performed sacrifices and offered milk, ghee, etc. to their. The Harappans worshipped Pashupati, mother goddess, animals, snake and nature. The fire-altars were discovered from only one Harappan site at Kalibangan.
- The Harappans practiced earth burials whereas the Aryans practiced cremation.
- Harappan Pottery called black or red pottery was wheel made and very distinctive in nature. The distinctive Aryan pottery is known as PGW (painted grey ware).
- The Harappans were short stature, black in complexion; Aryans were tall, well-built and handsome.
- The Harappans ate all birds and animals including cow and calf. They ate wheat, barley and bread. The Aryans preferred Barley, milk and its products, specially ghee or butter and enjoyed Soma drink.
- Cotton was the basic fabric of the Harappans while the Aryans put on woollen garments
- Vedic Sanskrit is the mother of all non-Dravidian languages, Indus script still remains undeciphered.
- It was quite clear that Indus people were literate whereas the Vedic people were illiterate (In terms of writing) because there is not a single word for writing in any of the Vedic texts.
,
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were two ancient civilizations that flourished in the Indian subcontinent. The Indus Valley Civilization was located in the northwestern regions of South Asia, while the Vedic Civilization was located in the Ganges River valley. Both civilizations were agricultural societies, with a focus on farming and cattle herding. They also both had complex religious beliefs and practices.
The Indus Valley Civilization was a major urban civilization, with cities such as Harappa and Mohenjo-daro. These cities were well-planned, with streets laid out in a grid pattern. They also had sophisticated Drainage Systems and water supply systems. The Indus Valley people were skilled craftsmen, and they produced a variety of pottery, jewelry, and other objects.
The Vedic Civilization was a more rural civilization, with people living in small villages. The Vedic people were skilled warriors, and they often fought with other tribes. They also had a complex religious system, based on the Vedas, a collection of hymns, rituals, and philosophical texts.
The Indus Valley Civilization declined around 1900 BCE, for reasons that are not fully understood. Some possible causes include Climate change, invasion, or internal conflict. The Vedic Civilization continued to flourish until around 500 BCE, when it was gradually replaced by the Hindu civilization.
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were two important civilizations that had a major impact on the development of India. They both contributed to the development of Indian culture, religion, and society.
The Indus Valley Civilization was a major urban civilization that flourished in the northwestern regions of South Asia from about 2600 to 1900 BCE. The civilization is named after the Indus River, which flows through the region. The Indus Valley Civilization was one of the earliest urban civilizations in the world, and it was also one of the most advanced.
The Indus Valley Civilization was a complex society with a sophisticated System of Government, religion, and trade. The people of the Indus Valley were skilled farmers and craftsmen, and they built large cities with well-planned streets and drainage systems. The Indus Valley Civilization was a major center of trade, and it had extensive contacts with other civilizations in the region.
The Indus Valley Civilization declined around 1900 BCE, for reasons that are not fully understood. Some possible causes include Climate Change, invasion, or internal conflict. However, the Indus Valley Civilization left a lasting legacy on the region, and its influence can still be seen in the culture and society of modern India.
The Vedic Civilization was an ancient civilization that flourished in the Indian subcontinent from about 1500 to 500 BCE. The civilization is named after the Vedas, a collection of sacred texts that are the foundation of Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism. The Vedic Civilization was a pastoral society, with people living in small villages and herding cattle. The Vedic people were skilled warriors, and they often fought with other tribes. They also had a complex religious system, based on the Vedas, which included a belief in a pantheon of gods and goddesses.
The Vedic Civilization gradually declined after 500 BCE, as the Aryans began to move into the Ganges River valley. The Aryans brought with them new ideas and customs, which led to the development of the Hindu civilization. However, the Vedic Civilization left a lasting legacy on the region, and its influence can still be seen in the culture and society of modern India.
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were two major civilizations that existed in the Indian subcontinent in ancient times. The Indus Valley Civilization was located in the northwestern part of the subcontinent, while the Vedic Civilization was located in the northern part. The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that flourished from about 2600 to 1900 BCE. The Vedic Civilization was an Iron Age civilization that flourished from about 1500 to 500 BCE.
The Indus Valley Civilization was a highly urbanized civilization with a complex social structure. The Vedic Civilization was a more rural civilization with a simpler social structure. The Indus Valley Civilization was a polytheistic civilization with a pantheon of gods and goddesses. The Vedic Civilization was a monotheistic civilization with a belief in a single supreme god.
The Indus Valley Civilization was a major center of Trade and Commerce. The Vedic Civilization was a major center of Learning and culture. The Indus Valley Civilization declined and disappeared around 1900 BCE. The Vedic Civilization continued to flourish until the rise of the Mauryan Empire in the 4th century BCE.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Indus Valley Civilization:
- What was the Indus Valley Civilization?
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that flourished from about 2600 to 1900 BCE in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent. - Where was the Indus Valley Civilization located?
The Indus Valley Civilization was located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, in what is now Pakistan and northwestern India. - What were the major cities of the Indus Valley Civilization?
The major cities of the Indus Valley Civilization were Harappa, Mohenjo-daro, Dholavira, and Rakhigarhi. - What was the social structure of the Indus Valley Civilization?
The social structure of the Indus Valley Civilization was complex, with a ruling class, a middle class, and a working class. - What was the economy of the Indus Valley Civilization?
The economy of the Indus Valley Civilization was based on agriculture, trade, and manufacturing. - What was the religion of the Indus Valley Civilization?
The religion of the Indus Valley Civilization was polytheistic, with a pantheon of gods and goddesses. - What was the art and architecture of the Indus Valley Civilization?
The art and architecture of the Indus Valley Civilization was highly developed, with a distinctive style. - What was the writing system of the Indus Valley Civilization?
The writing system of the Indus Valley Civilization is still undeciphered. - What was the cause of the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization?
The cause of the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization is still unknown.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Vedic Civilization:
- What was the Vedic Civilization?
The Vedic Civilization was an Iron Age civilization that flourished from about 1500 to 500 BCE in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. - Where was the Vedic Civilization located?
The Vedic Civilization was located in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, in what is now India and Nepal. - What were the major texts of the Vedic Civilization?
The major texts of the Vedic Civilization are the Vedas, which are a collection of hymns, rituals, and philosophical texts. - What was the religion of the Vedic Civilization?
The religion of the Vedic Civilization was a polytheistic religion with a belief in a pantheon of gods and goddesses. - What was the social structure of the Vedic Civilization?
The social structure of the Vedic Civilization was based on a caste system, with four main castes: Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras. - What was the economy of the Vedic Civilization?
The economy of the Vedic Civilization was based on agriculture, pastoralism, and trade. - What was the art and architecture of the Vedic Civilization?
The art and architecture of the Vedic Civilization was highly developed, with a distinctive style. - What was the writing system of the Vedic Civilization?
The writing system of the Vedic Civilization was the Brahmi Script, which is the ancestor of the modern Devanagari Script. - What was the cause of the decline of the Vedic Civilization?
The Vedic Civilization did not decline, but rather evolved into the Hindu civilization.
Question 1
The Indus Valley Civilization was located in:
(A) India
(B) Pakistan
(C) Both India and Pakistan
(D) None of the above
Answer
(C) Both India and Pakistan
The Indus Valley Civilization was an ancient civilization that flourished in the Indus River valley from 3300 to 1300 BCE. It was located in what is now Pakistan and northwestern India.
Question 2
The Indus Valley Civilization was known for its:
(A) Advanced urban planning
(B) Elaborate system of writing
(C) Sophisticated art and architecture
(D) All of the above
Answer
(D) All of the above
The Indus Valley Civilization was a highly advanced civilization. It was known for its urban planning, system of writing, art, and architecture.
Question 3
The Indus Valley Civilization declined due to:
(A) A natural disaster
(B) Invasion by another civilization
(C) A combination of factors
(D) None of the above
Answer
(C) A combination of factors
The Indus Valley Civilization declined due to a combination of factors, including a natural disaster, invasion by another civilization, and internal strife.
Question 4
The Vedic Civilization was located in:
(A) India
(B) Pakistan
(C) Both India and Pakistan
(D) None of the above
Answer
(A) India
The Vedic Civilization was an ancient civilization that flourished in India from 1500 to 500 BCE. It was the precursor to Hinduism and Buddhism-2/”>Buddhism.
Question 5
The Vedic Civilization was known for its:
(A) Rig Veda
(B) Upanishads
(C) Brahmanas
(D) All of the above
Answer
(D) All of the above
The Vedic Civilization was a highly religious civilization. It is known for its sacred texts, including the Rig Veda, Upanishads, and Brahmanas.
Question 6
The Vedic Civilization declined due to:
(A) A natural disaster
(B) Invasion by another civilization
(C) A combination of factors
(D) None of the above
Answer
(C) A combination of factors
The Vedic Civilization declined due to a combination of factors, including a natural disaster, invasion by another civilization, and internal strife.
Question 7
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were both:
(A) Ancient civilizations
(B) Located in India
(C) Highly advanced
(D) All of the above
Answer
(D) All of the above
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were both ancient civilizations that were located in India. They were both highly advanced civilizations.
Question 8
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were both:
(A) Hindu
(B) Buddhist
(C) Neither Hindu nor Buddhist
(D) Both Hindu and Buddhist
Answer
(C) Neither Hindu nor Buddhist
The Indus Valley Civilization was pre-Hindu and pre-Buddhist. The Vedic Civilization was the precursor to Hinduism and Buddhism.
Question 9
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were both:
(A) Patriarchal
(B) Matriarchal
(C) Neither patriarchal nor matriarchal
(D) Both patriarchal and matriarchal
Answer
(A) Patriarchal
The Indus Valley Civilization was a patriarchal society. The Vedic Civilization was also a patriarchal society.
Question 10
The Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic Civilization were both:
(A) Agricultural
(B) Pastoral
(C) Both agricultural and pastoral
(D) Neither agricultural nor pastoral
Answer
(A) Agricultural
The Indus Valley Civilization was an agricultural society. The Vedic Civilization was also an agricultural society.