- Recent News: The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) convened to discuss national security matters. The announcement was made by Foreign Secretary Vikram Misri after a 2.5-hour meeting chaired by PM Modi.
- Purpose: The CCS is responsible for discussions, debates, and decisions on defense policy, expenditure, and national security matters, including appointments to national security bodies.
- Composition: Headed by the Prime Minister, it includes the Ministers of Home Affairs, Defence, Finance, and External Affairs. The National Security Advisor (NSA) acts as the secretary-level coordinator.
- Functions: It deals with defense, foreign affairs, intelligence, nuclear issues, space policy, major appointments related to national security, law and order, and internal security. The CCS also deliberates on policy matters concerning foreign affairs on security-related issues and atomic energy.
- Cabinet Committees: Extra-constitutional bodies designed to reduce the Union Cabinet’s burden by focusing on specific policy areas. There are eight cabinet committees, with most headed by the PM.
- Historical Significance: CCS meetings have been called during major events like wars with Pakistan, the Kargil conflict, and the Kandahar hijack, demonstrating its role in critical decision-making.
- Decision Making: The CCS resolves issues, formulates proposals for the Cabinet, and makes decisions on assigned matters. The Cabinet can review these decisions.
26.04.25
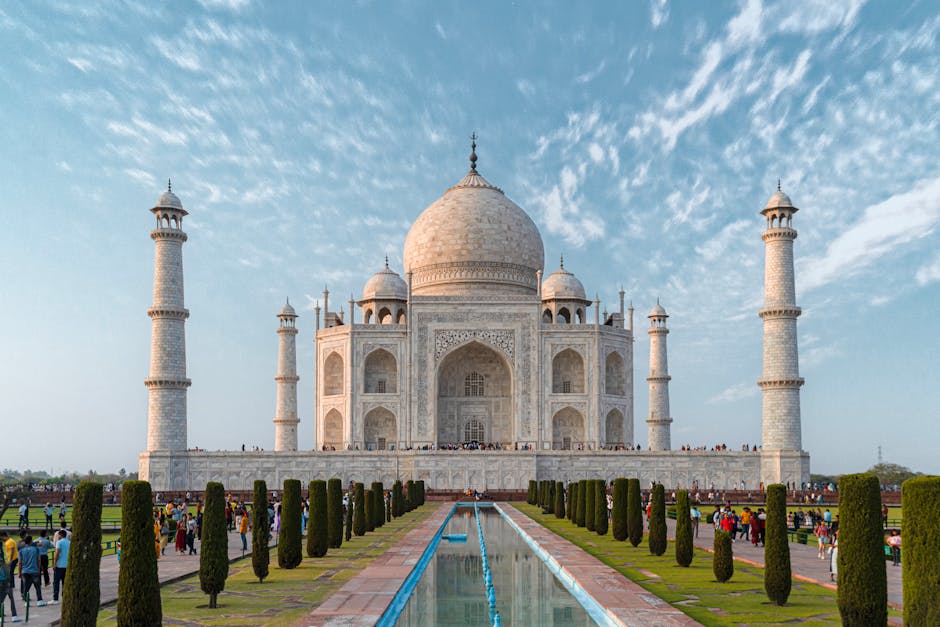
Taj Mahal Protection
- SC Directive to NEERI: The Supreme Court has directed NEERI to assess the environmental impact of glass industries near the Taj Mahal.
- Concerns over Industrial Pollution: This stems from growing worries about pollution within the Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ) and its effect on the monument.
- Potential Relocation: The SC indicated it would order the removal of polluting industries if NEERI’s assessment is adverse.
- UPPCB Involvement: The UP Pollution Control Board has been directed to form a team to inspect highlighted industrial units and submit an interim report on pollutant production.
- Court’s Frustration: The Supreme Court has previously criticized the TTZ authority’s ineffectiveness in protecting the Taj Mahal’s environment.
- TTZ Purpose: The TTZ was established to protect the Taj Mahal from pollution, encompassing a 10,400 sq km area.
- Past Efforts: Previous SC judgments banned coal/coke use in TTZ industries, mandating cleaner fuels.
- Threats to Taj: The Taj Mahal faces threats from vehicular emissions, industrial pollution, biomass burning, construction, and untreated sewage, leading to discoloration of the marble.
- Inadequate TTZ Authority: A parliamentary report highlighted the TTZ Authority’s lack of resources and effectiveness.
- Need for Stronger Measures: Recommendations include flue gas recirculation in glass industries, transition to clean energy, integrated traffic management, stronger TTZ authority, and relocation of polluting industries.
Dhubri-Phulbari Bridge
-
Construction Progress: 59% of the 19.3 km Dhubri-Phulbari Bridge is complete. This indicates steady advancement towards project completion.
-
Strategic Importance: The 4-lane bridge connects Dhubri, Assam, and Phulbari, Meghalaya, on NH 127B. Its significance lies in improving connectivity between Northeast India and the rest of the country.
-
Length and Structure: With a total length of 19.3 km, the bridge features a 12.625 km navigation bridge and approach viaducts (3.5 km on the Dhubri side, 2.2 km on the Phulbari side), supported by 199 pillars. It’s poised to be the longest river bridge in India.
-
Reduced Travel Time: The bridge will drastically cut travel distance by over 200 km between Phulbari and Dhubri. This translates to faster and more efficient transportation for people and goods.
-
Project Details: Larsen & Toubro (L&T) is handling the civil construction for the National Highways & Infrastructure Development Corp Ltd. (NHIDCL). Funding is provided by the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
-
Cost: The project is estimated to cost Rs 3165.99 crore. This is a substantial investment demonstrating the commitment to improving infrastructure in the region.
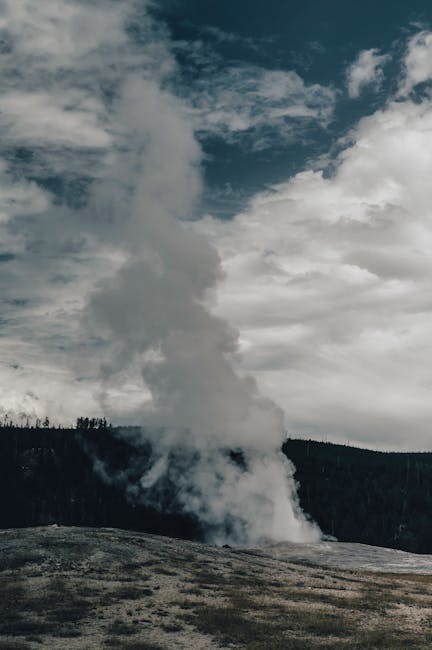
Yellowstone’s Fury
-
Magma Cap Discovery: A “breathing” cap of magma has been found inside the Yellowstone supervolcano. This could help scientists predict future eruptions.
-
Location: Yellowstone supervolcano is located beneath Yellowstone National Park in the western United States.
-
Size & Type: It’s one of the world’s largest active volcanic systems, characterized as a caldera (a large crater) and an active supervolcano. The caldera is 55 x 72 km (34 x 45 miles) in size.
-
Formation: The caldera formed from the collapse of land after massive pyroclastic eruptions emptied the magma chamber beneath.
-
Past Eruptions: Yellowstone has had three major eruptions: 2.1 million, 1.3 million, and 640,000 years ago. Two of these qualify it as a supervolcano.
-
Supervolcano Definition: A supervolcano is defined by eruptions of more than 1,000 cubic kilometers of deposits.
-
Potential Impact: A future supereruption could blanket North America in ash, with areas near the volcano potentially covered by over a meter of debris.
-
Climate Effects: Supervolcanoes can cause global cooling for several years due to sulfur dioxide released into the atmosphere, which blocks sunlight.
CBIC
- Trade Facilitation Measures: CBIC introduced measures to enhance logistics efficiency and simplify customs procedures for Air Cargo and Transhipment, aligning with Union Budget 2025-26 goals.
- Transhipment Permit Fee Waived: Effective April 24, 2025, the transhipment permit fee is waived for all transhipment movements to ease business operations and reduce delays, as per Notification No. 30/2025-Cus (N.T).
- Temporary ULD Removal: Simplified procedure introduced for temporary import of Unit Load Devices (ULDs) outside Customs areas for high-value or perishable cargo, aligning with international best practices.
- Continuity Bond for Air Carriers: Air carriers/air console agents can now temporarily import ULDs by executing a Continuity Bond, taking responsibility for re-export within a specified timeframe.
- All-India National Transhipment Bond: The ‘All-India National Transhipment Bond’ facility, operational since 2022, avoids multiple bond submissions at different Customs stations.
- Online Transhipment Application: Online filing of transhipment applications is enabled in ICEGATE, eliminating the need to visit service centers.
- Aim: These measures aim to ease compliance and facilitate trade at Air Cargo complexes, encouraging Airlines, Console Agents, and stakeholders to utilize the facilities.
- CBIC Role: CBIC administers Customs, Central Excise, CGST, IGST, and Narcotics (where applicable), formulating policies related to indirect tax levy and collection. It manages customs at various international locations and is headed by a Chairman.
- Statutory Body: CBIC operates under the Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963, making it a statutory authority.
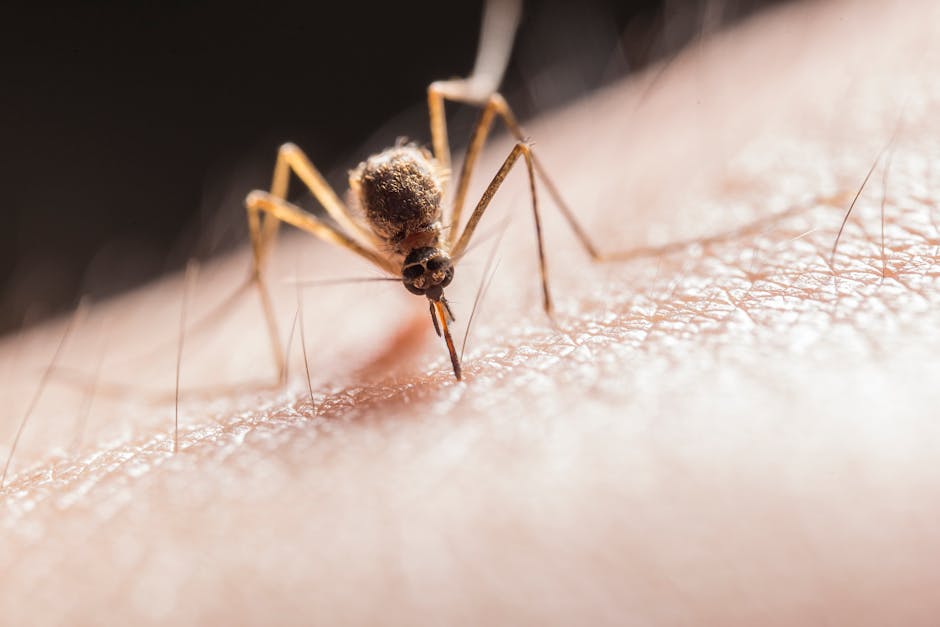
The Bite of Malaria
- World Malaria Day (April 25): Observed annually, promoting global action against malaria. The 2025 theme is “Malaria Ends With Us: Reinvest, Reimagine, Reignite,” emphasizing innovation, collaboration, and sustained commitment.
- India’s Progress: Achieved an 80.5% decline in malaria cases between 2015-2023 and a 78.38% reduction in deaths over the same period, exiting WHO’s High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group in 2024.
- India’s Targets: Aims for zero indigenous malaria cases by 2027 and full elimination by 2030.
- Key Strategies: “Test, Treat, Track” approach, intensified malaria elimination projects (IMEP), and vector control measures (mosquito nets, repellents). National Framework for Malaria Elimination (2016–2030) and National Strategic Plan (2023–2027) guide efforts.
- Malaria Basics: Caused by Plasmodium parasites transmitted via Anopheles mosquitoes. Symptoms include fever, chills, and headache, appearing 10-15 days post-infection. Early diagnosis and treatment (ACTs, chloroquine) are critical.
- Global Context: Malaria remains a significant global health issue, with an estimated 597,000 deaths in 2023.
- Elimination Focus: Intensified Malaria Elimination Project-3 (IMEP-3) targets 159 high-burden districts. Community participation and inter-sectoral collaboration are emphasized.
- Prevention: Preventing malaria can be achieved by avoiding mosquito bites and, in some cases, by taking preventive medicines.
Crimea
- Trump’s Proposal: Ex-US President Donald Trump has proposed formally recognizing Crimea as Russian territory, reversing long-standing US opposition to the annexation.
- Reversing US Policy: Accepting Crimea as part of Russia would fundamentally alter American foreign policy.
- Strategic Importance: Crimea’s location is strategically valuable to Russia as a warm water port giving access to the Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea, also the location of Sevastopol, home to the Black Sea Fleet.
- Historical Context: Russia’s long-term quest for warm water ports is a key driver, with Crimea providing crucial access to the Mediterranean.
- Sevastopol’s Significance: The deep-water port of Sevastopol is vital for Russia’s Black Sea Fleet.
- 2014 Annexation: Russia annexed Crimea in 2014 following a pro-Western revolution in Ukraine, driven by the desire to secure Sevastopol and prevent Ukraine from joining NATO.
- Water Supply: Control of the North Crimean Canal, which supplies water to Crimea, is crucial for Russia and was a factor in the 2022 invasion.
- Russian Perspective: Putin views Crimea as historically Russian and does not accept the transfer of control to Ukraine in 1954.
- Ukrainian Stance: Ukraine’s President Zelenskyy has stated that ceding any territory, including Crimea, is unacceptable and unconstitutional.
- Geopolitical Ramifications: Recognition of Russian control over Crimea could set a precedent for other authoritarian regimes, such as China’s claim over Taiwan.